
When was the first unit of measurement used in France?
Before the French Revolution, which started in 1789, French units of measurement that were founded on the Carolingian system, introduced by the first Holy Roman Emperor Charlemagne (AD 800–814), which in turn were based on contemporaneous Byzantine and ancient Roman measures.
What is the equivalent of 1 fr to 1 mm?
The millimeters unit number 0.33 mm converts to 1 Fr, one French gauge. It is the EQUAL Diameter Size value of 1 French gauge but in the millimeters length unit alternative. 1 French gauge to millimeters = 0.33 mm 2 French gauge to millimeters = 0.67 mm 3 French gauge to millimeters = 1.00 mm
Are the weights and measures in France metric or Imperial?
In general, weights & measures in France and the Continent are metric. Credit for originating the metric system is usually given to Gabriel Mouton, a French vicar, somewhere around 1670, but the basis of the system we know today was designed during the French Revolution in the 1790’s,...
What were medieval units of length based on?
The medieval royal units of length were based on the toise, and in particular the toise de l'Écritoire, the distance between the fingertips of the outstretched arms of a man, which was introduced in 790 by Charlemagne. The toise had 6 pieds (feet) each of 326.6 mm (12.86 in).

Is the metric system French?
Today, the metric system, which was created in France, is the official system of measurement for every country in the world except three: the United States, Liberia and Myanmar, also known as Burma. And even then, the metric system is still used for purposes such as global trade.
What did the French use as their standard of measurement?
On 22nd July 1799 the definitive standards of the metric system, the platinum metre and the platinum kilogramme, were ceremonially deposited in the French National Archives (1), and on 10th December 1799 a law was passed confirming their status as the only legal standards for measuring length and mass in France (2).
Which unit of measurement was created by the French?
Metric systemMetric system was first introduced in France but was widely accepted by both the world scientific community and many countries as the system of measurement.
How much is a French measurement?
The French system is simple, one increment on the French scale is equal to 1/3 millimeter, e.g. 8 Fr catheter is 8 x 0.33 mm = 2.67 mm in caliber.
What is unit of mass in French system?
The gramme, for mass—defined as the mass of one cubic centimetre of water. The franc, for currency.
How does France measure weight?
Like most of the world, the French use the metric system for weights and measures.
When did France convert to metric?
1795The French are widely credited with the originating the metric system of measurement. The French government officially adopted the system in 1795, but only after more than a century of sometimes contentious bickering over its value and suspicion surrounding the intent of metric proponents.
What is a French mile?
In France, distances are expressed in kilometres. A mile is about 1.6 kilometres.
When did France go decimal?
5 October 1793Decimal time was introduced in the decree of 5 October 1793 under which the day was divided into 10 "decimal hours", the "hour" into 100 " decimal minutes" and the "decimal minute" into 100 "decimal seconds".
Is French and gauge the same?
By convention, needles or single lumen catheters are sized by gauge and multi-lumen catheters are measured by French size. Whereas French size and diameter are related directly, gauge and size are related inversely; a lower gauge indicates a greater diameter.
What size is a French 38?
What is the American equivalent to size 38 in France? A French size 38 should be close to an American size 8 or a medium.
How many mm is 4 French?
Size CorrespondenceFrench GaugeDiameter (mm)Diameter (inches)41.330.05351.670.06662.000.07972.330.09221 more rows•Apr 6, 2014
Did France use imperial measurements?
Although in the pre-revolutionary era (before 1795) France used a system and units of measure that had many of the characteristics of contemporary English units (or the later Imperial System of units), France still lacked a unified, countrywide system of measurement.
Do the French use miles or km?
The national speed limit in France uses the metric system, which is different to the UK. The speed limit is listed in kilometres rather than miles, so British drivers need to be extra vigilant during a French road trip. The national speed limit in France is as follows: Motorways: 130 kph (80 mph)
When did France convert to metric?
1795The French are widely credited with the originating the metric system of measurement. The French government officially adopted the system in 1795, but only after more than a century of sometimes contentious bickering over its value and suspicion surrounding the intent of metric proponents.
When did France adopt the metric system?
1795metric system, international decimal system of weights and measures, based on the metre for length and the kilogram for mass, that was adopted in France in 1795 and is now used officially in almost all countries.
Who invented the metric system?
Credit for originating the metric system is usually given to Gabriel Mouton, a French vicar, somewhere around 1670, but the basis of the system we know today was designed during the French Revolution in the 1790’s, and brought order out of the conflicting and confusing traditional systems of weights and measures then being used in Europe.
Do people in Britain still refer to the old traditional measurements?
People in Britain still commonly refer to the old traditional measurements though.
Does the USA use the metric system?
The USA and UK. With the switch of the UK to the metric system (although not completely), only the USA still uses the weights and measures system it inherited from Britain. However, although some American measures have the same name as old English measures, they’re not the same….
What is the French measure of cloth?
Other units of measure such as the aune ( ell ), the perche ( perch or rood ), the arpent and the lieue ( league) had a number of variations, particularly the aune (which was used to measure cloth).
Who invented the French measure system?
Before the French Revolution, which started in 1789, French units of measurement that were founded on the Carolingian system, introduced by the first Holy Roman Emperor Charlemagne (AD 800–814), which in turn were based on contemporaneous Byzantine and ancient Roman measures. Charlemagne brought a consistent system of measures across ...
How many livres are in a quintal?
The livre actuelle could be sub-divided into 2 demi-livres (half-pounds), 4 quarterons, or 8 demi-quarterons. Conversely, there were 100 livres in a quintal (c.f. English hundredweight ). The fractional parts of an once had different names in Apothecary measure (used in medicine) and measure of precious metals, but the fractional ratios were themselves the same: 1 once was 8 drachme (Apothecary, c.f. English dram) or gros; 1 drachme / gros was 3 scruples (Apothecary, c.f. English scruple) or deniers, and 1 scruple / denier was 24 grains. This makes 384 deniers in a livre in weight measure, which contrasts with the old monetary livre in France which was divided into 240 deniers.
What was the reference standard in 1668?
In 1668 the reference standard was found to have been deformed, and it was replaced by the toise du Châtelet which, to accommodate the deformation of the earlier standard, was 11 mm (0.55%) shorter.
What is the length of a toise?
The toise had 6 pieds (feet) each of 326.6 mm (12.86 in). In 1668 the reference standard was found to have been deformed, and it was replaced by the toise du Châtelet which, to accommodate the deformation of the earlier standard, was 11 mm (0.55%) shorter. In 1747 this toise was replaced by a new toise of near-identical length – the Toise du Pérou, custody of which was given to l'Académie des Sciences au Louvre.
What does "demi" mean in French?
demi in French means "half": in this case, half a chopine, and – coincidentally – also approximately half a US pint. Although etymologically related to the English unit pint, the French pint is about twice as large. It was the main small unit in common use, and measured 1⁄36 of a cubic pied du roi .
How many didot points are there in French?
The French typographic point, the Didot point, was 1⁄72 of a French inch, i.e. two royal points. The French pica, called Cicéro, measured 12 Didot points or 1⁄6 inch.
What is the French number for approximate?
Most approximate French numbers are formed with the cardinal number, minus the final e (if there is one), plus the suffix -aine .
Is an approximate number a noun?
Approximate numbers are treated grammatically as expressions of quantity. Like all expressions of quantity, approximate numbers must be joined to the noun they modify with de .
What is distance in metric?
Distance in the metric sense is a measure between any two A to Z points. Applies to physical lengths, depths, heights or simply farness. Tool with multiple distance, depth and length measurement units.
What is the unit number of 0.33 mm?
The millimeters unit number 0.33 mm converts to 1 Fr, one French gauge. It is the EQUAL Diameter Size value of 1 French gauge but in the millimeters length unit alternative.
Overview
History
Although in the pre-revolutionary era (before 1795) France used a system and units of measure that had many of the characteristics of contemporary English units (or the later Imperial System of units), France still lacked a unified, countrywide system of measurement. Whereas in England the Magna Carta had decreed that "there shall be one unit of measure throughout the realm", Charle…
Tables of units of measure
These definitions use the Paris definitions for the coutume of Paris, and definitions for other Ancien régime civil jurisdictions varied, at times quite significantly.
The medieval royal units of length were based on the toise, and in particular the toise de l'Écritoire, the distance between the fingertips of the outstretched arm…
See also
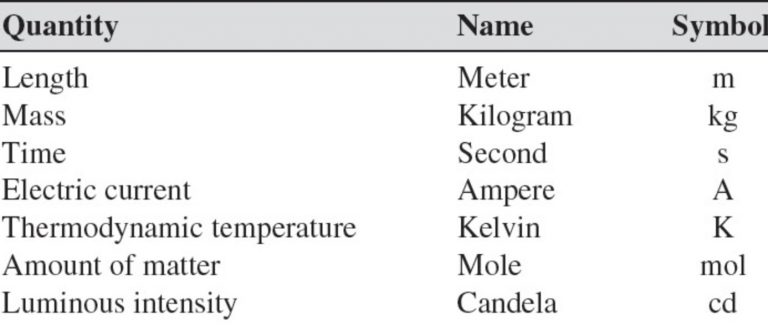
• International System of Units
• Jean-Antoine Chaptal
• Mansus
• Mesures usuelles
• Réaumur scale
Further reading
• "Pile de poids de 50 marcs dite "pile de Charlemagne" et son écrin". Musée des Arts et Métiers.
• Charbonnier, Pierre, ed. (1990). Les anciennes mesures locales du Midi méditerranéen, d'après les tables de conversion. Clermont-Ferrand: Presses universitaires Blaise Pascal. ISBN 9782877410649.