
What is para virtualization ideal for?
Using a convenient synthesizable flow and IP deliverables, the Cortex-A9 processor provides an ideal upgrade path for existing ARM11 ... to enhance the capabilities of a solution utilizing a paravirtualization manager. Advanced Bus Interface Unit ...
Which CPU is best for virtualization?
ROUND UP
- AMD Ryzen 7 3700X. It may not come close to surpassing the Ryzen 9 3900X, , especially in multi-threaded workloads, and it has inherited the Ryzen 7 2700X ’s 8-core, ...
- AMD Ryzen 5 3600. Those new chips have now taken over the top ranks on our CPU Benchmark Hierarchy. ...
- Intel Core i9-9900K. ...
- Intel Core i9-10900. ...
- Intel Core i5-9400F. ...
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600. ...
What is the best VM?
What is the best VM?
- VMware Workstation Player. 20 years of development shines through. …
- VirtualBox. Not all good things cost money. …
- Parallels Desktop. The best Apple Mac virtuality. …
- QEMU. A virtual hardware emulator. …
- Citrix Hypervisor. A highly scalable solution from Citrix. …
- Xen Project. …
- Microsoft Hyper-V.
What is full virtualization ideal for?
In Cloud Computing Full virtualization is ideal for systems that need the reflection of the hardware in all virtual machines including complete output/input, full instruction set, and memory sets. Also, for all the other systems that are incorporated in hardware that are intended to make the system run smoother and better. Full virtualization helps in significantly improving and enhancing the operational efficiency of the system.
What is full Para and partial virtualization?
The main difference between full virtualization and paravirtualization in Cloud is that full virtualization allows multiple guest operating systems to execute on a host operating system independently while paravirtualization allows multiple guest operating systems to run on host operating systems while communicating ...
What is the difference between full Para and hardware assisted virtualization?
In Hardware assisted full virtualization, Guest operating systems are unmodified and it involves many VM traps and thus high CPU overheads which limit the scalability. Paravirtualization is a complex method where guest kernel needs to be modified to inject the API.
What are the 3 types of virtualization?
Types of VirtualizationDesktop Virtualization.Application Virtualization.Server Virtualization.Network Virtualization.Storage Virtualization.
Is an example of para virtualization?
Examples of paravirtualization include VMware and Xen. The virtual machine doesn't implement full isolation of OS. It just provides a different API that can be utilized when the OS is subjected to changes. It is considered to be more secure in comparison to full virtualization.
Is ESXi full virtualization?
VMware's virtualization products such as VMWare ESXi and Microsoft Virtual Server are examples of full virtualization.
What are two types of virtualization?
When it comes to desktop virtualization, there are two main methods: local and remote. Local and remote desktop virtualization are both possible depending on the business needs. However, local desktop virtualization has many limitations, including the inability to use a mobile device to access the network resources.
What is Type 1 and Type 2 virtualization?
Definition. Type 1 hypervisor is a hypervisor that runs directly on the host's hardware to control the hardware and to manage guest operating systems while Type 2 hypervisors run on a conventional operating system just as other computer programs do. Thus, this is the main difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor ...
Who uses VDI?
VDI is an important technology for many types of workers across numerous industries. Remote employees, hybrid workers, contractors, kiosk and task workers, field technicians, medical professionals, teachers and many others regularly rely on VDI to access a reliable virtual desktop from one or more locations.
What are the types of virtualisation?
The 7 Types of VirtualizationOS Virtualization—aka Virtual Machines.Application-Server Virtualization.Application Virtualization.Administrative Virtualization.Network Virtualization.Hardware Virtualization.Storage Virtualization.
Why is paravirtualization used?
Paravirtualization enables several different operating systems to run on one set of hardware by effectively using resources such as processors and memory. In paravirtualization, the operating system is modified to work with a virtual machine.
What is the solution of full virtualization?
The solution was a combination of binary translation and direct execution on the processor that allowed multiple guest OSes to run in full isolation on the same computer with readily affordable virtualization overhead.
What is partial virtualization?
An example of partial virtualization is address space virtualization used in time-sharing systems; this allows multiple applications and users to run concurrently in a separate memory space, but they still share the same hardware resources (disk, processor, and network).
What are some examples of paravirtualization?
Examples of paravirtualization include VMware and Xen. The virtual machine doesn't implement full isolation of OS. It just provides a different API that can be utilized when the OS is subjected to changes. It is considered to be more secure in comparison to full virtualization.
Is a symlink less secure than a paravirtual?
It is considered to be less secure in comparison to paravirtualization.
Is binary translation faster than paravirtualization?
It is considered to be less secure in comparison to paravirtualization. It uses binary translation as the operational technique. It is slower in comparison to paravirtualization in terms of operation. It is considered to be portable and compatible in comparison to paravirtualization.
What is the difference between paravirtualization and full virtualization?
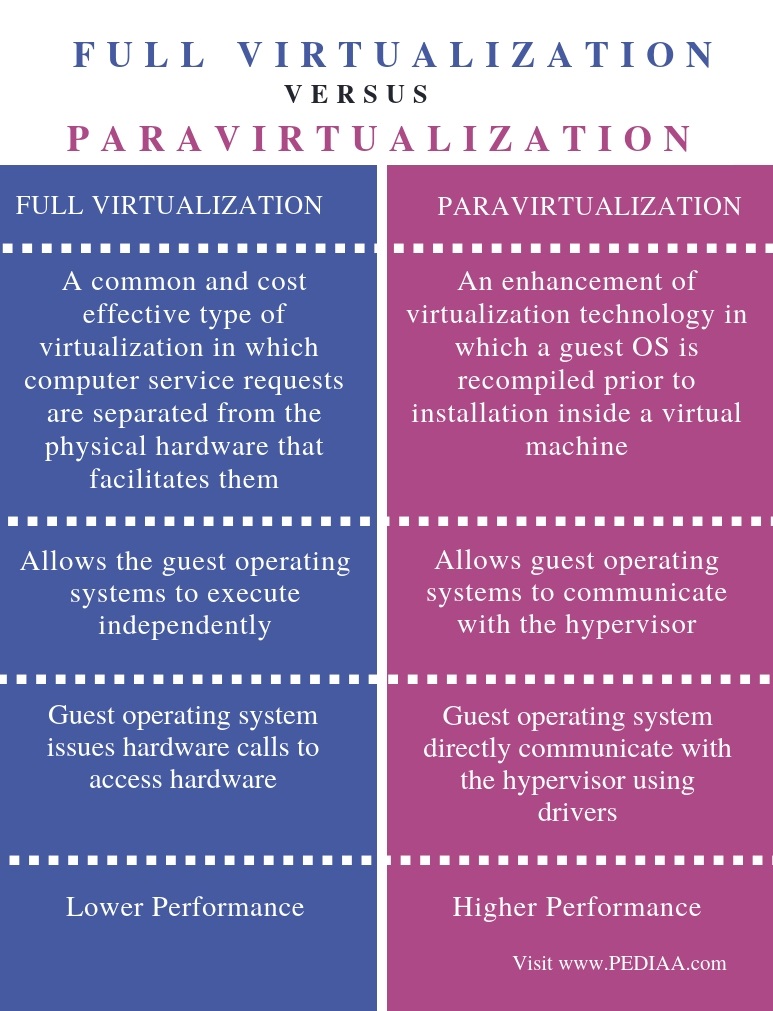
Full virtualization is a common and cost-effective type of virtualization in which computer service requests are separated from the physical hardware that facilitates them while paravirtualization is an enhancement of virtualization technology in which a guest OS is recompiled prior to installation inside a virtual machine.
What are the drawbacks of virtualization?
Moreover, one major drawback of full virtualization is that it affects the performance of the system. Hypervisor depends on the hardware emulator. Thus, the continuous translations between the physical and virtual resources such as memory and processor can impact the performance of the system.
What is virtualization in the cloud?
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of a server, desktop, operating system or a storage device. Moreover, Cloud provides applications with standard versions to the users. When there is a new version, the cloud provider has to provide the latest version to the cloud users. However, this is an expensive task. Virtualization provides an alternative to this issue. Here, a third party maintains the servers and software applications required by the other cloud providers. A hypervisor is a software that creates and manages virtual machines. Thus, after installing the hypervisor, the operating system and applications communicate with the virtualized resource created by the hypervisor.
What is a third party cloud provider?
Here, a third party maintains the servers and software applications required by the other cloud providers. A hypervisor is a software that creates and manages virtual machines. Thus, after installing the hypervisor, the operating system and applications communicate with the virtualized resource created by the hypervisor.
How does a host operating system work?
A host operating system runs directly on the hardware while a guest operating system runs on the virtual machine. In full virtualization, the guest operating systems do not concern about the presence of a hypervisor. Therefore, each virtual machine and its guest operating system operate as independent computers. In other words, multiple guest operating systems execute on a single host operating system in an isolated manner using direct execution and binary translation.
Do virtual machines have hypervisors?
In full virtualization, the guest operating systems do not concern about the presence of a hypervisor. Therefore, each virtual machine and its guest operating system operate as independent computers. In other words, multiple guest operating systems execute on a single host operating system in an isolated manner using direct execution ...
How is full virtualization different from para virtualization?
The full virtualization is different from para-virtualization because in full virtualization the unmodified OS runs in a complete isolated way. On the other hand, in the paravirtualization, the Virtual machine does not completely isolate the OS but modifies it in order to make it compatible with the certain API’s.
What is the difference between virtualization and paravirtualization?
Key Differences Between Full Virtualization and Paravirtualization 1 Full virtualization virtual machine simulates sufficient peripherals to permit the execution of the instructions in isolation of an unmodified guest OS. In contrast, in paravirtualization the virtual machine does not essentially simulate hardware but rather provides a specific API which is only utilized when the guest OS is subjected to modification. 2 The full virtualization uses binary translation and direct approach. On the contrary, paravirtualization utilizes hypercalls for its operations. 3 Paravirtualization is compelled by the aleration in the guest OS code for the generation of hypercalls. As against, in full virtualization, no modification in guest OS is required. 4 The speed, performance in terms of overhead produced and security of paravirtualization is a way better than the full virtualization. However, it is not that much compatible and portable relative to full-virtualization. 5 There are very few examples of paravirtualization such as VMware and Xen. Conversely, full virtualization is implemented in VMware, Microsoft and Parallels systems. 6 In full virtualization, the guest OS entirely relies on the hypervisor while this isn’t the case in paravirtualization.
What is the purpose of hypercalls?
The purpose of hypercalls is to interact with the virtualization layer hypervisor directly. In paravirtualization, there are various functions performed by hypervisor such as the arrangement of hypercalls interface for other crucial kernel functions like memory management, time keeping and interrupt handling.
What is full virtualization?
The full virtualization and paravirtualization are categorized under CPU virtualization. These are mainly distinguished by the fact that in full virtualization the unmodified OS is not awared about the virtualization and it uses binary translation to trap the OS calls at the run time. Conversely, in paravirtualization, ...
Which technologies provide full virtualization support?
The technologies provide full virtualization support are VMWare, ESXi and Microsoft virtual servers. Each time an OS instruction is generated the hypervisor translates it during run-time quickly and caches the outcome for the future references. While the user-level instructions are executed without modification at native speed. However, the storage of the translated instructions during the binary translation is intended to improve performance but this result in an increase in the cost of memory consumption.
What is the difference between a VMM and a hypervisor?
The lower layer is utilize d by the VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor or Hypervisor) while, the higher layer is captured by an operating system running inside a VM referred to as a guest operating system . Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitor located just over the hardware, intended to manage all the hardware resources. So, a hypervisor is accountable for running the guest OS directly on the CPU. This only functions well if the guest OS is running on the same instruction set as of the host OS; otherwise, an instruction translation takes place.
When was full virtualization first used?
Full virtualization is the first generation of the software solution regarding server virtualization and developed in the year of 1966 by IBM. It works by merging the binary translation and the direct execution where the guest OS is entirely separated from the elementary hardware and virtualization layer.
What is full virtualization?
Full Virtualization provides a complete simulation of the underlying hardware allowing execution of unmodified operating systems in the virtual machines. It requires that every salient feature of the hardware be reflected into every one of several virtual machines. In Full Virtualization machine language code of the guest OS is converted into the machine language code of the host through a binary translation process.
What is the paratualization method?
In the Paravirtualization method when a privilege command must be executed on the Guest OS, it is delivered to the hypervisor through a hypercall, a kind of system call, and the hypervisor receives this hypercall, accesses the hardware and returns the result. Paravirtualization requires some modifications to the guest operating system kernel in order to use the hypercall mechanism. Thanks to hypercalls, virtual machines applications and operating systems run in CPU Ring 3, the least privileged CPU mode.
Why is virtualization important?
Virtualization has become a critically important focus of the IT world in recent years. Virtualization technologies are used by countless thousands of companies to consolidate their workloads and to make their IT environments scalable and more flexible. If you want to learn cloud computing, you'll simply have to absorb the basic virtualization technology concepts at some point.
Does virtualization reduce overhead?
Unfortunately, the speed reflects this additional step. CPU manufacturers provide a variety of functionalities to reduce Full Virtualization overhead at the hardware level. A CPU supporting hardware assisted virtualization additionally provides Ring -1 level and the hypervisor runs on this ring while the guest OS runs on Ring 0. Consequently, it essentially circumvents the binary translation process with privilege commands and each command is executed directly on the hardware via the hypervisor. Thanks to CPU virtualization instructions, the performance gap between the Full Virtualization method and the Paravirtualization one has been significantly reduced. Here you can see a recap of the pros and cons for both techniques.
How does paravirtualization work?
Paravirtualization works differently from the full virtualization. It doesn’t need to simulate the hardware for the virtual machines. The hypervisor is installed on a physical server (host) and a guest OS is installed into the environment. Virtual guests aware that it has been virtualized, unlike the full virtualization (where the guest doesn’t know that it has been virtualized) to take advantage of the functions. In this virtualization method, guest source codes will be modified with sensitive information to communicate with the host. Guest Operating systems require extensions to make API calls to the hypervisor. In full virtualization, guests will issue a hardware calls but in paravirtualization, guests will directly communicate with the host (hypervisor) using the drivers. Here is the lisf of products which supports paravirtualization.
What is virtualization in computing?
Virtualization is nothing but abstracting operating system, application, storage or network away from the true underlying hardware or software. It creates the illusion of physical hardware to achieve the goal of operating system isolation. In last decade, data centers were occupied by a large number of physical servers, network switches, storage devices. It consumed a lot of power and manpower to maintain the data centers. In that period, there were many companies were researching about the hardware emulation/simulation like QEMU, virtual PC etc.. It’s very hard to list all the virtualization types here. So I have just listed down only the server virtualization types.
What is OS level virtualization?
Operating system-level virtualization is widely used.It also knowns “containerization”. Host Operating system kernel allows multiple user spaces aka instance.In OS-level virtualization, unlike other virtualization technologies, there will be very little or no overhead since its uses the host operating system kernel for execution. Oracle Solaris zone is one of the famous containers in the enterprise market. Here is the list of other containers.
What is virtual machine?
Virtual machine simulates hardware to allow an unmodified guest OS to be run in isolation. There is two type of Full virtualizations in the enterprise market. On both full virtualization types, guest operating system’s source information will not be modified.
What is virtual guest?
Virtual guests aware that it has been virtualized, unlike the full virtualization (where the guest doesn’t know that it has been virtualized) to take advantage of the functions. In this virtualization method, guest source codes will be modified with sensitive information to communicate with the host.
Does hardware assisted virtualization work on X86?
Hardware-assisted full virtualization eliminates the binary translation and it directly interrupts with hardware using the virtualization technology which has been integrated on X86 processors since 2005 (Intel VT-x and AMD-V). Guest OS’s instructions might allow a virtual context execute privileged instructions directly on the processor, even though it is virtualized.
Can Xen be paravirtualized?
Due to the architecture difference between windows and Linux based Xen hypervisor, Windows operating system can’t be para-virtualized. But it does for Linux guest by modifying the kernel. But VMware ESXi doesn’t modify the kernel for both Linux and Windows guests.
