What is the evolution of HBV?
The early evolution of HBV, like that of all viruses, is difficult to establish. The identification of hepadnaviruses in a wide range of vertebrates suggests a long coevolution. The identification of endogenous hepadnaviridae elements shared by various bird species shows the presence of these virus in birds for at least 70M years.
What is the role of HBx in the pathogenesis of HBV?
HBx is partly responsible for the approximate 10,000-fold increase in intracellular ROS upon chronic HBV infection. Increased ROS can be caused, in part, by localization of HBx to the mitochondria where HBx decreases the mitochondrial membrane potential.
What are the non-coding RNA elements in the HBV genome?
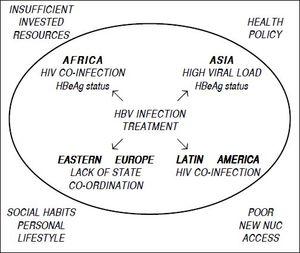
Several non-coding RNA elements have been identified in the HBV genome. These include: HBV PREalpha, HBV PREbeta and HBV RNA encapsidation signal epsilon. Genotypes differ by at least 8% of the sequence and have distinct geographical distributions and this has been associated with anthropological history.
Acronyms & Abbreviations
Get instant explanation for any acronym or abbreviation that hits you anywhere on the web!
A Member Of The STANDS4 Network
Get instant explanation for any acronym or abbreviation that hits you anywhere on the web!
How does HBV spread?
Sharing of needles. HBV easily spreads through needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood. Sharing IV drug paraphernalia puts you at high risk of hepatitis B. Accidental needle sticks.
What are the complications of HBV?
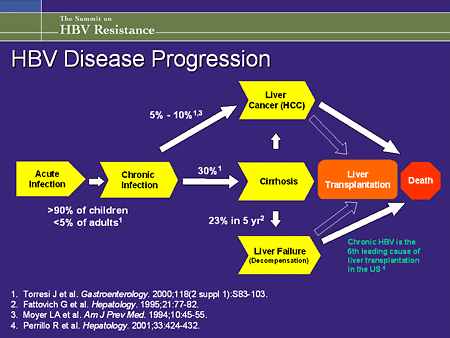
Complications. Having a chronic HBV infection can lead to serious complications, such as: Scarring of the liver (cirrho sis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. Liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B go undetected?
Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
How to avoid HBV?
Other ways to reduce your risk of HBV include: Know the HBV status of any sexual partner. Don't engage in unprotected sex unless you're absolutely certain your partner isn't infected with HBV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
What to do if you think you have hepatitis B?
If you think you have signs or symptoms of hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
Can hepatitis B be recovered?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
When does acute hepatitis B happen?
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
What to do if you test positive for hepatitis B?
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy.
How many people have hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
What is viral load?
A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you. You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin.
How many people are carriers of HBV?
Between 6% and 10% of those people who’ve been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers.
Where is hepatitis B most common?
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries , where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many don’t know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure you’ve been vaccinated against the virus.
How do you get hepatitis B?
People can become infected through: Birth (if a mother has hepatitis B, her baby can become infected) Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person. Contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person. Sex with an infected partner.
What is the difference between acute and chronic hepatitis B?
Acute hepatitis B infection is a short-term illness that can lead to fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, jaundice (yellow skin or eyes, dark urine, clay-colored bowel movements), and pain in the muscles, joints, and stomach. Chronic hepatitis B infection is a long-term illness that occurs when the hepatitis B virus remains in ...

Overview
- Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). For most people, hepatitis B is short term, also called acute, and lasts less than six months. But for others, the infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer ...
Symptoms
- Symptoms of acute hepatitis B range from mild to severe. They usually appear about 1 to 4 months after you've been infected, although you could see them as early as two weeks after you're infected. Some people, usually young children, may not have any symptoms. Hepatitis B signs and symptoms may include: 1. Abdominal pain 2. Dark urine 3. Fever 4. Joint pain 5. Loss …
Causes
- Hepatitis B infection is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The virus is passed from person to person through blood, semen or other body fluids. It does not spread by sneezing or coughing. Common ways that HBVcan spread are: 1. Sexual contact.You may get hepatitis B if you have unprotected sex with someone who is infected. The virus can pass to you if the person's blood, s…
Risk Factors
- Hepatitis B spreads through contact with blood, semen or other body fluids from an infected person. Your risk of hepatitis B infection increases if you: 1. Have unprotected sex with multiple sex partners or with someone who's infected with HBV 2. Share needles during IV drug use 3. Are a man who has sex with other men 4. Live with someone who has a chronic HBVinfection 5. Ar…
Complications
- Having a chronic HBVinfection can lead to serious complications, such as: 1. Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis).The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. 2. Liver cancer.People with chronic hepatitis B infection have an increased risk of liver cancer. 3. Liver failure.Acute liver fail…
Prevention
- The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given as two injections separated by a month or three or four injections over six months, depending on which vaccine is given. You can't get hepatitis B from the vaccine. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended by the United States Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for adults 19 to 59 years of age who do not have a contraindication t…