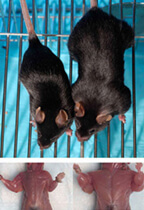
Fusion Definition in Biology and Medicine Fusion is the process by which uninuclear cells combine to form a multinuclear cell. This process is also known as cell fusion.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear fusion?
What are the six advantages of nuclear fusion?
- Clean. Fusion produces zero greenhouse gas emissions, emitting only helium as exhaust. …
- Safe. Fusion energy is inherently safe, with zero possibility of a meltdown scenario and no long lived waste.
- Abundant. There is enough fusion fuel to power the planet for hundreds of millions of years. …
- On Demand.
What is the definition of fission in science?
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a nucleus into smaller, stable nuclei, releasing tremendous energy. Learn the process and the science behind how the splitting of one of the smallest known ...
What is the scientific definition of fusion?
The term " fusion " refers to key concepts in science, but the definition depends on whether that science is physics, chemistry, or biology. In its most general sense, fusion refers to synthesis or to the joining of two parts. Here are the different meanings of fusion in science: Fusion has several meaning in science.
Why is energy released in nuclear fusion?
Why energy is released in nuclear fusion? The specific binding energy of the resultant heavier nuclei is greater than that of the lighter nuclei which undergo fusion. This accounts for the energy released in a nuclear fusion reaction. The binding energy of a nucleus is defined as the total energy to be supplied to break the nucleus completely into its constituent particles or it is the energy that is released during the formation of the nucleus.
Four methods
In human therapy
Microorganisms
What is fusion in biology reproduction?
During sexual reproduction, a male and female gamete will merge together to form a new organism. The two haploid cells will fuse together to form a diploid cell called a zygote.
What is called fusion?
Fusion occurs when two atoms slam together to form a heavier atom, like when two hydrogen atoms fuse to form one helium atom. This is the same process that powers the sun and creates huge amounts of energy—several times greater than fission.
What is cell fusion in biology?
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis.
What is fusion in biology class 8?
In this process of sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete (reproductive cells) fuse to form a single cell called Zygote. This zygote gradually develops into an adult, similar to the parents.
Why does fusion mean?
The noun fusion comes from the Latin word fundere, meaning melt, so fusion is the act of melting things together. In science, fusion is the process of merging atoms together to create energy. Fusion is also used as an adjective.
What is difference between fission and fusion?
The main difference between these two processes is that fission is the splitting of an atom into two or more smaller ones while fusion is the fusing of two or more smaller atoms into a larger one.
What is two cell fusion called?
1) Fusion of two cells is called Karyogamy (2) Fusion of protoplasms between two motile on non-motile gametes is called plasmogamy (3) Organisms that depend on living plants are called saprophytes (4) Some of the organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called sheath cells – India Site. Home.
What is fusion in evolution?
• Fusion is the combination of old parts to form novelties. • Fusion is common at all levels of organization and should be considered in phylogenetic analyses.
Can bacteria fuse?
Bacterial cells from different species can combine into unique hybrid cells by fusing their cell walls and membranes and sharing cellular contents, including proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA), the molecules which regulate gene expression and control cell metabolism.
What are 3 differences between fission and fusion?
In the case of nuclear fission, an atom divides into two or more smaller or lighter atoms....Nuclear Fission vs Nuclear Fusion.Nuclear FissionNuclear FusionLittle energy is needed to split an atom in a fission reactionHigh energy is needed to bring fuse two or more atoms together in a fusion reaction4 more rows•Jun 10, 2020
What is fusion class 10 biology?
It is a process involved in the sexual reproduction of angiosperms. Triple fusion is a fusion that involves a sperm nucleus and two polar nuclei which occurs in the double fertilization in a seed-bearing plant that results in the endosperm formation. The fusion process occurs in the embryo sac of the angiosperms.
What is fusion class 7th?
Fusion is a chemical change in which two lighter atoms bond togetgher to form a heavier one. It releases energy.
What is fusion class 9th?
Fusion : The heating process by which a solid changes into the liquid state is called fusion.
Why is melting called fusion?
This phenomenon is called fusion because when two separate solid objects made from the same substance are melted, they can get mixed together into a new one (they fuse). This can also apply to different substances, like alloys from different metals or mixtures of alcohol and water, or different waxes and oils.
What is fusion definition with example?
The definition of fusion is the act of melting or blending two or more separate things into one. An example of fusion is creating a dinner that combines Indian and Japanese elements.
What is the definition of fusion in chemistry?
Fusion means combining lighter atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus. Energy is absorbed or released by the process and the resulting nucleus is lighter than the combined masses of the two original nuclei added together.
What is the process of fusion?
But what drives this process? What is fusion? Fusion occurs when two light atoms bond together, or fuse, to make a heavier one. The total mass of the new atom is less than that of the two that formed it; the "missing" mass is given off as energy, as described by Albert Einstein's famous "E=mc 2 " equation.
What is the difference between fusion and fission?
Fusion differs from fission, which splits atoms and results in substantial radioactive waste, which is hazardous.
How does hydrogen become a plasma?
At this heat, the hydrogen is no longer a gas but a plasma, an extremely high-energy state of matter where electrons are stripped from their atoms.
Which is more promising, deuterium or tritium?
However, the process yields more energy than deuterium-tritium fusion.
Is hydrogen a gas or a plasma?
At this heat, the hydrogen is no longer a gas but a plasma, an extremely high-energy state of matter where electrons are stripped from their atoms. RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU... Scientists work long days often without taking time for a break.
Is fusion a potential energy source?
It is also a potential energy source on Earth. When set off in an intentionally uncontrolled chain reaction, it drives the hydrogen bomb. Fusion is also being considered as a possibility to power crafts through space. Fusion differs from fission, which splits atoms and results in substantial radioactive waste, which is hazardous.
What is the process of fusion?
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoblasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis. Cell fusion is a necessary event in the maturation of cells so that they maintain their specific functions throughout growth .
What is the term for fusion of two cells?
Homotypic cell fusion occurs between cells of the same type. An example of this would be osteoclasts or myofibers being fusing together with their respective type of cells. Whenever the two nuclei merge a synkaryon is produced. Cell fusion normally occurs with nuclear fusion, but in the absence of nuclear fusion, the cell would be described as a binucleated heterokaryon. A heterokaryon is the melding of two or more cells into one and it may reproduce itself for several generations. If two of the same type of cells fuse, but their nuclei do not fuse, then the resulting cell is called a syncytium.
What is a hybrid cell with a nucleus?
Each of the fused hybrid cells contained a single nucleus with chromosomes from both fusion partners. Synkaryon became the name of this type of cell combined with a nucleus. In the late 1960s biologists successfully fused cells of different types and from different species.
How do cells fuse?
This method begins when two cells are brought into contact by dielectrophoresis. Dielectrophoresis uses a high frequency alternating current, unlike electrophoresis in which a direct current is applied. Once the cells are brought together, a pulsed voltage is applied. The pulse voltage causes the cell membrane to permeate and subsequent combining of the membranes and the cells then fuse. After this, alternative voltage is applied for a brief period of time to stabilize the process. The result of this is that the cytoplasm has mixed together and the cell membrane has completely fused. All that remains separate is the nuclei, which will fuse at a later time within the cell, making the result a heterokaryon cell.
What are the functions of a fused cell?
New functions of the fused cell can include a reversion of phenotype, transdifferentiation and proliferation. If nuclear fusion occurs, the fused nucleus initially contains the complete chromosomal content of both fusion partners (4N), but ultimately chromosomes are lost and/or re-sorted (see arrows).
What is it called when two cells fuse but their nuclei do not fuse?
If two of the same type of cells fuse, but their nuclei do not fuse, then the resulting cell is called a syncytium. Heterotypic cell fusion occurs between cells of different types, making it the exact opposite of homotypic cell fusion.
How long does it take for Sendai virus to fusion?
Sendai virus induced cell fusion occurs in four different temperature stages. During the first stage, which lasts no longer than 10 minutes , viral adsorption takes place and the adsorbed virus can be inhibited by viral antibodies. The second stage, which is 20 minutes, is pH dependent and an addition of viral antiserum can still inhibit ultimate fusion. In the third, antibody-refractory stage, viral envelope constituents remain detectable on the surface of cells. During the fourth stage, cell fusion becomes evident and HA neuraminidase and fusion factor begin to disappear. The first and second stages are the only two that are pH dependent.
What is fusion gene?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. A fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia.
What happens when a gene fusion occurs?
If it happens in coding sequences, gene fusion cause the assembly of a new gene , then it allows the appearance of new functions by adding peptide modules into multi domain protein. The detecting methods to inventory gene fusion events on a large biological scale can provide insights about the multi modular architecture of proteins.
How does fusion affect cancer?
It has been known for 30 years that the corresponding gene fusion plays an important role in tumorgenesis. Fusion genes can contribute to tumor formation because fusion genes can produce much more active abnormal protein than non-fusion genes. Often, fusion genes are oncogenes that cause cancer; these include BCR-ABL, TEL-AML1 ( ALL with t (12 ; 21)), AML1-ETO ( M2 AML with t (8 ; 21)), and TMPRSS2 - ERG with an interstitial deletion on chromosome 21, often occurring in prostate cancer. In the case of TMPRSS2-ERG, by disrupting androgen receptor (AR) signaling and inhibiting AR expression by oncogenic ETS transcription factor, the fusion product regulates the prostate cancer. Most fusion genes are found from hematological cancers, sarcomas, and prostate cancer. BCAM-AKT2 is a fusion gene that is specific and unique to high-grade serous ovarian cancer.
Why do scientists use fusion genes?
Biologists may also deliberately create fusion genes for research purposes. The fusion of reporter genes to the regulatory elements of genes of interest allows researches to study gene expression. Reporter gene fusions can be used to measure activity levels of gene regulators, identify the regulatory sites of genes (including the signals required), identify various genes that are regulated in response to the same stimulus, and artificially control the expression of desired genes in particular cells. For example, by creating a fusion gene of a protein of interest and green fluorescent protein, the protein of interest may be observed in cells or tissue using fluorescence microscopy. The protein synthesized when a fusion gene is expressed is called a fusion protein .
What is the function of oncogenic fusion?
Alternatively, a proto-oncogene is fused to a strong promoter, and thereby the oncogenic function is set to function by an upregulation caused by the strong promoter of the upstream fusion partner. The latter is common in lymphomas, where oncogenes are juxtaposed to the promoters of the immunoglobulin genes. Oncogenic fusion transcripts may also be caused by trans-splicing or read-through events.
What causes fusion transcripts in lymphoma?
Oncogenic fusion transcripts may also be caused by trans-splicing or read-through events.
How does gene fusion affect evolution?
We can observe its effect if gene fusion occurs in coding sequences. Duplication, sequence divergence, and recombination are the major contributors at work in gene evolution. These events can probably produce new genes from already existing parts. When gene fusion happens in non-coding sequence region, it can lead to the misregulation of the expression of a gene now under the control of the cis-regulatory sequence of another gene. If it happens in coding sequences, gene fusion cause the assembly of a new gene, then it allows the appearance of new functions by adding peptide modules into multi domain protein. The detecting methods to inventory gene fusion events on a large biological scale can provide insights about the multi modular architecture of proteins.
Definition of fusion
a : a merging of diverse, distinct, or separate elements into a unified whole Opera is a fusion of several arts.
Examples of fusion in a Sentence
The show is a fusion of news and entertainment. The fusion of different cultural influences is evident in her sculpture.
History and Etymology for fusion
borrowed from Medieval Latin fūsiōn-, fūsiō "process of pouring, casting of molten metal," going back to Latin, "process of pouring, effusion," from fud-, variant stem of fundere "to pour, shed, cast (liquid metal)" (Medieval Latin also, "to melt down, make liquid") + -tiōn-, -tiō, suffix of verbal action — more at found entry 5
Medical Definition of fusion
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
What is the brain's ability to gather information from each eye separately and form a single, unified image?
Binocular fusion (simply "fusion") refers to the brain 's ability to gather information received from each eye separately and form a single, unified image. If the eyes are not precisely aligned, a patient may experience blur, double vision, or discomfort.
What is the ability to produce a three dimensional or floating image from two similar objects?
Stereopsis – the ability to produce a three dimensional or floating image from two similar objects. The similar pictures seen by each eye include a slight offset nature such that each picture is not truly superimposed onto the other but laterally displaced relative to each other.
What is the brain's adaptation to double vision?
The brain has an interesting adaptation specific to double vision. In young patients, the visual system is incredibly versatile - the fancy term for this "plastic" as in "neuroplasticity". What this means is that the visual system can adapt to the confusion of double vision by ignoring or suppressing the second image.
Can fusion be difficult?
Some patients may have difficulty with fusion only at certain distances. For example, a patient may have normal fusion at distance but struggle with fusion up close with reading. The result is blurry our doubled images when trying to do near work. This example is what happens to patients with convergence insufficiency.
Can motor fusion be sensory fusion?
Motor fusion must be achieved to allow an opportunity for sensory fusion to occur. However, it is not a given that motor fusion automatically gives rise to sensory fusion. Has your child’s vision been checked lately? If your loved one is struggling with vision fusion, call us to schedule an appointment to discuss the ways vision therapy can help!
Introduction
In-Fusion cloning or In-Fusion assembly is a ligation-free and directional molecular cloning method to clone one or multiple DNA fragments in any linearized vector in a single step and is a single-tube reaction. In conventional cloning, the presence and the availability of unique restriction enzyme sites in vectors and inserts limit the cloning.
Principle
In-Fusion cloning is a simple and efficient method of cloning that depends upon a 15 or 20 bp homology sequence. The 15 bp homology is sufficient for a successful In-Fusion reaction. however, increasing the size of homology sequence to 20 bp increases the cloning efficiency (Fig 2. Pairs of Yellow and red bars).
Preparation of Insert
The inserts for In-Fusion cloning will be amplified using In-Fusion-specific primers, which contains 20 bp homology with adjacent DNA fragments to which it will be joined. The adjacent DNA can be other insert DNA molecules or the plasmid backbone.
Preparation of vector (selecting a suitable vector and linearization)
The successful In-Fusion reaction requires a linearized vector. Select the suitable vector and linearize it using one of the following methods.
In-Fusion cloning reaction
The linearized plasmid/vector and insert (s) are mixed with a 2X In-Fusion HD enzyme reaction mixture and incubated at 50°C for 15 mins. After Keeping the samples on ice for 10-15 mins, the samples are will be ready for bacterial transformation.

Overview
Four methods
There are four methods that cell biologists and biophysicists use to fuse cells. These four ways include electrical cell fusion, polyethylene glycol cell fusion, and sendai virus induced cell fusion and a newly developed method termed optically controlled thermoplasmonics.
Electrical cell fusion is an essential step in some of the most innovative metho…
History
In 1847 Theodore Schwann expanded upon the theory that all living organisms are composed of cells when he added to it that discrete cells are the basis of life. Schwann observed that in certain cells the walls and cavities of the cells coalesce together. It was this observation that provided the first hint that cells fuse. It was not until 1960 that cell biologists deliberately fused cells for the first time. To fuse the cells, biologists combined isolated mouse cells, with the same kind of tiss…
Two types
There are two different types of cell fusion that can occur. These two types include homotypic and heterotypic cell fusion.
Homotypic cell fusion occurs between cells of the same type. An example of this would be osteoclasts or myofibers being fusing together with their respective type of cells. Whenever the two nuclei merge a synkaryon is produced. Cell fusi…
In human therapy
Alternative forms of restoring organ function and replacing damaged cells are needed with donor organs and tissue for transplantation being so scarce. It is because of the scarcity that biologists have begun considering the potential for therapeutic cell fusion. Biologists have been discussing implications of the observation that cell fusion can occur with restorative effects following tissue damage or cell transplantation. Though using cell fusion for this is being talked about and worke…
Microorganisms
Plasmogamy is the stage of the sexual cycle of fungi in which two cells fuse together to share a common cytoplasm while bringing haploid nuclei from both partners together in the same cell.
Cell fusion (plasmogamy or syngamy) is a stage in the Amoebozoa sexual cycle.
In Escherichia coli spontaneous zygogenesis (Z-mating) involves cell fusion, and appears to be a form of true sexuality in prokaryotes. Bacteria that perform Z-mating are called Szp .
Other uses
• To study the control of cell division and gene expression.
• To Investigate malignant transformations.
• To obtain viral replication.
• For gene and chromosome mapping.
See also
• Cell-cell fusogens
• Cellular differentiation
• Fertilisation
• Fusion mechanism
• Fusion protein