
What happens during gas exchange?
What are the 4 steps of gas exchange?
- Breathing. • Inhale. Diaphragm moves down, chest volume. increases, air enters lungs.
- Exhale. Diaphragm moves up, chest volume. decreases, air leaves lungs.
- O2 & CO2 Transport. O2. rich blood goes from lungs to cells. CO2.
- Internal Respiration. Exchange of O2 & CO2 between capillaries & body cells.
Where does gas exchange occur in the body?
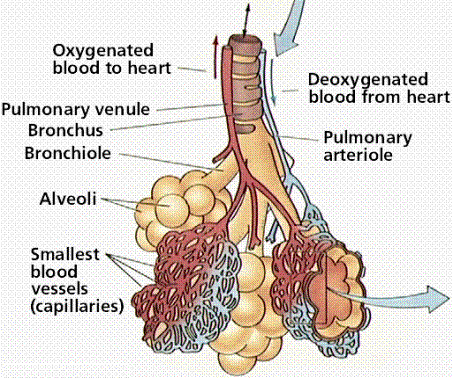
Gas exchange occurs within the lower airways, primarily the alveoli. Often called the "business end" of respiration. Blood entering the lungs via the pulmonary artery is deoxygenated. It becomes oxygenated when the capillaries pass through the alveoli and reenters the heart via the pulmonary vein with oxygenated blood. We can control the PEEP.
What is the process of gaseous exchange?
What are the five major steps of gas exchange?
- Pulmonary Ventilation. Movement of air in and out of the lungs passage (Thorax and Diaphragm).
- External Respiration. Exchange of gases between air and blood at pulmonary capillaries (Alveoli).
- Transport of gases through blood vessels.
- Internal Respiration.
- Cellular Respiration.
What is gas exchange in the respiratory system?
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system. It is essential to ensure a constant supply of oxygen to tissues, as well as removing carbon dioxide to prevent its accumulation.
What is gas exchange easy definition?
Gas exchange: The primary function of the lungs involving the transfer of oxygen from inhaled air into the blood and the transfer of carbon dioxide from the blood into the exhaled air.
Why is gas exchange in the lungs important?
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system. It is essential to ensure a constant supply of oxygen to tissues, as well as removing carbon dioxide to prevent its accumulation.
What are the 4 steps of gas exchange?
Once the de-oxygenated blood from internal respiration reaches the alveoli the whole four stage process of respiration starts again:Pulmonary ventilation.Pulmonary gas exchange.Respiratory gas transport.Peripheral gas exchange.
What is the gas exchange system?
The function of the respiratory system is to move two gases: oxygen and carbon dioxide. Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them.
What is the main function of gas exchange?
Gas exchange: The primary function of the lungs involving the transfer of oxygen from inhaled air into the blood and the transfer of carbon dioxide from the blood into the exhaled air.
What affects gas exchange?
What Factors Affect Gas Exchange In The Lungs?The thickness of the membrane.The surface area of the membrane.The difference in pressure across membranes.Diffusion coefficient of the gas.
What are the 3 principles of gas exchange?
Three processes are essential for the transfer of oxygen from the outside air to the blood flowing through the lungs: ventilation, diffusion, and perfusion.
What is the first phase of gas exchange?
Based on the above, pulmonary gas exchange is considered as a continuous process involving: 1) ventilation, 2) diffusion (including both physical diffusion across the pulmonary blood:gas barrier and subsequent chemical reactions (between O2 and haemoglobin (Hb) and for CO2 conversion to bicarbonate), and 3) perfusion.
Is respiration a gas exchange?
The exchange of gases between the blood and tissue cells is internal respiration. Finally, the cells utilize the oxygen for their specific activities: this is called cellular metabolism, or cellular respiration. Together, these activities constitute respiration.
What happens during gas exchange in the tissue?
Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body: in the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane, and at the tissues, where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up.
How does gas exchange take place in the alveoli?
Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them. As shown below, inhaled oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries, and carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries to the air in the alveoli.
What is the process of gas exchange in the alveoli called?
In a process called diffusion, oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood through the capillaries (tiny blood vessels) lining the alveolar walls.
What important activity takes place in the lungs?
The main function of the lungs is the process of gas exchange called respiration (or breathing). In respiration, oxygen from incoming air enters the blood, and carbon dioxide, a waste gas from the metabolism, leaves the blood.
What is needed for gas exchange?
Two important aspects of gas exchange in the lung are ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs, and perfusion is the flow of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. For gas exchange to be efficient, the volumes involved in ventilation and perfusion should be compatible.
What will happen if one of the breathing system fails to carry its function properly?
When a person has acute respiratory failure, the usual exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO2) in the lungs does not occur. As a result, the heart, the brain, or the rest of the body cannot get sufficient amounts of oxygen.
What are the 2 main functions of the lungs?
The lungs and respiratory system allow us to breathe. They bring oxygen into our bodies (called inspiration, or inhalation) and send carbon dioxide out (called expiration, or exhalation).
What is the gas exchange in the lungs?
Gas Exchange in the Lungs. Alveoli are the basic functional units of the lungs where gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. Alveoli (singular, alveolus) are tiny air sacs that consist of connective and epithelial tissues.
Where is the pulmonary gas exchange?
One of a cluster of tiny sacs at the ends of bronchioles in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place.
What is the structure that is specialized for gas exchange between inhaled air and the blood in pulmonary capillar?
The carbon dioxide can then be exhaled from the body. Figure 13.4.3 A single alveolus is a tiny structure that is specialized for gas exchange between inhaled air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries. Gas exchange by diffusion depends on having a large surface area through which gases can pass.
How are alveoli arranged?
As shown in Figure 13.4.2, alveoli are arranged in groups like clusters of grapes. Each alveolus is covered with epithelium that is just one cell thick. It is surrounded by a bed of capillaries, each of which has a wall of epithelium just one cell thick. As a result, gases must cross through only two cells to pass between an alveolus ...
How does diffusion affect gas exchange?
Gas exchange by diffusion depends on having a large surface area through which gases can pass. Although each alveolus is tiny, there are hundreds of millions of them in the lungs of a healthy adult, so the total surface area for gas exchange is huge. It is estimated that this surface area may be as great as 100 m 2 (or approximately 1,076 ft²). Often we think of lungs as balloons, but this type of structure would have very limited surface area and there wouldn’t be enough space for blood to interface with the air in the alveoli. The structure alveoli take in the lungs is more like a giant mass of soap bubbles — millions of tiny little chambers making up one large mass — this is what increases surface area giving blood lots of space to come into close enough contact to exchange gases by diffusion.
Where does oxygen diffuse into the blood?
As a result, oxygen diffuses from the air inside the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries. Carbon dioxide, in contrast, is more concentrated in the blood in the pulmonary capillaries than it is in the air inside the alveoli. As a result, carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction.
Which artery carries oxygenated blood to the lungs?
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it travels through pulmonary capillaries, picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins. Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across cell membranes.
What is the exchange of respiratory gases?
Respiratory gas exchange depends on prompt diffusion of respiratory gases between the tissue and plasma, the erythrocyte and plasma, the plasma and resident alveolar gas, and the alveolar gas and gas in the conducting airways.
How does respiration affect gas exchange?
Respiratory gas exchange during development is complicated by profound changes in the quantity of gases exchanged, the location on the body surface where gas is taken up or excreted, and the relative importance of diffusion and convection as a means of moving gases to and from the tissues.
How is gas transported between alveolar space and pulmonary capillary blood?
Thus the transport of gas is expressed by V · <pi>pt Dm (PA − P b) where Dm = alveolar-capillary membrane diffusion conductance and (PA − P b) represents the partial pressure difference across the membrane. To simplify the analysis, it is useful to study a single gas that binds firmly to hemoglobin. Because carbon monoxide combines avidly with hemoglobin, the P CO in pulmonary capillary plasma is virtually zero when small quantities of carbon monoxide are inspired, simplifying the analysis of diffusing capacity. In clinical practice, the diffusing capacity of the lung is expressed by the following:
What is the diffusing capacity of the lung?
The diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide is expressed as the volume of carbon monoxide transferred in milliliters of carbon monoxide per minute per millimeter of mercury of alveolar partial pressure of carbon monoxide. The diffusing capacity is usually abbreviated DL CO. Both a single-breath technique (which is difficult to perform in a neonate) and a steady-state technique can be used for assessing Pa co.
What are the factors that influence blood flow in the lung?
Other important factors influencing blood flow in the lung include the effects of gravity; the effects of inflation, pleural, and interstitial pressures on different segments of pulmonary circulation; and the baseline tone and reactivity of the blood vessels. Table 1. Pulmonary Hemodynamic Parameters. Species.
What is the only system through which the entire cardiac output passes?
The pulmonary circulation is the only system through which the entire cardiac output passes. Additionally, the pulmonary circulation has been shown to have minimal basal tone and minimal ability to change the forces that act upon it. Unlike many other organs, the lung does not, and cannot, control the blood flow delivered to it by the heart during normal steady states or during altered flow conditions. Despite this relative passivity, the lung is capable of significant redistributions of blood flow within itself, which, under normal circumstances, will accommodate any changes in blood flow imposed upon it, even when disease states compromise part of the vasculature itself. Thus, the physiology and pathophysiology of the pulmonary circulation is considerably more complicated than a first look might indicate.
Why is partial pressure of carbon dioxide a significant variable?
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide, rather than its percentage composition, is the significant variable because Henry law of solubility states that the gas is physically dissolved in liquid and in equilibrium with the gas phase at the same partial pressure. 2.
Where does carbon dioxide diffuse?
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli. These three features are particularly important to our lungs for efficient gas exchange. Most of them also apply to other exchange surfaces such as the small intestine, body tissues and placenta.
How much surface area does the lungs have?
Large surface area: human lungs contain about 500 million al veoli, which creates a surface area around half the size of a tennis court. This speeds up diffusion because gases have more area over which to diffuse.
Why do alveoli have a dense capillary network?
Good blood supply: the alveoli have a dense capillary network so that large volumes of gases can be exchanged.
What is the alveoli?
The alveoli are lined with mucus and are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries. They have very thin walls for gases to be absorbed through. An individual air sac is called an alveolus. The layer of moisture in the alveoli allows gases to dissolve so that they can diffuse quickly.
Where does air come from?
Air gets from the mouth and nose to the lungs through the windpipe (trachea). The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchi (one to each lung). The bronchi split into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles, which then end in microscopic alveoli (air sacs).
What is the waste product of aerobic respiration?
A waste product of aerobic respiration is carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide must be removed from the body or it makes the blood dangerously acidic. Oxygen and carbon dioxide enter and leave the blood by diffusion through the lining ...
Do alveoli have a good blood supply?
The alveoli have a very large total surface area and a very good blood supply, provided by the den se network of capillaries that sur round them. There is an exchange of gases between the alveoli and their surrounding capillary blood vessels. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood.
What is gas exchange?
Gas exchange is the process where carbon dioxide, a waste gas, is exchanged in the lungs for fresh oxygen. Let’s examine how it works.
How to treat impaired gas exchange?
Impaired gas exchange is often treated using supplemental oxygen. This helps counteract the effects of hypoxemia by delivering oxygen directly into your lungs. You’ll breathe in supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula or a mask.
What causes COPD?
COPD, and by extension the impaired gas exchange associated with it, is caused by long-term exposure to environmental irritants. When you breathe in these irritants over a long period of time, they can damage your lung tissue.
Why is gas exchange not efficient?
The health and flexibility of your airways and alveoli are vital in promoting effective gas exchange. However, in COPD, these structures have become damaged. Due to this, gas exchange cannot occur as efficiently.
What is it called when you can't get enough oxygen?
When this happens, it’s hard to provide your body with enough oxygen to support daily activities and to remove enough carbon dioxide — a condition called hypercapnia.
Where does carbon dioxide move?
At the same time as oxygen is moving into the blood, carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation. Pulmonary rehabilitation can teach you strategies on how to go about your daily activities when you have COPD. It may involve breathing techniques, an exercise plan, and counseling.
