Explore
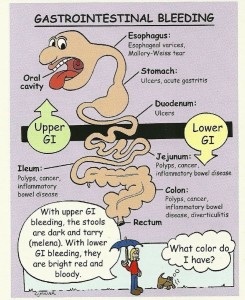
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding refers to any bleeding that starts in the gastrointestinal tract. Bleeding may come from any site along the GI tract, but is often divided into: Upper GI bleeding: The upper GI tract includes the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach), stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
What does gastrointestinal bleeding stand for?
Risk factors for lower GI bleeding can include:
- NSAID medicines
- Lack of timely screening for colon cancer and polyps
- Use of alcohol and smoking
- Conditions that lead to the development of angioectasias
What causes a lower GI bleed?
The overall mortality for severe GI bleeding is approximately 8 percent, but this number is diminishing with the arrival of superior diagnostic techniques and newer medical treatments. Many bleeding episodes resolve on their own, but it is still imperative that the bleeding site be determined.
Will gastrointestinal bleeding resolve itself?
- Water
- Aloe vera / Aloe vera juice
- Flaxseed / flaxseed oil
- Coconut water
- Leafy vegetables like kale, mustard greens, spinach etc
- High fiber fruits like figs, apples, pears and berries
- Psyllium husk
- Prune juice and other prune products
- Chia seeds
- Probiotic rich foods like coconut kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi etc
How to stop GI bleeding?
What causes gastrointestinal bleeding?
There are many possible causes of GI bleeding, including hemorrhoids, peptic ulcers, tears or inflammation in the esophagus, diverticulosis and diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, colonic polyps, or cancer in the colon, stomach or esophagus.
How do you treat gastrointestinal bleeding?
If you have an upper GI bleed, you might be given an IV drug known as a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to suppress stomach acid production. Once the source of the bleeding is identified, your doctor will determine whether you need to continue taking a PPI .
Is gastrointestinal bleeding serious?
Massive bleeding from the GI tract can be dangerous. However, even very small amounts of bleeding that occur over a long period of time can lead to problems such as anemia or low blood counts. Once a bleeding site is found, many therapies are available to stop the bleeding or treat the cause.
What does a gastrointestinal bleed feel like?
Symptoms also vary depending on how quickly you bleed. If sudden, massive bleeding happens, you may feel weak, dizzy, faint, short of breath, or have cramp-like belly pain or diarrhea. You could go into shock, with a rapid pulse and drop in blood pressure. You may become pale.
What are the warning signs of gastrointestinal bleeding?
SymptomsVomiting blood, which might be red or might be dark brown and resemble coffee grounds in texture.Black, tarry stool.Rectal bleeding, usually in or with stool.
How do you know if you have gastrointestinal bleeding?
What are the symptoms of GI bleeding?black or tarry stool.bright red blood in vomit.cramps in the abdomen.dark or bright red blood mixed with stool.dizziness or faintness.feeling tired.paleness.shortness of breath.More items...
How long can you live with a GI bleed?
Forty patients died during the study; the median survival duration was 60 months after lower GI bleeding. The most common causes of death were sepsis, myocardial dysfunction, and cancer.
What medication can cause gastrointestinal bleeding?
Drugs that can lead to gastrointestinal bleeding include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like diclofenac and ibuprofen, platelet inhibitors such as acetylsalicylic acid (ASS), clopidogrel and prasugrel, as well as anticoagulants like vitamin-K antagonists, heparin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOAKs).
What happens if a GI bleed goes untreated?
Shock — GI bleeds that come on quickly and progress rapidly can lead to a lack of blood flow to the rest of the body, damaging organs and causing organ failure. Without treatment, shock can worsen, causing irreversible damage or even death.
What is the most common cause of lower GI bleeding?
Colonic Bleeding Causes Colonic diverticulosis continues to be the most common cause, accounting for about 30 % of lower GI bleeding cases requiring hospitalization. Internal hemorrhoids are the second-most common cause.
What color is your stool if you have internal bleeding?
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the stomach, small intestine, or right side of the colon. The term melena is used to describe this finding.
Can internal bleeding heal on its own?
Sometimes, internal bleeding from trauma stops on its own. Ongoing or severe internal bleeding due to trauma requires surgery to correct the problem. When internal bleeding is severe, emergency surgery may take place within minutes after arrival at the hospital.
How long does it take to recover from GI bleed?
Even in the presence of a low Hb level at discharge, an acceptable outcome is expected after endoscopic hemostasis for nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Recovery of the Hb level after discharge is complete within 45 days.
What happens if a GI bleed goes untreated?
Shock — GI bleeds that come on quickly and progress rapidly can lead to a lack of blood flow to the rest of the body, damaging organs and causing organ failure. Without treatment, shock can worsen, causing irreversible damage or even death.
How long can you live with a GI bleed?
Forty patients died during the study; the median survival duration was 60 months after lower GI bleeding. The most common causes of death were sepsis, myocardial dysfunction, and cancer.
Can internal bleeding heal on its own?
Sometimes, internal bleeding from trauma stops on its own. Ongoing or severe internal bleeding due to trauma requires surgery to correct the problem. When internal bleeding is severe, emergency surgery may take place within minutes after arrival at the hospital.
What Do I Need to Know About Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding?
GI bleeding may occur in any part of your digestive tract. This includes your esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, or anus. Bleeding may be mild...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of GI bleeding?
Symptoms depend on where the bleeding is, what is causing it, and how much blood you have lost. You may have any of the following: 1. Blood in your...
How Is GI Bleeding Diagnosed?
You may need treatment and monitoring in the hospital. Tell the healthcare provider if you take blood thinner medicine. You may need medicine to re...
How Is GI Bleeding Treated?
Your bleeding may get better without treatment. If bleeding is severe or causes symptoms, you may need any of the following: 1. Treatment during en...
What Can I Do to Prevent GI bleeding?
1. Manage GI conditions as directed. Examples of GI conditions include gastroesophageal reflux, peptic ulcer disease, and ulcerative colitis. Take...
Call 911 For Any of The Following
1. You have shortness of breath or trouble breathing. 2. You faint or lose consciousness. 3. You have chest pain.
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. You feel dizzy or are too weak to stand. 2. Your heart is beating faster than usual. 3. You vomit blood, or your vomit looks like coffee grounds...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have bowel movements that are tarry or black. 2. You have nausea or are vomiting. 3. You have heartburn. 4. You have questions or concerns a...
What is GI bleeding?
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is any type of bleeding that starts in your GI tract, also called your digestive tract. GI bleeding is a symptom of a disease or condition, rather than a disease or condition itself.
How likely are men to have upper GI bleeding?
Men are twice as likely as women to have upper GI bleeding.
What is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases?
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
Is GI bleeding sudden?
Acute GI bleeding is sudden and can sometimes be severe. Chronic GI bleeding is slight bleeding that can last a long time or may come and go. Learn more about your digestive system and how it works.
What is GI bleeding?
What do I need to know about gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding? GI bleeding may occur in any part of your digestive tract. This includes your esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, or anus. Bleeding may be mild to severe.
What are the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding?
Symptoms depend on where the bleeding is, what is causing it, and how much blood you have lost. You may have any of the following:
How is GI bleeding diagnosed?
You may need treatment and monitoring in the hospital. Tell the healthcare provider if you take blood thinner medicine. You may need medicine to reverse the effects of blood thinner medicine. You may need any of the following to find the cause of GI bleeding:
What can I do to prevent GI bleeding?
Manage GI conditions as directed. Examples of GI conditions include gastroesophageal reflux, peptic ulcer disease, and ulcerative colitis. Take all medicines for these conditions as directed.
How do you know if you have a bloody bowel movement?
You may have any of the following: Blood in your vomit, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds. Dark or bright red blood in your bowel movements. Bleeding from your rectum. Cramping or pain in your abdomen.
What is an endoscopy?
An endoscopy is a procedure to find the cause of bleeding in your esophagus, stomach, or small intestine. A capsule endoscopy may be done as an outpatient procedure. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about a capsule endoscopy.
How to stop bleeding after colonoscopy?
Medicine may be injected into your esophagus, stomach, or intestines to stop bleeding. Heat or an electrical current may also be applied to stop bleeding. Other procedures, such as banding, may be used.
What is GI bleeding?
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a serious symptom that occurs within your digestive tract. Your digestive tract consists of the following organs: GI bleeding can occur in any of these organs. If bleeding occurs in your esophagus, stomach, or initial part of the small intestine (duodenum), it’s considered upper GI bleeding.
What are the symptoms of GI bleeding?
GI bleeding could signal a life-threatening condition. Immediate medical treatment is essential. Also, seek treatment immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms: 1 paleness 2 weakness 3 dizziness 4 shortness of breath
How to diagnose upper GI bleeding?
Upper GI bleeding is most commonly diagnosed after your doctor performs an endoscopic examination. Endoscopy is a procedure that involves the use of a small camera located atop a long, flexible endoscopic tube your doctor places down your throat. The scope is then passed through your upper GI tract.
What to do if your doctor can't find the source of your bleeding?
If your doctor can’t find the source of your bleeding with an endoscopy or a GI bleeding scan, they may perform a Pillcam test. Your doctor will have you swallow a pill that contains a small camera that will take pictures of your bowel to find the source of your bleeding.
Why does my stool turn red?
Your stool might become darker and sticky, like tar, if bleeding comes from the stomach or upper GI tract. You may pass blood from your rectum during bowel movements, which could cause you to see some blood in your toilet or on your toilet tissue. This blood is usually bright red in color.
Why does my esophagus bleed?
pylori bacteria usually causes peptic ulcers. Also, enlarged veins in your esophagus can tear and bleed as a result of a condition called esophageal varices. Tears in the walls of your esophagus can also cause GI bleeding. This condition is known as Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
What does it mean when you vomit blood?
This blood is usually bright red in color. Vomiting blood is another sign that there’s bleeding somewhere in your GI tract. If you experience any of these symptoms, or if you have vomit that looks like coffee grounds, call your doctor immediately. GI bleeding could signal a life-threatening condition.
What are the two main sources of gastrointestinal bleeding?
Gastrointestinal bleeding can fall into two broad categories: upper and lower sources of bleeding. The anatomic landmark that separates upper and lower bleeds is the ligament of Treitz, also known as the suspensory ligament of the duodenum. This peritoneal structure suspends the duodenojejunal flexure from the retroperitoneum. Bleeding that originates above the ligament of Treitz usually presents either as hematemesis or melena whereas bleeding that originates below most commonly presents as hematochezia. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of gastrointestinal bleeding and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and improving care for patients with this condition.
What is the name of the duct that bleeds from the pancreas?
Hemosuccus pancreaticus (bleeding from the pancreatic duct)
What is the treatment for upper GI tract?
Allows visualization of the upper GI tract (typically including from the oral cavity up to the duodenum) and treatment with injection therapy, thermal coagulation, or hemostatic clips/bands
Can you be discharged for GI bleeding?
Most patients with GI bleeding will require hospitalization. However, some young , healthy patients with self-limited and asymptomatic bleeding may be safely discharged and evaluated on an outpatient basis.
Can abdominal pain be a sign of perforation?
Abdominal pain may raise suspicion for perforation or ischemia.
Can you provide oxygen to a patient with hematemesis?
Provide supplemental oxygen if the patient is hypoxic (typically via nasal cannula, but patients with ongoing hematemesis or altered mental status may require intubation). Avoid non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) due to the risk of aspiration with ongoing vomiting.
What causes GI bleeding?
Many conditions can cause GI bleeding. A doctor can try to find the cause of your bleeding by finding its source. The following conditions, which are listed in alphabetical order, include possible causes of GI bleeding:
How do you know if you have GI bleeding?
Symptoms of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding may include. black or tarry stool. bright red blood in vomit. cramps in the abdomen. dark or bright red blood mixed with stool. dizziness or faintness. feeling tired.
Why does esophagitis cause sores?
GER happens when your lower esophageal sphincter is weak or relaxes when it should not. Stomach acid can damage your esophagus and cause sores and bleeding. Gastritis. Some common causes of gastritis include.
What is it called when you have abnormal blood vessels in your GI tract?
Angiodysplasia. Angiodysplasia is when you have abnormal or enlarged blood vessels in your GI tract. These blood vessels can become fragile and bleed.
Why do my rectums swell?
Constipation and straining during bowel movements cause hemorrhoids to swell. Hemorrhoids cause itching, pain, and sometimes bleeding in your anus or lower rectum. Anal fissures are small tears that also can cause itching, tearing, or bleeding in your anus. Mallory-Weiss tears.
What is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases?
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
Can you have occult bleeding?
Symptoms of anemia may include feeling tired and shortness of breath, which can develop over time. Some people may have occult bleeding. Occult bleeding may be a symptom of inflammation or a disease such as colorectal cancer.
Why do I have GI bleeding?
GI bleeding is a type of bleeding that occurs anywhere in the digestive system. It may be due to an injury, infection, or inflammation. The bleeding may appear suddenly and produce a lot of blood, or a person may notice gradual or periodic bleeding. Sudden, heavy bleeding is more immediately dangerous. However, both types of bleeding may signal ...
Where does GI bleeding occur?
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is bleeding in the digestive tract, anywhere from the throat to the rectum. A person can experience a small loss of blood, such as when a hemorrhoid bleeds, or a hemorrhage, which causes a substantial blood loss. In this article, we discuss GI bleeding, its symptoms, severity, potential causes, risk factors, ...
What are the risk factors for GI bleeding?
Anyone can have a GI bleed, especially if they experience other digestive issues, such as colitis or peptic ulcers. Risk factors for GI bleeding include: using anticoagulants, which are a group of drugs that can thin the blood and may therefore increase bleeding.
Why does my stomach burn when I have peptic ulcers?
Bleeding peptic ulcers. Peptic, or stomach, ulcers may be due to a Helicobacter pylori infection or overuse of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). A person with peptic ulcers may experience a burning sensation in the stomach. To help treat these, doctors may prescribe medication.
How to stop bleeding from varices?
A doctor may stop bleeding from varices with the use of elastic bands.
How do you know if you have a GI bleed?
they have lost a significant amount of blood, for example, by constantly bleeding from the rectum or mouth.
What does it mean when you have blood on your toilet paper?
blood on toilet paper or baby wipes after wiping. bleeding from the anus. red blood in stool. A serious, significant bleed, especially in the upper GI tract, may cause other symptoms, such as: little or no urine to pass. a drop in blood pressure . confusion. intense nausea. loss of consciousness.
What to do if bleeding is not severe?
If your bleeding is not severe, you might start by seeing your primary care provider. Or you might be referred immediately to a specialist in gastrointestinal disorders (gastroenterologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment.
What tests are needed for occult bleeding?
Tests might include: Blood tests. You may need a complete blood count, a test to see how fast your blood clots, a platelet count and liver function tests. Stool tests. Analyzing your stool can help determine the cause of occult bleeding. Nasogastric lavage.
What is balloon assisted enteroscopy?
Balloon-assisted enteroscopy. A specialized scope inspects parts of your small intestine that other tests using an endoscope can't reach. Sometimes, the source of bleeding can be controlled or treated during this test. Angiography.
How does endoscopy work?
In this procedure, you swallow a vitamin-size capsule with a tiny camera inside. The capsule travels through your digestive tract taking thousands of pictures that are sent to a recorder you wear on a belt around your waist. This enables your doctor to see inside your small intestine.
What questions should I ask my doctor about a syringe?
Your doctor is likely to ask you questions, such as: 1 Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional? 2 How severe are your symptoms? 3 What, if anything, seems to improve your symptoms? 4 What, if anything, appears to worsen your symptoms? 5 Do you take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, either over-the –counter or prescribed, or do you take aspirin? 6 Do you drink alcohol?
Can you take PPI if you have a bleed?
Once the source of the bleeding is identified, your doctor will determine whether you need to continue taking a PPI. Depending on the amount of blood loss and whether you continue to bleed, you might require fluids through a needle (IV) and, possibly, blood transfusions. If you take blood-thinning medications, including aspirin or nonsteroidal ...
Can a CT scan show a GI bleed?
A variety of other imaging tests, such as an abdominal CT scan, might be used to find the source of the bleed. If your GI bleeding is severe, and noninvasive tests can't find the source, you might need surgery so that doctors can view the entire small intestine. Fortunately, this is rare.
