
Full Answer
What are some criticisms of the general strain theory?
One of the major criticisms is the fact that the strain theory is based on weak empirical support. Scholars have argued that the strain theory was improperly measured suggesting that the main concept of the strain theory was improperly measured in previous research (Burton & Cullen, 1992).
What is classic strain theory?
Strain theory attempts to explain conflict or deviance via the four functions of deviance. Merton’s classic definition: “Strain theory has been defined as an approach to deviance which regards deviance as a product of the insufficient adaptation of the social system to the moral expectations of its members.”
What is classical strain theory?
Classical strain theory predicts that deviance is more likely to occur if one’s culturally determined aspirations for monetary success and the opportunity to achieve that success are not congruent.
What is strain theory in criminal justice?
What is the strain theory in criminal justice? Strain theories state that certain strains or stressors increase the likelihood of crime. These strains lead to negative emotions, such as frustration and anger. All strain theories acknowledge that only a minority of strained individuals turn to crime. Click to see full answer.
What is meant by General Strain Theory?
Overview. General strain theory (GST) states that strains increase the likelihood of crime, particularly strains that are high in magnitude, are seen as unjust, are associated with low social control, and create some pressure or incentive for criminal coping.
What is General Strain Theory based on?
According to Robert Agnew' s General Strain Theory, strain is based on three different factors: failure to achieve a goal, the existence of harmful impulses, and the removal of positive impulses.
What is general strain theory examples?
Examples of General Strain Theory are people who use illegal drugs to make themselves feel better, or a student assaulting his peers to end the harassment they caused. GST introduces 3 main sources of strain such as: Loss of positive stimuli (death of family or friend)
What are the key components of general strain theory?
Key components of general strain theory included its consideration for the role of emotion in strain-derived crime and its consideration of a broad range of possible sources of societal pressure that might cause a person to commit crime.
Is General Strain Theory macro or micro?
Although general strain theory was initially advanced as a micro-social theory, Agnew (1999) has recently proposed a macro-social version of the theory.
What is Robert Merton's strain theory?
According to Merton's strain theory, societal structures can pressure individuals into committing crimes. Classic Strain Theory predicts that deviance is likely to happen when there is a misalignment between the “cultural goals” of a society (such as monetary wealth) and the opportunities people have to obtain them.
Who came up with the General Strain Theory?
Robert Merton (1938) offered the first modern version of strain theory, which attempted to explain social class differences in offending.
How does General Strain Theory explain murder?
General strain theory suggests that men and women who kill an intimate partner experience different types of strain and emotions, and that homicide occurs in response to these experiences.
What is general strain theory?
General strain theory. General strain theory ( GST) is a theory of criminology developed by Robert Agnew. General strain theory has gained a significant amount of academic attention since being developed in 1992. Robert Agnew's general strain theory is considered to be a solid theory, has accumulated a significant amount of empirical evidence, ...
When was the general strain theory developed?
General strain theory has gained a significant amount of academic attention since being developed in 1992. Robert Agnew's general strain theory is considered to be a solid theory, has accumulated a significant amount of empirical evidence, and has also expanded its primary scope by offering explanations of phenomena outside of criminal behavior.
Which of the following characteristics of strains is most likely to lead to crime?
Agnew described 4 characteristics of strains that are most likely to lead to crime: 1) strains are seen as unjust, 2) strains are seen as high in magnitude, 3) strains are associated with low social control, and 4) strains create some pressure or incentive to engage in criminal coping.
What is the general strain theory?
The general strain theory looks at gender differences and how strains are perceived. Do those perceptions lead men to have a different response to the stressors involved compared to women?
What is Robert Agnew's theory of strain?
The Robert Agnew general strain theory suggests that the biological differences between men and women are responsible for how each reacts to the strains they experience. If coping is possible, then crime can be avoided. If coping is not possible, however, then not is crime an option, but some people may begin a path toward self-destruction.
What does Agnew suggest about stress?
Unlike other forms of strain theory, Agnew suggests that any negative experience can lead a person to experience stress. That stress creates a strain on the person and on society in general, which requires a coping mechanism to reduce its influence. The severity of the strain increases or decreases the risks of criminal conduct.
How many strains of delinquency are there?
Although these characteristics can be seen in any general strain a person might experience, Agnew suggests that there are only three categories of strains that typically lead a person toward delinquency.
What are the characteristics of crime?
The 4 Characteristics That Lead to Crime 1 When there is an inability to achieve a goal that contains a positive value for the individual involved. 2 When there is a threat to remove or the removal of stimuli that has been positively valued by the individual involved. 3 When there is a threat presented to an individual which involves stimuli with noxious or negative values.
What is the focus of strain theory?
Classic strain theories focused primarily on disadvantaged groups, wherein common aspirations (e.g., realizing the “American dream”) and the inability to achieve those goals was considered a driving factor behind crime.
Who developed strain theory?
The ideas underlying strain theory were first advanced in the 1930s by American sociologist Robert K. Merton, whose work on the subject became especially influential in the 1950s.
What is social structural strain theory?
Social-structural-strain theories attempt to explain the high rate of theft for monetary gain in the United States as a product of the class structure of American society. They hold that pressures to achieve financial success drive people to engage in this type of crime. They…
What is the origin of strain theory?
The original strain theory has its roots in Merton’s Anomie Theory and Cohen’s Social Control Theory, which deal with the social structures that might influence an individual to commit crime. General strain theory has been a very popular theory in Criminology for the fact that it offers an expanded view of why adolescents ...
How does strain theory work?
The idea behind general strain theory is just as its name implies, it looks at the strain on an individual and whether they will gravitate toward criminal behaviors to reduce the strain. The main concepts of general strain theory deal with how a negative relationship affects an individual and their future possible development towards crime. Negative relationships are defined as relationships of others that are not consistent on how an individual believes they should be treated. Strain theory looked at only one type when it was first established, the prevention of achieving positively valued goal in society. Robert Agnew added two more types to fully develop strain theory. The first new type of strain looked at when you took away or threatened to take away a positively valued stimulus that one possesses. The second new type of strain looked at the presence of a negative stimuli or the threat of presenting a negative stimuli. With the addition of these new types of strain, general strain theory was able to distinguish itself from previous theories because of the addition of negative stimuli in its theory. Other criminological theories looked more at the positive effects on an individual, whether it’s from parents keeping the adolescents in control or the positive influence of other adolescents in a delinquent group. The first type of strain, the prevention of achieving positively valued goals, looked at the different views one might have towards certain goals. Agnew first looked at the strain on an individual caused by the difference between ones aspirations and actual achievements. An example would be when an individual has aspirations of becoming wealthy, but their actual achievements have them living a middle class existence. Agnew thought that this could cause enough strain in an individual that they could resort to criminal behaviors to achieve those aspirations. With this first type of strain, Agnew expanded it beyond just having the goal being about monetary values. He expanded the view to be about goals in general that individuals have for themselves. This could also range from a student wanting to get better grades, and having to resort to deviant behavior to achieve those goals. Agnew then looked at the strain on an individual caused by the difference between fair outcomes and actual outcomes. This was a more realistic outlook on the strain caused by not meeting positively valued goals. In the previous type mentioned, Agnew believed that an individual could always decrease the strain associated by different coping mechanisms like decreasing the importance of meeting that aspiration. The individuals could tell themselves that money is not that important. With the second part of the first type of strain, it would be harder for an individual to decrease the importance of this goal because they would not be meeting what they deem they should be worth. Therefore if a businessman at a large office continually works over forty hours a week, but does not receive any recognition or pay compensation for their extra effort, the strain caused might lead to criminal acts. The second type of strain mentioned deals with the removal or threat of removal of a positively valued stimulus. Agnew looked at events that could have a strain on an individual like the possible loss of a boyfriend/girlfriend, the death of a loved one, the moving to another school or suspension from school, and the divorce or separation of one’s parents. Agnew argued that these events could cause a high strain on an individual as one tries to get back the original or substitute another positively valued stimulus. If they are unsuccessful, an individual could become angered in general, or try to get revenge on those responsible for the loss of positive stimulus. The last type of strain on an individual dealt with the addition or repetition of negative stimuli. With this theory Agnew does not look at the negative stimulus itself, but more to the fact that the individual cannot escape the negative stimulus. Anger could arise in the individual because they cannot escape the negative stimulus that is being presented in front of them. This type of strain could also lead to delinquency because the individual will try escaping the source, or if that does not work, they will either seek revenge against the source or end the source of the negative stimuli. One of the major factors in the general strain theory is the effect that anger has towards deviant behavior and possible criminal outcomes. Adversity that followed the strain itself is said to produce a general state of arousal, where anger is a significant part of that emotion. Because of this, anger is a large part of the general strain theory and how one looks at possible future deviant behaviors or crime.
What is the first type of strain?
The first type of strain, the prevention of achieving positively valued goals, looked at the different views one might have towards certain goals. Agnew first looked at the strain on an individual caused by the difference between ones aspirations and actual achievements.
How is strain measured?
General strain theory is measured by the magnitude and duration of particular negative events or relationships. The theory looks at those two key elements and then looks at the amount of strain caused from those two elements. The higher the magnitude and duration of a negative event or relationship, the possible increase in an individual’s strain.
What are two interactions that were not related to total crime that was different than expected?
There were two interactions that were not related to total crime that was different than expected: emotional abuse/self-esteem and victimization/self-efficacy. General strain theory has grown in popularity over the last decade and a half that it has been introduced to the criminological society.
What is the name of the journal that Agnew refined his theory?
The name of the journal is “General Strain, Street Youth and Crime: A Test of Agnew’s Revised Theory.”. Agnew refined his theory for the fact that if the theory did not focus on what types of strain would lead to crime and delinquency, researchers would not be able to prove and expand on general strain theory.
What is general strain theory?
General strain theory was tested by examining the relationship among strain, anger, negative emotions, legitimate coping, and criminal/deviance outcomes.
What are the variables of the central general strain theory?
The central general strain theory variables, strain, negative emotions, and legitimate coping all appear to be important in explaining the likelihood of illegitimate/criminal outcomes. However, the nature of the relationship among these variables appears to be more complex than the theory suggests. Study limitations are discusses.
What are the three types of strain?
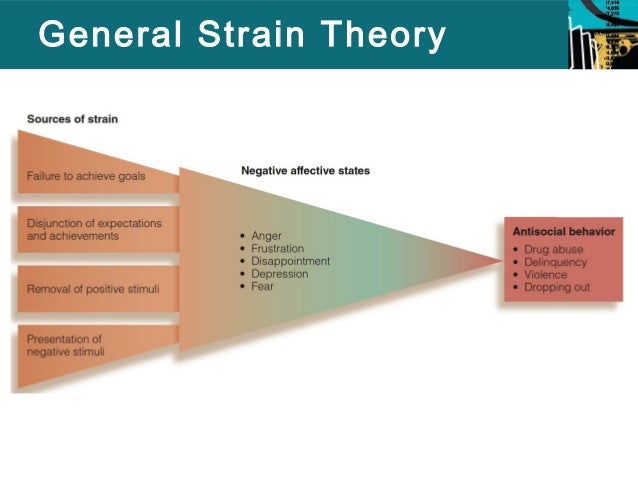
General strain theory identified three types of strain: the failure to achieve positively valued goals, the removal of positively valued stimuli, and the presentation of negative stimuli. The theory proposed an indirect relation in which strain was linked to crime through its relation to negative emotions ...
Is strain a cause of crime?
Abstract. Previous research on strain theory has assumed that strain was a direct cause of crime and delinquency. However, not all individuals who experienced strain responded in criminal or delinquent ways. According to general strain theory (introduced by Robert Agnew in 1992), strain triggered negative emotions, which in turn necessitated coping.
Does strain cause anger?
Results suggested that strains were associated with anger and other negative emotions, but differed by type of strain and by type of negative emotion. In keeping with general strain theory, strain-induced anger significantly increased the likelihood of illegitimate/criminal outcomes, but anger was unrelated to the likelihood of legitimate coping, ...
Why is Strain Theory Important?
Strain theory suggests that when people cannot achieve their goals, they feel strained—this strain leads them to commit crimes to reduce that strain.
Who proposed strain theory?
Strain theory was proposed by Robert Merton, an American sociologist who is also well-known for his works on the functionalist theory. It is an aspect of functionalism, which in itself is a constructivist theory. Strain theory attempts to explain conflict or deviance via the four functions of deviance.
What is the weak form of strain theory?
The weak form of strain theory suggests that people who are blocked from legitimate means to achieve goals will simply accept their situation and not commit crimes.
What is deviance theory?
According to labeling theory, deviance occurs when a label has been attached to someone, leading them to be seen as deviant. As a result of this, the deviant person will have a difficult time in society and may even become involved with other deviants
What is the rational decision to commit a crime?
For Merton, the decision to commit a crime is a rational one based on cultural goals and societal expectations. His theory assumes that an individual experiences strain when culturally prescribed means to achieve goals are blocked and therefore uses illegitimate means to achieve a goal. Both culturally prescribed goals and institutionalized means are concepts that originate in the work of Émile Durkheim.
What is individual strain?
Individual strain refers to the painful psychological state when an individual possesses characteristics that conflict with cultural values.
Is strain theory innately criminal?
It is important to clarify that strain theory does not imply that people who have been socialized into crime are ‘innately criminal’ or that everyone who experiences strain will turn to crime. Robert K. Merton proposed two versions of strain theory, ‘weak’ and ‘strong.’
What is strain theory?
According to Robert Agnew’ s General Strain Theory, strain is based on three different factors: failure to achieve a goal, the existence of harmful impulses, and the removal of positive impulses.
What is Agnew's theory of strain?
With the General Strain Theory, Agnew has succeeded in expanding anomie theory, which is limited to lower class crime, and in combining it with other theoretical concepts such as social control, social disorganisation and emotions.
Why does Agnew see the reasons why some react to the psychological stress with norm-compliant and others with criminal behaviour?
Agnew sees the reasons why some react to the psychological stress with norm-compliant and others with criminal behaviour in the lack of coping skills (e.g. intelligence, creativity, problem-solving skills, etc.). In addition, negative factors such as a criminal environment or criminal character traits have a negative influence on dealing with stress.
Why do deviances produce strain?
According to Agnew there are three main reasons for deviance-producing strain: The failure to achieve a goal (e.g. good grades) The removal of positive impulses (e.g. death of a parent, end of relationship) The existence of harmful impulses (e.g. school problems)
What is Agnew's theory of criminal policy?
Agnew’s criminal policy demands can be regarded as manifold, as his theory also has several different causal factors: First of all, it can be assumed that General Strain Theory, as a theory related to Merton’s considerations of good social policy with the possibility of achieving his individual (e.g.
Is strain a class specific phenomenon?
The existence of harmful impulses (e.g. school problems) According to Agnew “strain” can occur in all strata of the population and is not a class-specific phenomenon. He tries to explain how “strain” leads to criminal acts.

Overview
General strain theory (GST) is a theory of criminology developed by Robert Agnew. General strain theory has gained a significant amount of academic attention since being developed in 1992. Robert Agnew's general strain theory is considered to be a solid theory, has accumulated a significant amount of empirical evidence, and has also expanded its primary scope by offering explanations of phenomena outside of criminal behavior. This theory is presented as a micro lev…
Agnew's three categories of strain
1) Failure to achieve positively valued goals.
2) Removal of positive stimuli.
3) Introduction of negative stimuli.
In an attempt to explain the high rate of male delinquency as compared to female delinquency, Agnew and Broidy analyzed the gender differences between the perception of strain and the res…
General Strain Theory of Terrorism
In 2010, Robert Agnew published a research paper applying Strain Theory to Terrorism. He finds that terrorism is most likely when people experience ‘collective strains’ that are:
• high in magnitude, with civilians affected
• unjust
• inflicted by significantly more powerful others, including ‘complicit’ civilians
Criticisms and Policy Recommendations
• The theory is too complex for any everyday person to understand, it's really hard to test because of how complex it is.
• By receiving very mixed results of what has been tested and the theory does not explain the why factor: "Why does a person commit a crime or crimes?"
The criticisms were made because of the research conducted by Agnew in the early 1990s. The …