The properties or the characteristics of the genetic code are stated below: The genetic code is the set of rules which dictates the linear sequence of nucleotides in the linear sequence of a polypeptide. They specify how a nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
What is the feature of genetic code?
The genetic code has four main features: Three nucleotides/bases encode an amino acid, there are 20 different amino acids which are the building blocks for proteins. The genetic code is non-overlapping, for example a sequence UGGAUCGAU is read UGG AUC GAU rather than UGG GGA GAU etc.
What are the characteristics of a codon?
Summary
- The genetic code consists of the sequence of bases in DNA or RNA.
- Groups of three bases form codons, and each codon stands for one amino acid (or start or stop).
- The codons are read in sequence following the start codon until a stop codon is reached.
- The genetic code is universal, unambiguous, and redundant.
What is true about the genetic code?
The genetic code is defined as the sequence of three nucleotides in RNA that determines the sequence of amino acids for the synthesis of proteins. In other words, the genetic code is defined as the set of rules by which information encoded in the DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins by the living cells.
What is the importance of the genetic code?
What is the importance of genetic code? The genetic code is (nearly) universal. A genetic code shared by diverse organisms provides important evidence for the common origin of life on Earth. That is, the many species on Earth today likely evolved from an ancestral organism in which the genetic code was already present.
What is genetic code?
The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the 20-letter code of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
What are the two properties of genetic code?
Solution : (a) Genetic code is degenerate. i.e, some amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
(b) Genetic code is unambiguous and specific i.e, one codon codes for only one amino acid.
What are the properties of genetics?
1.3: Properties of GenesGenes are on Chromosomes.Linked genes lie along chromosomes in a linear array. Individual map distances are (roughly) additive.
What are the properties of the genetic code allows the use of?
The eight important properties of genetic code are: (1) Code is a Triplet (2) The Code is Degenerate (3) The Code is Non-overlapping (4) The Code is Comma Less (5) The Code is Unambiguous (6) The Code is Universal (7) Co-linearity and (8) Gene-polypeptide Parity.
What are the four properties of genetic code?
Properties of Genetic CodeTriplet code.Non-ambiguous and Universal.Degenerate code.Nonoverlapping code.Commaless.Start and Stop Codons.Polarity.
What are the two types of genetic code?
The genetic code is of two types. The genetic code can be expressed as either RNA codons or DNA codons. RNA codons occur in messenger RNA (mRNA) and are the codons that are actually “read” during the synthesis of polypeptides (the process called translation).
What is genetic code example?
genetic code, the sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information for protein sequences, proteins are not made directly from DNA.
What is the importance of genetic code?
A genetic code shared by diverse organisms provides important evidence for the common origin of life on Earth. That is, the many species on Earth today likely evolved from an ancestral organism in which the genetic code was already present.
What are the 3 types of genetics?
Genetic diseases can be categorized into three major groups: single-gene, chromosomal, and multifactorial.
What is genetic code and its characteristics Class 12?
Genetic code is the sequence of nucleotides in DNA and RNA that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. i) Commaless: Genetic code is commaless. This means that the arrangement of triplet codons on m-RNA is one after another without a gap. ii) Non-ambiguous nature: Each codon specifies a particular amino acid.
Who discovered genetic code?
In 1961, Francis Crick, Sydney Brenner, Leslie Barnett, and Richard Watts-Tobin first demonstrated the three bases of DNA code for one amino acid [7]. That was the moment that scientists cracked the code of life.
What is genetic code PDF?
carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Therefore, Genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequence) into proteins.
Can you now correlate which two properties of genetic code you have?
Can you now correlate which two properties of genetic code you have learned? Hint: Genetic codes exist in the form of triplets and each code for a unique amino acid. AUG is also known as a start codon and codes for a sulfur-containing amino acid.
What is genetic code example?
genetic code, the sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information for protein sequences, proteins are not made directly from DNA.
What property of the genetic code allows the use of several codons?
The genetic code has 64 codon and each specifies only one amino acids but there are some codons such as GAA and GAG both specify one amino acid i.e., glutamic acid and are called as redundancy or degeneracy.
Is overlapping property of genetic code?
The code is non-overlapping: In translating mRNA molecules the codons do not overlap but are “read” sequentially (Fig. 38.27).
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotides, in ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. It is discussed using codons found in mRNA (the messenger RNA) that carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. The genetic code is largely invariant throughout the extent of all species, therefore, it is referred to as the canonical or universal genetic code. There are deviations in both cell organelle and nuclear genomes and they are known as non-canonical or deviant codes. These canonical codes are studies to find the origin and the evolution of the genetic code and the connection between certain mitochondrial diseases with mitochondrial code deviations and translational errors.
How does the genetic code work?
The genetic code can be explained as a collection of rules used by all living cells in all organisms to translate information encoded within the genetic material into proteins. Translation or protein synthesis is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order which is specified by the mRNA, using tRNA molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA codons at a time. The genetic code definition shows how codons or sequences of three nucleotides specify which amino acid will be added next during translation.
How many codons are there in amino acids?
The amino acids, arginine, alanine and leucine have 6 same codons. There are two types of degeneracy observed in the genetic code: partial and complete. In partial degeneracy, the first 2 nucleotides are identical by the 3rd nucleotide differs. Example: CUU and the CUC codon for leucine.
How many codons are in a gene?
The genetic code consists of 64 different codons and each code for 1 of the 20 amino acids. Codons can be defined as a group of 3 nucleotides which is read by a cell to decode an mRNA. The codons are read during translation, beginning at the start codon till the stop codon.
How many sense codons are there in the genetic code?
Sense codons: 61 codons of the genetic code table are known as the sense codons. All of them code for particular amino acids. Non-sense codons: As UAA, UAG, and UGA do not code for any amino acid, they are also known as non-sense codons. Share this with your friends. Share.
How many codons are in a polypeptide?
Thus it explains the relationship between nucleotide sequences is of the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide. The genetic code consists of 64 different codons and each code for 1 of the 20 amino acids.
What is the genetic code of a polypeptide?
The genetic code is the set of rules which dictates the linear sequence of nucleotides in the linear sequence of a polypeptide .
What is the purpose of the triplet codon?
4. The code uses codons to make the amino acids that, in turn, constitute proteins. 5. Each triplet [codon] specifies one amino acid in a protein structure or a start signal or stop signal in protein synthesis.
How many sense codons are there in the genetic code?
Those codons that code for amino acids are called sense codons. There are 61 sense codons in the genetic code which code for 20 amino acids. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Signal Codons: Those codons that code for signals during protein synthesis are known as signal codons. There are four codons which code for signal.
How many bases are in a codon?
In other words, a set of three nucleotide bases constitutes a codon. 2. In a triplet code, three RNA bases code for one amino acid. 3. There are 64 codons which correspond to 20 amino acids and to signals for the initiation and termination of transcription.
How does mRNA acquire its sequence of nucleotides?
But each mRNA molecule acquires its sequence of nucleotides by transcription from the corresponding gene [DNA], Because DNA sequencing has become so rapid and because most genes are now being discovered at the level of DNA before they are discovered as mRNA or as a protein product, it is extremely useful to have a table of codons expressed as DNA. Both tables are given here.
How many nucleotides are in a codon?
Types of Codon: The genetic code consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons. With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. This produces some redundancy in the code.
What is the meaning of the genetic code?
Meaning of Genetic Code: The genetic code may be defined as the exact sequence of DNA nucleotides read as three letter words or codons, that determines the sequence of amino acids in protein synthesis.
What are the two types of genetic codes?
Types of Genetic Code: The genetic code is of two types. The genetic code can be expressed as either RNA codons or DNA codons. RNA codons occur in messenger RNA (mRNA) and are the codons that are actually “read” during the synthesis of polypeptides (the process called translation).
How many codons are there in amino acids?
As pointed out earlier, the coding units or codons for amino acids comprise three letter words, 4 x 4 x 4 or 4 3 = 64. 64 codons are quite adequate to specify 20 proteinous amino acids. 2. The Code is Degenerate: The occurrence of more than one codon for a single amino acid is referred to as degenerate.
What is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain?
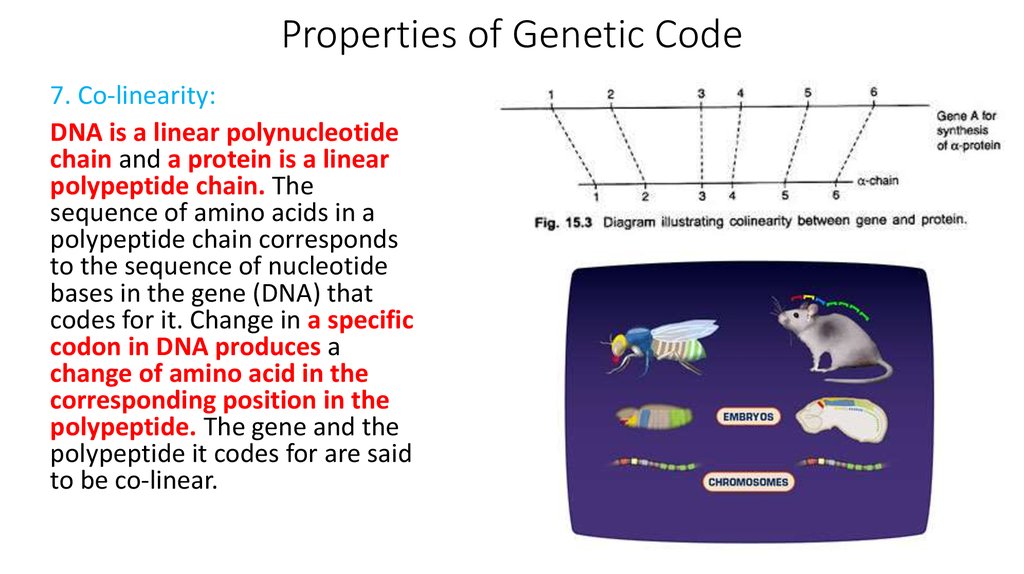
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain corresponds to the sequence of nucleotide bases in the gene (DNA) that codes for it. Change in a specific codon in DNA produces a change of amino acid in the corresponding position in the polypeptide. The gene and the polypeptide it codes for are said to be co-linear. 8.
What are the special purpose codons in ribosomal synthesis?
Other special-purpose codons are UAA (Ochre), UAG (Amber), and UGA (Umber), all of which signal STOP. When the ribosomal synthesis site encounters one of these stop codons, the peptide chain is released and assumes its secondary and tertiary structures.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
Proteins are made of 20 different amino acids. The information about the number and sequence of these amino acids forming protein is present in DNA, and during transcription is passed over to mRNA. The form in which it is transferred was not understood for long.
How many codons are there in the genetic code?
This break through resulted into 64 codons dictionary — the Genetic Code. According to Bark (1970) the genetic code is a code for amino acids, specifically it is concerned with as to what codons specify what amino acids. Genetic code is the outcome of experiments performed by M. Nirenberg, S. Ochoa, H. Khorana, F. Crick and Mathaei.
How many nucleotides are in a codon?
This difficult problem was solved with the discovery that a codon (hereditary unit of a gene) containing coded information for one amino acid consists three nucleotides (i.e., a triplet code). Thus for twenty amino acids, 64 (4 x 4 x 4 or 4 3 = 64) possible permutation are available. This break through resulted into 64 codons dictionary — the Genetic Code.
What is the relationship between the four letters language of nucleotides and the twenty letters language of amino acids?
In other words, the relationship between the 4 letters language of nucleotides and twenty letters language of amino acids is known as genetic code. ADVERTISEMENTS: DNA (or RNA) carries all the genetic information and it is expressed in the form of proteins. Proteins are made of 20 different amino acids.
What is a Genetic Code?
The genetic code can be defined as the set of certain rules using which the living cells translate the information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences). The ribosomes are responsible to accomplish the process of translation. They link the amino acids in an mRNA-specified (messenger RNA) order using tRNA (transfer RNA ) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time.
How many bases are there in a nucleotide?
The four bases of nucleotide i.e, (A, G, C, and U) are used to produce three-base codons. The 64 codons involve sense codons (that specify amino acids). Hence, there are 64 codons for 20 amino acids since every codon for one amino acid means that there exist more than code for the same amino acid.
What is triplet code?
Triplet code. A codon or a code word is defined as a group of bases that specify an amino acid. There is strong evidence, which proves that a sequence of three nucleotides codes for an amino acid in the protein, i.e., the code is a triplet. The four bases of nucleotide i.e, (A, G, C, and U) are used to produce three-base codons.
What is the complete set of relationships among amino acids and codons?
The complete set of relationships among amino acids and codons is said to be a genetic code which is often summarized in a table. It can be seen that many amino acids are shown in the table by more than one codon. For example, there are six ways to write leucine in mRNA language.
What direction is a triplet read?
Each triplet is read from 5’ → 3’ direction and the beginning base is 5’ followed by the base in the middle then the last base which is 3’. This implies that the codons have a fixed polarity and if the codon is read in the reverse direction, the base sequence of the codon would reverse and would specify two different proteins.
What does "no room for punctuation in between" mean?
No room for punctuation in between which indicates that every codon is adjacent to the previous one without any nucleotides between them.
How many letters are in a protein synthesis?
Genetic Code. Synthesizing a protein with the help of the information in RNA is similar to translating a language to another. A four-letter language is translated to 20 letter language during protein synthesis. There should be a specific relationship among the four bases of DNA and sequence of 20 amino acids in the protein.
What is nonsense mutation?
A nonsense mutation occurs when the incorrect base pair is used during DNA replication – but where the resulting codon does not code for an incorrect amino acid.
What is codon in DNA?
When we talk about “codons,” we usually mean codons in mRNA – the “messenger RNA” that is made by copying the information in DNA. For that reason, we talk about codons made of RNA, which uses Uracil, instead of the original DNA code which uses Thymine. Each amino acid is represented in our genetic instructions by one or more codons, as seen below.
What is glycine coded for?
Glycine, for example, is coded for by the codons GGA, GGC, GGG, and GGU. A mutation resulting in the wrong nucleotide being used for the last letter of the glycine codon, then, would make no difference. A codon starting in “GG” would still code for glycine, no matter what letter was used last.
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is the code our body uses to convert the instructions contained in our DNA the essential materials of life. It is typically discussed using the “codons” found in mRNA, as mRNA is the messenger that carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Everything in our cells is ultimately built based on ...
Why is DNA important?
The reason for this is that DNA is very much like computer source code – one piece of code might be crucial for the system to turn on at all, while other pieces of code might just ensure that a website looks pretty or loads quickly.
How are amino acids represented in DNA?
One of the most remarkable evidences for the common descent of all life on Earth from a single ancestor is the fact that all organisms use the same genetic code to translate DNA into amino acids. There are a few slight exceptions to be found, but ...
How many letters are in DNA?
While binary uses only ones and zeroes, DNA has four letters – the four nucleotides Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine /Uracil.
What is the genetic code of a cell?
Genetic Code. Genetic Code. =. The instructions in a gene that tell the cell how to make a specific protein. A, C, G, and T are the "letters" of the DNA code; they stand for the chemicals adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), respectively, that make up the nucleotide bases of DNA. Each gene's code combines the four chemicals in ...
How many words are in a gene's code?
Each gene's code combines the four chemicals in various ways to spell out three-letter "words" that specify which amino acid is needed at every step in making a protein.
The Genetic Code and Properties
A codon is a set of three nucleotides (triplets) in mRNA, functioning as a unit of genetic coding by specifying a particular amino acid during the synthesis of polypeptides/proteins in a cell. The genetic code comprises of 64 such triplets of nucleotides which code for twenty amino acids.
Properties of the Genetic Code
The triplet nucleotide base sequences in mRNA or DNA that act as code words for the synthesis of amino acids in proteins, constitute the genetic code or simply codons.
1. Universal
The same codons are used to code for the same amino acids in all living organisms. Thus, genetic code has been preserved during evolution and is universal. However, there are a few exceptions like AUA code for methionine in Mitochondria and Isoleucine in Cytoplasm.
2. Specificity
A particular codon always codes for the same amino acid which makes the genetic code highly specific. For eg. UGG codes for Tryptophan, GGC codes for Glycine (as given in the table).
3. Non-Overlapping
The genetic code is read from a fixed point as a continuous base sequence. It is non-overlapping, commaless and without punctuation. Eg. UAAGUGUGA is read as UAA/GUG/UGA. The deletion of one or two bases causes mutations and the protein synthesized will be completely different (Frameshift Mutation).
4.Degenerate
Most of the amino acids are coded by more than one codon, which is the degeneracy of the code. Thus, the codon is degenerate or redundant, since there are 61 codons for only 20 amino acids. Eg. Glycine is coded by four codons. They are also called synonyms.
What is the number of amino acids that can be coded by more than one codon?
One particular codon never codes for more than one amino acid. (iii) Degeneracy of the genetic code. Most of the amino acids — except methionine and tryptophan — are coded by more than one codon. The number varies between 2 and 6. (iv) The genetic code is non-overlapping and unpunctuated.
What are the characteristics of the genetic code?
The genetic code has a number of characteristic properties: (i) Triplet nature of the code. The codons for different amino acids, as well as those for chain termination, always consist of three successive nucleotides of DNA or m-RNA. The DNA and m-RNA codons are mutually complementary. For example, the DNA codon CGT is complementary to ...
What does universality mean in genetics?
This means that the same codons specify the same amino acids in all organisms starting from bacteria to plants and animals and even in viruses. Although viruses have no amino acids of their own, they have the ability to direct protein synthesis in the host cells.
What is the whole sequence of m-RNA?
The whole sequence of m-RNA — starting from the initiator codon up to the triplet preceding the termination codon — is known as the reading-frame. Since the reading-frame is a continuous sequence of nucleotides, addition or deletion of a single nucleotide results in a change of the triplets from that point downstream.
How many combinations can be made with 3 nucleotides?
From a purely mathematical consideration, it is apparent that such a unit must contain a sequence of at least 3 nucleotides, because less than 3 nucleotides cannot give 20 combinations. When the 4 different nucleotides are taken 3 at a time, 4 3 or 64 different combinations are possible.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
Both DNA and m-RNA consist of only 4 different nucleotides, represented by A, T, G, C or A, U, G, C.
How many units of nucleotide sequence are there in a protein?
In other words, there must be a unit of nucleotide sequence for each of the 20 protein amino acids. Such a unit functions as a code for a particular amino acid, and for 20 amino acids, there must be at least 20 such units or codes.
How many codons are in the genetic code of 20 amino acids?
There are 64 codons in the genetic code for 20 amino acids of which 4 codons are the signals. Therefore, 60 codons are to code for amino acids. It means that more than one codons may be coding for individual amino acid.
What is the meaning of "non-ambiguous"?
The non-ambiguous means that a particular codon will always code for the same amino acid. It may also be that the same amino acid may be coded by two different codons (degenerate). However, when one codon codes for two amino acids, it is called ambiguous. For example, UUU codon codes for phenylalanine, but in the presence of streptomycin it may code for isoleucine, leucine or serine.
Why are three of 64 codons called non-sense codons?
Moreover, three of 64 codons are called as non-sense codons because they do not specify any tRNA. These codons are amber (UAG), Ochre (UAA) and Opal or amber (UGA). These also bring about termination of polypeptide chain; therefore, they are also called termination codons.
How many amino acids are in DNA?
Thus, there are four alphabets (A, G, T, C) of DNA. We know that there are 20 different amino acids that constitute a protein as the nitrogen bases constitute nucleotides.
How many alphabets are there in a protein?
Hence, there are 20 alphabets of the language of a protein. From DNA to protein the information pass through an mRNA. One mRNA carries the genetic information of one protein. The synthesis of specific protein under the guidance of mRNA required the evolution of a code by which the polynucleotide sequence specifies the amino acid sequence that makes up the protein.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
It has became obvious that nucleic acids are the genetic material. The nucleic acids being polynucleotide, function to store genetic information’s and to replicate. The genetic information flow from polynucleotide to polypeptide.
What happens if introns are present?
However, if the introns are present, the coding process is interrupted. See introns i.e. split genes in preceeding section.

What Is Genetic Code?
- The information transferred or passed from the parent generation to the offspring is called genetic code. The process begins at the cellular level when the genes get split into the parental reproductive cells and then get united to form a hybrid set of genes during fertilization. Apart from the union of the male and female reproductive cells in sexual reproduction, there are other mean…
Characteristics of Genetic Code
- The intricate process of decoding genes and then recording to form a new set of genes in the offspring is fascinating. The entire biochemical process comprises millions of chemical reactions occurring within a minute yet controlled environment of a cell. To understand its features, first, we need to observe the scientific discovery and theories behind it. George Gamow, a renowned phy…
Genetic Code - Properties
- It is a must that the genetic codes properties are known by all the students who are in touch with their Biology, or who study it: 1. They are mostly triplet coded 2. They are unambiguous as well as universal in nature 3. They have a degenerate code 4. They contain start and stop codons 5. They showcase polarity 6. Their code is mostly non overlapp...
Mutations of Genetic Codes
- Not every individual is similar. In fact, it has been observed that a particular physiological trait goes missing. It happens when the genetic codes get rearranged and deleted during transcription and replication. The different segments of DNA get rearranged and deleted during the process resulting in mutations. Genes are gained and lost in the process resulting in new physical traits …
What Is A Genetic Code?
Genetic Code Table
- The complete set of relationships among amino acids and codons is said to be a genetic code which is often summarized in a table. It can be seen that many amino acids are shown in the table by more than one codon. For example, there are six ways to write leucine in mRNA language. Note: A codonis a sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a …
Properties of Genetic Code
- Triplet code
- Non-ambiguous and Universal
- Degenerate code
- Nonoverlapping code
Exceptions to The Code
- The genetic code is universal since similar codons are assigned to identical amino acids along with similar START and STOP signals in the majority of genes in microorganisms and plants. However, a few exceptions have been discovered and most of these include assigning one or two of the STOP codons to an amino acid. Apart from this, both the codons GUG and AUGmay code …