How to Find Your Genotype?
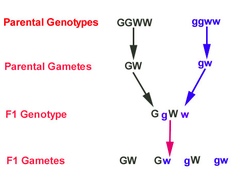
Using Punnett Squares to Calculate Phenotypic Probabilities
- Determining Parental Genotypes. You will need to be given information about the P generation before conducting a Punnett Square cross.
- Set Up the Punnett Square. Draw a square with four boxes within it. ...
- Cross the P Generation. Find the first column in the square. ...
- Determine the Phenotypes of the F1 Generation. ...
- Calculate Phenotypic Probabilities. ...
- Conclusion
What are the different types of genotype?
Types of genotype - What are they?
- GENOTYPE AA
- GENOTYPE AS
- GENOTYPE SS
- GENOTYPE AC
How do you describe genotype?
Genotype is the collection of genes responsible for the various genetic traits of a given organism. Genotype refers specifically to the genes, not the traits; that is, the raw information in an organism’s DNA. Genotype is determined by the makeup of alleles, pairs of genes responsible for particular traits.
What does an organism's genotype describe?
Genotype Definition The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its DNA, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. A genotype consists of all the nucleic acids present in a DNA molecule that code for a particular trait.

What is a genotype in simple terms?
An individual's genotype is the combination of alleles that they possess for a specific gene. An individual's phenotype is the combination of their observable characteristics or traits.
Why is genotype?
genotype, the genetic constitution of an organism. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood. Among organisms that reproduce sexually, an individual's genotype comprises the entire complex of genes inherited from both parents.
What is phenotypes in science?
(FEE-noh-tipe) The observable characteristics in an individual resulting from the expression of genes; the clinical presentation of an individual with a particular genotype.
What are the 3 types of genotypes?
The different types of genotypes are- homozygous recessive (pp), homozygous dominant (PP), and heterozygous (Pp). The homozygous dominant and the heterozygous genotypes show the same phenotypes.
What is genotype and example?
A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. It can be represented by symbols. For example, BB, Bb, bb could be used to represent a given variant in a gene.
What are the types of genotype?
The different possible genotypes are AA, AO, BB, BO, AB, and OO. How are blood types related to the six genotypes? A blood test is used to determine whether the A and/or B characteristics are present in a blood sample.
Which genotype is the best?
What Blood Genotypes Are Compatible? The AA genotype has the best compatibility ratio. An individual with the AA genotype can choose a life partner from virtually all other genotype categories with an extremely minimal possibility of sickle-celled offspring.
What does homozygous mean?
(HOH-moh-ZY-gus JEE-noh-tipe) The presence of two identical alleles at a particular gene locus. A homozygous genotype may include two normal alleles or two alleles that have the same variant.
Why is AA genotype?
An individual with the AA genotype can choose a life partner from virtually all other genotype categories with an extremely minimal possibility of sickle-celled offspring. Some research also shows that while the AA genotype is the best in terms of compatibility, it is also the most susceptible to malaria.
What is AA and AA genotype?
Genotype AA is the universally compatible genotype that is, regardless of who they partner up with, there is no possibility of them birthing a child with sickle cell disease. Here are the compatible and incompatible genotypes: AA + AA = compatible. AA + AS = compatible. AA + SS = compatible.
What does genotype AA stands for?
homozygous dominantThe genetic symbols can be understood as. A = dominant. a = recessive. AA- homozygous dominant. Aa- heterozygous dominant (individual has both dominant and recessive gene, but only one is expressed)
Is aa better than as genotype?
One study involving 372 children at the University of Uyo Teaching Hospital found that “children with genotype AA (92.3%) were more susceptible to malaria parasite than AS (5.1%) and SS (2.6%)”.
What is the meaning of genotype?
Genotypes. Encyclopedic Entry. Vocabulary. In one sense, the term “ genotype ”—like the term “genome”—refers to the entire set of genes in the cells of an organism. In a narrower sense, however, it can refer to different alleles, or variant forms of a gene, for particular traits, or characteristics. An organism’s genotype is in contrast ...
What is a homozygous genotype?
An organism with two dominant alleles for a trait is said to have a homozygous dominant genotype. Using the eye color example, this genotype is written BB. An organism with one dominant allele and one recessive allele is said to have a heterozygous genotype. In our example, this genotype is written Bb. Finally, the genotype of an organism ...
What is the genotype of an organism with two dominant alleles?
An organism with two dominant alleles for a trait is said to have a homozygous dominant genotype. Using the eye color example, this genotype is written BB. An organism with one dominant allele and one recessive allele is said to have a heterozygous genotype. In our example, this genotype is written Bb. Finally, the genotype of an organism with two recessive alleles is called homozygous recessive. In the eye color example, this genotype is written bb.
What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype?
An organism’s genotype is in contrast with its phenotype, which is the individual’s observable characteristics, resulting from interactions between the genotype and the environment. There is a complex connection between the genotype and the phenotype. Since the phenotype is the result of an interaction between genes and the environment, ...
Why do different environments lead to different traits in individuals with a particular genotype?
Since the phenotype is the result of an interaction between genes and the environment, different environment s can lead to different traits in individuals with a particular genotype. In addition, different genotypes can lead to the same phenotype.
How are physical traits determined?
Many physical traits like hair color and texture, eye color, and skin color are determined by the genotypes that parents pass down to their children.
Which genotypes only account for some genes and some traits?
The homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, and heterozygous genotypes only account for some genes and some traits. Most traits actually are more complex, because many genes have more than two alleles, and many alleles interact in complex ways. Many physical traits like hair color and texture, eye color, and skin color are determined by ...
What determines the broad limits of the features an organism can?
Although the genotype determines the broad limits of the features an organism can…. evolution: Genetic equilibrium: the Hardy-Weinberg law. It states that genotypes, the genetic constitution of individual organisms, exist in certain frequencies that are a simple function of the allelic frequencies—namely, the square expansion of the sum ...
What is the term for the organism's outward appearance and the developmental outcome of its genes?
heredity. …each, is called the organism’s genotype. The genotype is contrasted to the phenotype, which is the organism’s outward appearance and the developmental outcome of its genes. The phenotype includes an organism’s bodily structures, physiological processes, and behaviours.
What is the meaning of genotype?
See Article History. Genotype, the genetic constitution of an organism. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood.
What is the encyclopaedia Britannica?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree.... Genotype, the genetic constitution of an organism. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual ...
What is dominant in biology?
Related Biology Terms. Dominant – Having the ability to mask the effects of a recessive allele. Recessive – An allele that only shows phenotypic effects in the presence of another recessive allele. Heterozygous – A genotype containing two types of alleles. Homozygous – A genotype containing one type of allele.
What is the genotype of cystic fibrosis?
The genotype of people with cystic fibrosis is homozygous recessive. In other words, they carry two copies of the non-functioning allele for the gene that creates specific ion-channels. Some people, known as “carriers” can have a functioning, normal phenotype, while having a heterozygous genotype. This means that a carrier can pass a non-functioning allele on to their child. Unknowingly, two carriers can both pass on the non-functioning allele, and the child with receive a non-functioning homozygous recessive genotype. However, if one or both carrier parents passes on their good allele, the child will not have the symptoms of cystic fibrosis. If the child receives one functioning and one non-functioning allele, they will be a carrier as well. The child will not be carrier if they receive two functional alleles.
What does it mean when a child has a blue eye?
The parents conceive a child. The child has blue eye. This tells us that the child is homozygous recessive, or “ee”, because only two recessive alleles can produce blue eyes.
How are alleles produced?
The different alleles are produced by mutations to the DNA , and may give rise to beneficial or detrimental changes. In bacteria, the DNA exists in a ring and only one allele for each genotype is present. Sometime, an allele will mutate in a beneficial way, the organism will reproduce more and the genotype will increase in the population.
What does the E signify in the phenotype?
Therefore, “E” will represent brown eyes. Traits that are recessive are written in lower case. The allele for blue eyes is recessive to the allele for brown eyes, so we can call it “e”. A set of parents has brown eyes. Having brown eyes only tells us their phenotype, not their genotype. The parents could be “Ee”, “EE”, or there could be one of both.
What is heterozygous genotype?
Heterozygous – A genotype containing two types of alleles.
How many letters are in a genotype?
Although a particular genotype consists of many nucleic acids, scientists typically represent genotypes with single letters, or two letters in the case of sexually reproducing organisms that receive one allele from each parent. For example, the trait for eye color could be represented with the letter “E”.
What are the three possible genotypes?
The three genotypes are homozygous dominant (PP), Heterozygous (Pp) and Homozygous (pp).
What is genotype in biology?
Genotype Definition. Genotype refers to the genetic constitution of living organisms. A genotype is the total sum of genes transferred from parents to offspring. Alternatively, a genotype can also be defined as the complete set of heritable genes that can be transferred to the offsprings from its parents. These genes help to encode specific ...
What is the blood type allele?
Blood type alleles are an interesting mix, and to better understand them, let's look at background information prior to this. The allele for type A blood is a dominant one. In other words, when someone inherited this allele from a parent, he or she will exhibit the antigen of type A. It is true of the same type B allele: if someone inherited the allele of type B from a parent, he or she would have the type B antigen. The allele of type O is recessive, which means, it will be masked or hidden by the alleles of either A or B.
What is genotype in biology?
The genotype of an organism defines the hereditary restrictions and potentials from the foetal stage during pregnancy through adulthood. In a simple manner, a genotype definition is given by, the sum of total genes transferred from parents to offspring. Therefore, the genotype of a specific person is their own personal genetic makeup. This genotype is expressed when the information from genes' DNA has utilized to make RNA molecules and proteins.
How is blood type determined?
The type of blood is determined by our genes. These genes are the segments of DNA that code for specific traits. Different versions of genes are referred to as alleles. When determining something like blood type, individuals receive one allele from their biological mother and another from their biological father. The genotype is simply the combination of these alleles that creates the gene for blood type. This allele combination is called a genotype. Now let us relate this genotype (allele combination) to the blood types.
How many alleles can a biological parent donate to their child?
Ans. Every biological parent donates one ABO alleles to their child from their available two alleles. A mother who is with a Type - O blood can only pass an O allele to her daughter or son. A father who is with Type - AB blood could pass either an A or a B allele to his daughter or son. This couple (mother and father) could have children of either blood type A (Type-O from mother and Type-A from father) or blood type B (Type-O from mother and Type-B from father).
What is DNA fragment analysis?
The analysis of DNA fragment can also be used to determine such diseases causing genetic aberrations as microsatellite instability (MSI), loss of heterozygosity (LOH), and trisomy or aneuploidy. LOH and MSI in specific have been associated with cancer cell genotypes for breast, colon, and cervical cancer.
How to determine a genotype?
Ans. We can determine the Genotype by sending a sample DNA test. Until we have done that, all we can do is only a wild guess. Our genotype is not the ethnicity results. It is exactly how our deoxyribonucleic acids are lined up in each chromosome. Also, there are some phenotypes that cannot be any other genotype. Someone who is albino knows they don't have a gene that codes for active melanin.
Which chromosome is most likely to be aneuploidy?
The most common chromosomal aneuploidy is the trisomy of chromosome 21, which manifests itself as Down syndrome. Typically, the current technological limitations allow only a fraction of an individual's genotype to be efficiently determined.
What is the most common genotype of hepatitis C?
Genotype 1 is the most common genotype, accounting for 60% to 80% of all hepatitis C. Genotype 1 is more difficult to eradicate with treatment than other common genotypes. Treatment for chronic hepatitis C infection is with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Phenotype is the product of the interaction between genotype and “environmental” factors. Some phenotypes are almost completely determined by heredity, such as blood groups (discussed earlier), but most, such as human height, are also greatly impacted by nonhereditary factors, such as nutrition.
How long does it take to determine the genotype of an RV?
In settings with 10 or more years of continuous surveillance of RV genotypes, cycling of the predominant genotypes is observed. The period of oscillations in the prevalence of different genotypes has been found to vary between 3 and 11 (or more) years ( Pitzer et al., 2011a ). Therefore, at least 4 years of surveillance data are needed to reliably determine the underlying distribution of RV genotypes in any given location.
How many people have genotype 6?
Genotype 6 infections are also of considerable epidemiological importance: there are an estimated 62 million HCV-infected people in the WHO-defined Western Pacific region, which represents approximately one-third of all infections worldwide [3,4,8].
How to find the frequency of a genotype?
Genotype frequencies are obtained by dividing the number of individuals having each genotype by the total number of people sampled.
What is genotype frequency?
A genotype frequency is the proportion of the total number of people represented by a single genotype. For example, if the genotype AA (for a locus having three different alleles) is found to be present in six people out of 200 sampled, the genotype frequency is 6/200 = 0.03. The sum of all genotype frequencies for a single locus should be equal to 1.0. If it is not, the frequency calculations should be checked again.
Which genotype is more likely to develop steatosis?
It has been suggested that genotype 1b is associated with a more severe disease progression than genotype 1a or 2. People with HCV genotype 3 are more likely to develop steatosis; it is believed that this genotype is an independent risk factor and may actually play a direct role in the development of steatosis.
What is a Genotype?
As the name suggests, a person's genotype refers to the types of genes he or she has for a particular inheritable trait. Genotypes determine which characteristics an individual will express, for example: whether they have freckles or not, if they are lactose intolerant, if they have hair on their knuckles or if their eyes will be blue, brown or another color.
What is it called when a person has two dominant alleles for a gene?
When a person has two dominant alleles for a gene (e.g. LL), they are referred to as being homozygous dominant for that trait. If they have two recessive alleles (ll), they are homozygous recessive. If they inherited one of each allele (Ll), they are heterozygous for that trait. How Genotypes Are Passed Down.
Why is the lactase enzyme represented by a capital letter?
Notice that the allele for lactase enzyme is represented by a capital letter because it is dominant over faulty lactase production. The 'weaker' allele is referred to as recessive and uses a 'lowercase letter. So, whenever the person has both versions of the gene, in this case Ll, the ability to produce lactase, being the dominant allele, will be the one expressed. For someone to be lactose intolerant, they have to have inherited two recessive 'l' alleles, one from each parent.
What does LL mean in milk?
LL means a person is able to make lactase and therefore can digest milk just fine. Ll means a person is able to make lactase and therefore can digest milk just fine. ll means a person is not able to digest milk properly because they can't make lactase, and they are said to be lactose intolerant.
How do genes come about?
How do Genotypes Come About? Genes are found on chromosomes, those tightly-packed DNA structures in the cell nucleus. In sexually-reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in pairs, one from the mother and one from the father. For example, each person will have two 'Chromosome 1s' and two 'Chromosome 2s'.
Why are chromosomes called homologous?
Chromosomes in a pair (except sex chromosomes) are called homologous chromosomes because they contain the same genes. For example, both chromosome 8s contain, among many others, the gene that determines whether or not a hairline forms a widow's peak.'. There are always two copies of each gene, one from each parent.
Where is the gene that determines if a person is lactose intolerant?
To better understand how alleles and genotypes work, let's take a look at the gene that determines whether a person is lactose intolerant, which is found on chromosome 2. This gene contains the recipe for the body to make lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose sugar in milk.
Why is genotype important?
It comes from the German word Gynotypus, which means “type of genes.” Your genotype is the type of genes you specifically have and determines what your cells will do.
Did you know … ?
Sometimes, both alleles in a genotype are visible in a phenotype with neither dominating the other. We can see this in plants’ petal color genotype. If a red rose combines with a white rose, it is possible that their offspring will have both color alleles and have both red and white petals.
How many genes are there in the human body?
Human beings have around 20,000 genes in their DNA. Most of these genes are identical in all humans. However, several genes can vary from person to person. We call these different genes alleles, which result in the physical differences we can see, such as eye or hair color. An allele is created when the genes that you inherited from your father and ones you inherited from your mother combine. Your genotype is your specific arrangement of alleles that have to do with a certain trait, such as eye color.
What is genotype in genetics?
In genetics, a genotype is the arrangement of alleles.
What is the genotype of late blight?
The first late blight sample found in a crop in Angus last week has been confirmed as genotype 6_A1, or Pink 6 as it is often known.
What is the genetic arrangement that makes up the traits that an organism inherited from its parents?
A genotype is the genetic arrangement that makes up the traits that an organism inherited from its parents.
What is genotype in biology?
genotype. noun Genetics. the genetic makeup of an organism or group of organisms with reference to a single trait, set of traits, or an entire complex of traits. the sum total of genes transmitted from parent to offspring.