Which foods to avoid with Gerd?
Giulia recommends:
- Eating smaller portions, even if it means you need to eat more frequently
- Trying to lose weight if you’re overweight
- Make sure you aren’t overly stressed: find ways to relax
- Avoid eating within three to four hours before going to bed
- Don’t smoke
- Don’t drink much alcohol
How to cure Gerd without medication?
- Avoid eating or drinking anything within 2 hours of bedtime.
- Minimize brown liquid intake (coffee, colas, chocolate) with or without caffeine. ...
- Avoid excess alcohol, especially before bedtime.
- Avoid fatty meals, especially before bedtime.
- Avoid mint, peppermint, and spearmint. ...
What type of diet is best for GERD?
Our Editor 10 diet for gerd Review:
- The Acid Watcher Diet: A 28-Day Reflux Prevention and Healing Program
- Acid Reflux Diet: 101 Best Foods To Treat & Cure GERD
- The Complete Acid Reflux Diet Plan: Easy Meal Plans & Recipes to Heal GERD and LPR
What is the best treatment of Gerd?
Treatment Approaches for GERD
- GERD Treatment: Lifestyle and Dietary Changes. Dietary and lifestyle changes are the first step in treating GERD. ...
- GERD Treatment: Medication. If lifestyle and dietary changes do not work, your doctor may prescribe certain medications. ...
- TIF and Other Endoscopic Therapy. ...
- Surgery for GERD

What is the main cause of GERD?
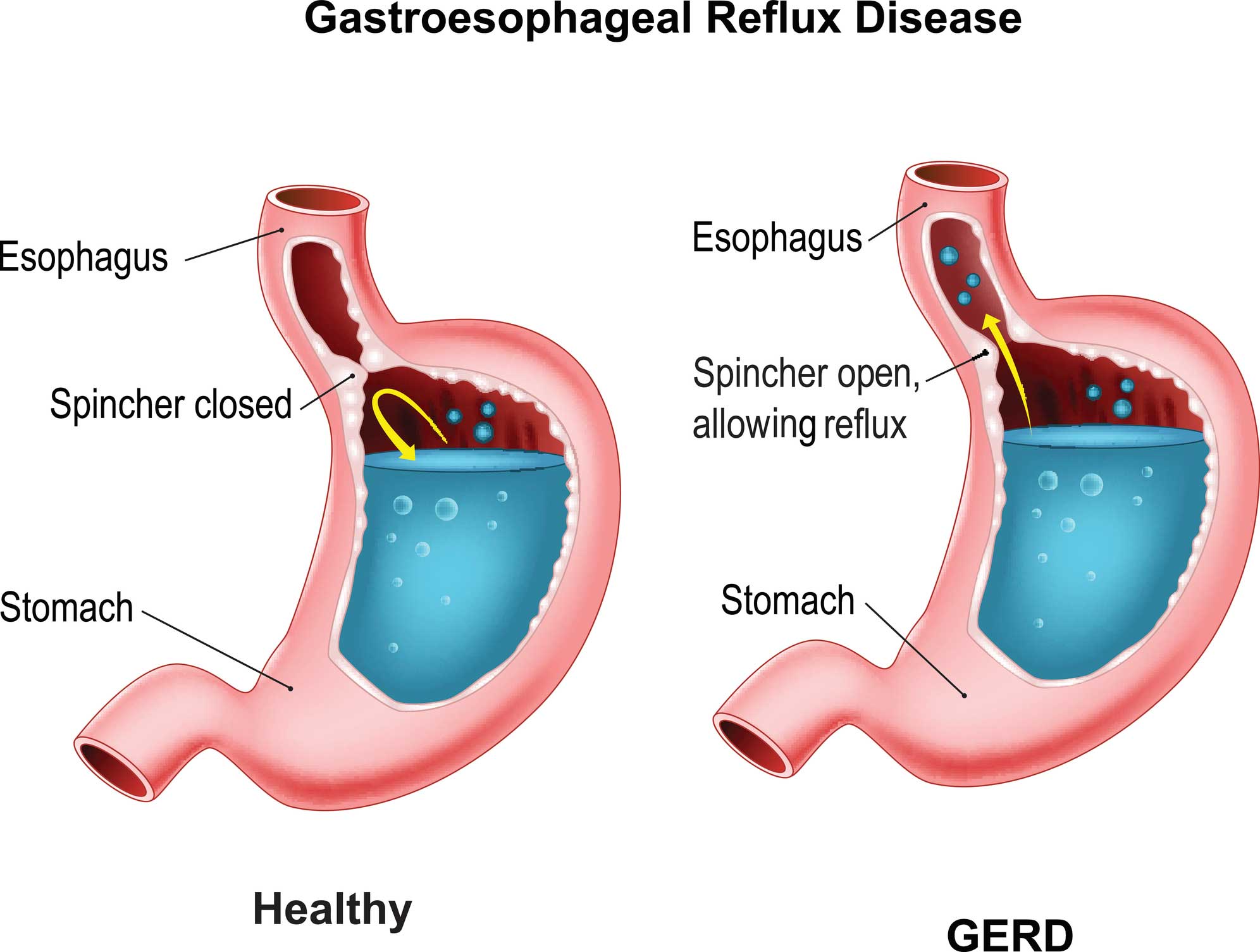
GERD is caused by frequent acid reflux. When you swallow, a circular band of muscle around the bottom of your esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter) relaxes to allow food and liquid to flow into your stomach. Then the sphincter closes again.
What is esophageal reflux without esophagitis?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that occurs when acidic stomach juices, or food and fluids back up from the stomach into the esophagus. GERD affects people of all ages—from infants to older adults. People with asthma are at higher risk of developing GERD.
What is the difference between GERD and esophagitis?
Reflux esophagitis is an esophageal mucosal injury that occurs secondary to retrograde flux of gastric contents into the esophagus. Clinically, this is referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Typically, the reflux disease involves the distal 8-10 cm of the esophagus and the gastroesophageal junction.
Is GERD serious?
Is GERD (chronic acid reflux) dangerous or life-threatening? GERD isn't life-threatening or dangerous in itself. But long-term GERD can lead to more serious health problems: Esophagitis: Esophagitis is the irritation and inflammation the stomach acid causes in the lining of the esophagus.
How do you treat GERD without esophagitis?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) treatmentLosing weight through maintaining a healthy diet and undertaking regular exercise.Avoiding reflux-inducing foods and drinks, such as caffeine, chocolate and alcohol.Quitting smoking.Avoiding late, very fatty and very large meals.More items...•
What are the 4 types of GERD?
GERD is broken down into different stages based on how serious your symptoms are and how often they occur:Stage 1: Mild GERD. Minimal acid reflux occurs once or twice a month. ... Stage 2: Moderate GERD. ... Stage 3: Severe GERD. ... Stage 4: Precancer or cancer.
How long does GERD take to heal?
GERD is a medical condition in which acidic liquids in the stomach leak up into the esophagus. Minor cases of GERD can heal in less than a month while moderate cases can take 6 to 12 weeks of treatment.
Does GERD go away?
GERD is a potentially serious condition, and it will not go away on its own. Untreated GERD can lead to inflammation of the esophagus and cause complications like ulcers, strictures and increased risk of Barrett's esophagus, which is a precursor to esophageal cancer.
Can GERD be cured?
Yes, most cases of acid reflux, sometimes referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, can be cured.
Can Covid make GERD worse?
Can coronavirus cause GERD? COVID-19 is a disease that can cause what doctors call a respiratory tract infection. It can affect your upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, and throat) or lower respiratory tract (windpipe and lungs). There is no information yet on whether COVID-19 causes GERD.
How do you know if your GERD is severe?
If you experience severe chest pain or pressure, especially in combination with pain in the jaw, neck, or back, nausea and vomiting, or difficulty breathing, seek medical help immediately.
What foods should be avoided with GERD?
Items that people with GERD are often advised to avoid include:Alcohol.Caffeine.Carbonated beverages.Chocolate.Citrus fruits and juices.Tomatoes and tomato-based foods.Garlic.Mint.More items...•
What are the risks of GERD?
Conditions that can increase your risk of GERD include: Obesity. Bulging of the top of the stomach up into the diaphragm (hiatal hernia) Pregnancy. Connective tissue disorders, such as scleroderma. Delayed stomach emptying. Factors that can aggravate acid reflux include: Smoking.
How do you know if you have GERD?
Symptoms. Common signs and symptoms of GERD include: A burning sensation in your chest (heartburn), usually after eating, which might be worse at night. Chest pain. Difficulty swallowing. Regurgitation of food or sour liquid. Sensation of a lump in your throat.
What is the cause of acid reflux?
Acid reflux occurs when the sphincter muscle at the lower end of your esophagus relaxes at the wrong time, allowing stomach acid to back up into your esophagus. This can cause heartburn and other signs and symptoms. Frequent or constant reflux can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) ...
How often does acid reflux occur?
Many people experience acid reflux from time to time. GERD is mild acid reflux that occurs at least twice a week, or moderate to severe acid reflux that occurs at least once a week. Most people can manage the discomfort of GERD with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications. But some people with GERD may need stronger medications ...
What happens when you swallow?
When you swallow, a circular band of muscle around the bottom of your esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter) relaxes to allow food and liquid to flow into your stomach. Then the sphincter closes again. If the sphincter relaxes abnormally or weakens, stomach acid can flow back up into your esophagus. This constant backwash of acid irritates the ...
What causes scar tissue in the esophagus?
Over time, chronic inflammation in your esophagus can cause: Narrowing of the esophagus (esophageal stricture). Damage to the lower esophagus from stomach acid causes scar tissue to form. The scar tissue narrows the food pathway, leading to problems with swallowing.
Why does stomach acid flow back up into the esophagus?
If the sphincter relaxes abnormally or weakens, stomach acid can flow back up into your esophagus. This constant backwash of acid irritates the lining of your esophagus, often causing it to become inflamed.
How to reduce GERD symptoms?
Stopping smoking is important to reduce GERD symptoms. Elevate your head: Raising the head of your bed on 6-inch blocks or sleeping on a specially designed wedge lets gravity lessen the reflux of stomach contents into your esophagus. Don’t use pillows to prop yourself up.
What is the difference between gastroesophageal reflux and gastroesophageal reflux?
GERD Causes. The term “gastroesophageal” refers to the stomach and esophagus. Reflux means to flow back or return. Gastroesophageal reflux is when what’s in your stomach backs up into your esophagus. In normal digestion, your LES opens to allow food into your stomach.
What is the ring between the esophagus and stomach called?
This ring is called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). If you have it, you may get heartburn or acid indigestion.
What is the best treatment for GERD?
Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter or prescription medications to treat your symptoms. Antacids: These drugs can help neutralize acid in the esophagus and stomach and stop heartburn.
What causes scar tissue in the esophagus?
Esophageal stricture: Stomach acid damages the lower part of your esophagus and causes scar tissue to form. This scar tissue builds up until it narrows the inside of the esophagus and makes it hard to swallow food. Barrett’s esophagus: Acid reflux changes the cells in the tissue that lines your esophagus.
How long do you need to take antacids for heartburn?
If you need antacids for more than 2 weeks , talk to your doctor. H2 blockers: For chronic reflux and heartburn, the doctor may recommend medications to reduce acid in the stomach. These medicines include H2 blockers, which help block acid secretion in the stomach.
How to stop reflux from stomach?
Fundoplication: This is a procedure that raises the pressure in your lower esophagus. The doctor will wind the top of your stomach around the LES. This tightens the muscle and raises pressure in your lower esophagus to stop reflux.
What is the procedure to treat GERD?
Treatment. Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery for GERD may involve a procedure to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter, called Nissen fundoplication. In this procedure, the surgeon wraps the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus after reducing the hiatal hernia, if present.
How to reduce acid reflux?
Lifestyle changes may help reduce the frequency of acid reflux. Try to: Maintain a healthy weight. Excess pounds put pressure on your abdomen, pushing up your stomach and causing acid to reflux into your esophagus. Stop smoking. Smoking decreases the lower esophageal sphincter's ability to function properly.
What is the surgeon's job to wrap the stomach around the lower esophagus?
In this procedure, the surgeon wraps the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus after reducing the hiatal hernia, if present. This reinforces the lower esophageal sphincter, making it less likely that acid will back up in the esophagus. Substitute for esophageal sphincter. Open pop-up dialog box.
How long does it take for a monitor to pass through your esophagus?
The monitor might be a thin, flexible tube (catheter) that's threaded through your nose into your esophagus, or a clip that's placed in your esophagus during an endoscopy and that gets passed into your stool after about two days. Esophageal manometry. This test measures the rhythmic muscle contractions in your esophagus when you swallow.
How to get heartburn out of bed?
If you regularly experience heartburn while trying to sleep, place wood or cement blocks under the feet of your bed so that the head end is raised by 6 to 9 inches. If you can't elevate your bed, you can insert a wedge between your mattress and box spring to elevate your body from the waist up.
What is the procedure that involves inserting a long, flexible tube (endoscope) down your throat and into
Endoscopy. Endoscopy. An endoscopy procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube (endoscope) down your throat and into your esophagus. A tiny camera on the end of the endoscope lets your doctor examine your esophagus, stomach and the beginning of your small intestine (duodenum). Your doctor might be able to diagnose GERD based on ...
How to stop a swollen stomach from eating?
Eat food slowly and chew thoroughly. Put down your fork after every bite and pick it up again once you have chewed and swallowed that bite. Avoid foods and drinks that trigger reflux. Common triggers include fatty or fried foods, tomato sauce, alcohol, chocolate, mint, garlic, onion, and caffeine.
What is GERD and LPRD?
While GERD is sometimes the result of a weak or faulty lower esophageal sphincter (LES), LPRD can be the result of a weak or faulty upper esophageal sphincter (UES). That's the valve at the junction of the throat and esophagus. "If the upper valve fails, it can be pretty serious," says Kaufman.
What does a 15 esophg score mean?
Heartburn, chest pain, indigestion, or stomach acid coming up. A score of 15 or more means that you have a 90 percent chance of having esophageal or airway reflux.
Can you have reflux without heartburn?
And yes, that's a classic symptom of reflux, but you can have reflux disease without having heartburn symptoms. Reflux can affect the larynx and throat, too, not just the esophagus. When that happens, it's called laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPRD), and may not cause heartburn.
What is gastroesophageal reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux occurs when the LES barrier is somehow compromised. Occasional reflux occurs normally, and without consequence other than infrequent heartburn, in people who do not have GERD. In people with GERD, reflux causes frequent symptoms or damages the esophageal tissue.
What causes reflux in the stomach?
What causes reflux? After swallowed food travels down the esophagus, it stimulates cells in the stomach to produce acid and pepsin (an enzyme), which aid digestion. A band of muscle at the lower part of the esophagus, called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), acts as a barrier to prevent the back-flow ...
What is IFFGD?
IFFGD is a nonprofit education and research organization. Our mission is to inform, assist, and support people affected by gastrointestinal disorders. Our original content is authored specifically for IFFGD readers, in response to your questions and concerns.
Can GERD be caused by gastric reflux?
There is no known single cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It occurs when the esophageal defenses are overwhelmed by gastric contents that reflux into the esophagus. This can cause injury to tissue. GERD can also be present without esophageal damage (approximately 50 – 70% of patients have this form of the disease).
Can a hernia cause acid reflux?
If the diaphragm is not intact, it can compromise the ability of the LES to prevent acid reflux. A hiatal hernia may decrease the sphincter pressure necessary to maintain the anti-reflux barrier. Even when the LES and the diaphragm are intact and functioning normally, reflux can still occur.
Why does GERD not work?
The major cause of GERD is that this valve does not function the way it should -- either because it is weak or because it relaxes inappropriately. A hiatal hernia (in which a portion of the stomach protrudes above the diaphragm into the chest) and poor esophageal muscle contractions can also contribute to GERD.
What is the most common complication of GERD?
One major complication which occurs in about 10% to 15% of people with chronic or longstanding GERD is Barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus results when the normal cells of the esophagus are replaced with cells similar to those of the intestine. This increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
What is the term for the back up of food in the stomach?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease ( GERD) can be thought of as chronic symptoms of heartburn. The term refers to the frequent backing up (reflux) of stomach contents (food, acid) into the esophagus -- the tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
How often do you get acid regurgitation?
About 20% of adults in the U.S. experience symptoms such as heartburn and acid regurgitation at least once a week. But if you have heartburn frequently and it is untreated, your stomach's acid may inflame the lining of your esophagus or swallowing tube, potentially narrowing it.
Can GERD cause esophagitis?
Esophagitis, or inflammation of the esophagus, is a complication of GERD. If GERD is left untreated, esophagitis can cause bleeding, ulcers, and chronic scarring. This scarring can narrow the esophagus, eventually interfering with your ability to swallow.
Can you get GERD at any age?
Your stomach's contents can also move into your throat, irritating your throat or vocals cords and causing hoarseness and a chronic, dry cough. Anyone can develop GERD at any age but you are more likely to develop it as you get older. Pregnant women are especially prone to reflux.
Does stomach acid affect esophagus?
Stomach acid may also change the cells of the lining of your esophagus. This change, called Barrett's esophagus, increases the likelihood of certain cancers of the esophagus. Only a small percentage of people with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus. Your stomach's contents can also move into your throat, irritating your throat or vocals cords ...

Overview
Definition
Pathophysiology
Signs and symptoms
Treatment