
What is glucose and what does it do?
Glucose is a tiny, simple sugar that is used as a key source of energy for the brain, muscles, and a variety of other organs and tissues in the body. It is also a component of the body’s bigger structural molecules, such as glycoproteins and glycolipids. These levels in the human body are tightly regulated.
What is glucose used for in an organism?
Glucose is key to keeping the mechanisms of the body in top working order. When our glucose levels are optimal, it often goes unnoticed. But when they stray from recommended boundaries, you’ll notice the unhealthy effect it has on normal functioning. So what is glucose, exactly? It’s the simplest of the carbohydrates, making it a monosaccharide.
What does glucose do to the brain?
- We provide a comprehensive overview of the role of glucose metabolism for normal brain function.
- We analyze the contribution of glucose metabolism to brain physiology.
- We discuss controversies in energy substrate consumption and utilization.
- We highlight the connection between glucose metabolism and cell death.
What is the main function of glucose?
Which natural sugar is best?
- Stevia. Share on Pinterest. Stevia is a very popular low-calorie sweetener.
- Erythritol. Erythritol is another low-calorie sweetener.
- Xylitol. Xylitol is a sugar alcohol with a sweetness similar to sugar.
- Yacon Syrup. Yacon syrup is another unique sweetener.

What is glucose and its functions?
Glucose comes from the Greek word for "sweet." It's a type of sugar you get from foods you eat, and your body uses it for energy. As it travels through your bloodstream to your cells, it's called blood glucose or blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose from your blood into the cells for energy and storage.
What is glucose small answer?
Glucose is a simple sugar which can be readily absorbed by the body. Unlike other foods such as carbohydrates, glucose does not have to be processed by the digestive system for energy. It is directly absorbed into the bloodstream and all cells.
What is glucose made from?
Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but glucose syrup is also made from potatoes and wheat, and less often from barley, rice and cassava.
What is glucose and example of?
Glucose and fructose are examples of monosaccharides, meaning they consist of a single sugar unit, while sucrose is an example of a disaccharide. However, sugar units can be bonded or linked together to form polysaccharides , which consist of many sugars linked together to form extensive chains of sugars.
What is your glucose?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main sugar found in your blood. It comes from the food you eat, and is your body's main source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to all of your body's cells to use for energy.
What is glucose in photosynthesis?
Plants use a process called photosynthesis to make food. During photosynthesis, plants trap light energy with their leaves. Plants use the energy of the sun to change water and carbon dioxide into a sugar called glucose. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to make other substances like cellulose and starch.
Where is glucose found?
Glucose (from Greek glykys; “sweet”) has the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals. It is the source of energy in cell function, and the regulation of its metabolism is of great importance (see fermentation; gluconeogenesis).
What is glucose also known as?
Glucose is a simple sugar with six carbon atoms and one aldehyde group. This monosaccharide has a chemical formula C6H12O6. It is also known as dextrose. It is referred to as aldohexose as it contains 6 carbon atoms and an aldehyde group.
Is glucose a sugar?
Glucose is the simplest sugar and your body's preferred source of energy. It's the sugar that's measured in blood sugar tests. Other monosaccharides are fructose and galactose, which are metabolized into glucose ( 1 , 2 ). Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharide sugars bound together.
What is a glucose easy definition?
Glucose is the main type of sugar in the blood and is the major source of energy for the body's cells. Glucose comes from the foods we eat or the body can make it from other substances. Glucose is carried to the cells through the bloodstream. Several hormones, including insulin, control glucose levels in the blood.
Why do cells need glucose?
Importance of Glucose Glucose provides quick energy for cells. Fat has more energy than glucose, but it requires some chemical conversions before we can get it into the process of cellular respiration, so it takes longer to use. Glucose, on the other hand, is stored as glycogen, or long chains of glucose inside muscle.
What is the function of glucose in the body?
Glucose is a simple sugar used by the body to make ATP , which is used by the body for energy. The body converts carbohydrates in food into simple sugars in the digestive system; the glucose enters the bloodstream, causing its level to rise and triggering the pancreas to produce insulin to regulate it.
Why is glucose important?
The glucose molecule is an important carbohydrate, essential for the production of ATP, or the molecule of energy in the body. Glucose is tightly regulated, and both excessive and inadequate glucose levels result in disease states. Create an account.
What is the molecule that releases glucose into the blood?
This situation is also sensed by the pancreas, which releases a different molecule called glucagon. Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert glycogen (a starch-like stored form of glucose) to glucose and release it into the blood. Glucagon release stops when blood glucose levels rise back into a safe range.
How many atoms are in the glucose regulatory loop?
Here is a diagram of the glucose regulatory loop. The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. This means that there are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms bonded together to make one molecule of glucose. These atoms are arranged in a very specific order and orientation in three-dimensional space.
What is the function of insulin in the pancreas?
Insulin is a regulatory molecule whose purpose is to control carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Once released into the blood, insulin directs cells of the liver, skeletal muscle, and fat tissue to absorb glucose from the blood.
What happens when you eat carbs?
When you eat, the carbohydrates in your food are either already simple sugars or are re-broken down into simple sugars . The simple sugars are readily absorbed into your bloodstream from your digestive system, causing your blood glucose level to rise. Your pancreas detects rising blood glucose and responds by secreting insulin. Insulin is a regulatory molecule whose purpose is to control carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
What is the term for a person who has low blood glucose?
Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) occurs when there is not enough glucose in the blood. This too is harmful and potentially deadly. The body has several ways to detect changing glucose levels and mechanisms to correct harmful situations. When the body cannot regulate glucose levels, diseases such as diabetes occur.
Why is glucose important?
Glucose is key to keeping the mechanisms of the body in top working order. When our glucose levels are optimal, it often goes unnoticed. But when they stray from recommended boundaries, you’ll notice the unhealthy effect it has on normal functioning.
How does the body process glucose?
Our body processes glucose multiple times a day, ideally. When we eat, our body immediately starts working to process glucose. Enzymes start the breakdown process with help from the pancreas. The pancreas, which produces hormones including insulin, is an integral part of how our body deals with glucose. When we eat, our body tips the pancreas ...
Why does diabetes occur?
One way diabetes occurs is when the pancreas doesn’t produce insulin in the way it should. In this case, people need outside help (insulin injections) to process and regulate glucose in the body. Another cause of diabetes is insulin resistance, where the liver doesn’t recognize insulin that’s in the body and continues to make inappropriate amounts ...
What is the normal glucose level?
People who have diabetes have to pay special attention to their glucose levels. Before eating, a healthy range is 90–130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Why does the pancreas need insulin?
When we eat, our body tips the pancreas off that it needs to release insulin to deal with the rising blood sugar level. Some people, however, can’t rely on their pancreas to jump in and do the work it’s supposed to do. One way diabetes occurs is when the pancreas doesn’t produce insulin in the way it should.
How to increase blood sugar levels?
Eating a meal or drinking juice can help to increase glucose levels. People with diabetes also often take glucose pills, which can be purchased over-the-counter at a pharmacy. It’s possible for low blood sugar to result in a loss of consciousness. If this occurs, it’s important to seek out medical care.
What are the long term consequences of unregulated glucose levels?
It can lead to a variety of conditions, including: neuropathy. heart disease. blindness. skin infections. problems in the joints and extremities, especially the feet. severe dehydration. coma.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms.
How much glucose is in the blood?
All animals are also able to produce glucose themselves from certain precursors as the need arises. Nerve cells, cells of the renal medulla and erythrocytes depend on glucose for their energy production. In adult humans, there are about 18 g of glucose, of which about 4 g are present in the blood.
Why is glycogen not returned to the blood?
Liver cell glycogen can be converted to glucose and returned to the blood when insulin is low or absent; muscle cell glycogen is not returned to the blood because of a lack of enzymes. In fat cells, glucose is used to power reactions that synthesize some fat types and have other purposes.
What is the open-chain form of glucose?
The open-chain form of glucose makes up less than 0.02% of the glucose molecules in an aqueous solution. The rest is one of two cyclic hemiacetal forms. its open-chain form, the glucose molecule has an open (as opposed to cyclic) unbranched backbone of six carbon atoms, where C-1 is part of an aldehyde group H (C=O)−.
What is the most important source of energy for all organisms?
In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar.
Why is glucose the most abundant monosaccharide?
One possible explanation for this is that glucose has a lower tendency than other aldohexoses to react nonspecifically with the amine groups of proteins. This reaction— glycation —impairs or destroys the function of many proteins, e.g. in glycated hemoglobin. Glucose's low rate of glycation can be attributed to its having a more stable cyclic form compared to other aldohexoses, which means it spends less time than they do in its reactive open-chain form. The reason for glucose having the most stable cyclic form of all the aldohexoses is that its hydroxy groups (with the exception of the hydroxy group on the anomeric carbon of d -glucose) are in the equatorial position. Presumably, glucose is the most abundant natural monosaccharide because it is less glycated with proteins than other monosaccharides. Another hypothesis is that glucose, being the only D-aldohexose that has all five hydroxy substituents in the equatorial position in the form of β-D-glucose, is more readily accessible to chemical reactions, for example, for esterification or acetal formation. For this reason, D-glucose is also a highly preferred building block in natural polysaccharides (glycans). Polysaccharides that are composed solely of Glucose are termed glucans .
What is the process of releasing glucose?
In animals, glucose is released from the breakdown of glycogen in a process known as glycogenolysis . Glucose, as intravenous sugar solution, is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the safest and most effective medicines needed in a health system.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose in the blood is derived from three main sources: ○. Intestinal absorption. ▪. Glucose is the end-product of carbohydrate digestion, absorbed by enterocytes. ▪.
Where is glucose stored in the body?
Any glucose not immediately needed for energy is stored as glycogen in the liver. The healthy organism tries to maintain a constant level of glucose in blood and serum by secretion of insulin to reduce too high a level and mobilises glucose from glycogen of the liver if levels fall below normal.
How is GLC maintained?
Overall homeostasis is maintained through directing the flux of Glc to or from glycogen stores, balancing glycolysis versus gluconeogenesis, and promoting protein catabolism in times of need.
How is glucose homeostasis controlled?
The physiology of glucose homeostasis is controlled primarily by insulin release in response to elevated glucose levels (postprandial), although in birds, glucagon appears to serve as the primary regulator. Significant species variations in glucose levels have been noted.
What hormones increase GLC?
Insulin promotes uptake and oxidation of Glc by tissues and favors storage, particularly in the postprandial phase. Glucagon in response to low blood Glc concentration increases Glc release from storage and synthesis from precursors. Adrenaline (epinephrine) mobilizes stores and accelerates utilization.
Why is glycolysis so inefficient?
Glycolytic breakdown of Glc to lactate is an inefficient mode of fuel utilization, because it generates only two ATP per glucose molecule. The advantages are that glycolysis is fast, because only 11 reactions are needed, and that it operates anaerobically (i.e. does not require oxygen).
How do GE and GI neurons differ?
GE and GI neurons have differing properties with regard to their sensitivity to glucose and to other hormones and metabolic substrates. GE neurons are more sensitive to glucose than are GI neurons, but the range over which both respond to glucose is also a function of their anatomic location. For example, GE neurons in the VMN are maximally activated over a range of 0.1–2.5 mM glucose, while ARC GE neurons continue to increase their activity up to 5 mM glucose. These differences in sensitivity may reflect inputs from surrounding astrocytes or neurons but might also be due to the fact that the KATP channel has different proportions of sulfonylurea-binding subunits, which could alter their sensitivity to glucose. Also, because the K ATP channel is subject to modulatory effects of G-protein-coupled receptors, phosphoinositol 3-kinase (as modulated by both leptin and insulin), and levels of intracellular long-chain CoA molecules derived from fatty acids, the milieu in which a given neuron finds itself combines with its intrinsic metabolic and physiological characteristics to determine how it will respond to glucose. Thus, glucose-sensing neurons are really metabolic sensors in which the combined input of metabolites, peptides, transmitters, and hormones can affect both their short-term and long-term ability to sense and respond to glucose.
Where is glucose found in nature?
Occurrence. Glucose is abundantly present in nature. Plants are the major source of glucose as they make it by the process of photosynthesis. It is present in free form in all fruits being abundantly present in dates, figs, grapes, etc.
How is glucose synthesized?
Glucose is mainly synthesized in plants by the process of photosynthesis. However, animals are also capable of synthesizing glucose to some extent from non-carbohydrate sources by a process known as gluconeogenesis.
What is the most important monosaccharide in the body?
Glucose is the most important monosaccharide present in our body. It belongs to the hexose category of monosaccharides. Glucose provides energy to all the cells in our body except the cardiac myocytes. Excess glucose is stored in the body in the form of storage molecules.
What is the ring structure of glucose?
Closed chain. Glucose makes a ring when it is dissolved in an aqueous solution. The ring formed by glucose is hexagonal in structure. Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, belonging to the aldehydic functional group, make the corners or angles of the hexagon. This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose.
How many carbon atoms are in glucose?
Glucose is a monosaccharide made up of six carbon atoms. It is the most important hexose present in our body. The molecular formula of glucose is represented as C 6 H 12 O 6. The structural formula of glucose can be represented in two ways;
What is the name of the molecule that has the same molecular formula but differs with respect to the arrangement
Isomers are the molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ with respect to the arrangement of atom in the three-dimensional space. The number of isomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral carbons in it. A chiral carbon is the one that is attached to four different groups of atoms.
What is the shape of a ring formed when a molecule is dissolved in water?
When either D-glucose or L-glucose is dissolved in water, it forms a hexagonal ring structure known as glucopyranose. The ring formed by each of these molecules can have alpha or beta orientation.
Where is glucose formed in a cell?
Glucose is formed in the CALVIN CYCLE of PHOTOSYNTHESIS and acts as a primary energy supply for both plant and animal cells, although usually it is converted to an insoluble form for long-term storage: STARCH in plants, GLYCOGEN in animals. see MONOSACCHARIDE for structure.
How many times can you test for glucose?
During this second test, called the 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test, your blood glucose level will be tested four times during a three-hour period after drinking the cola-like drink. If two out of the four blood tests are abnormal, you are considered to have gestational diabetes. More discussions about Glucose.
What is the primary source of energy for the body?
A simple sugar produced when carbohydrates are broken down in the small intestine. It is the primary source of energy for the body. Various tests that measure blood glucose levels are used in diagnosing insulin resistance.
When to give glucose test for pregnancy?
The test is given between week 24 and week 28 of the pregnancy. First you drink glucose, which is very sweet. You can mix it will water to help it go down easier. Then, after an hour you will have a blood test to check your glucose levels. Q.
Does fructose sugar require insulin?
Whereas fructose sugar had a slight different metabolic route inside the body and it does not requires insulin. Glucose requires insulin. As a diabetic lacks insulin production; the glucose increases the sugar level of the body but fructose is out of this system of functioning by our body and makes a diabetic to control it well.
Is glucose a monosaccharide?
glu·cose. A dextrorotatory monosaccharide found in a free form in fruits and other parts of plants, and in combination in glucosides, glycogen, disaccharides, and polysaccharides; chief source of energy in human metabolism, the final product of carbohydrate digestion, and the principal sugar of the blood; insulin is required for the use ...
Is corn sugar a monosaccharide?
Grape or corn sugar. Glucose is a simple monosaccharide sugar present in the blood as the basic fuel of the body. Glucose is essential for life; a severe drop in the blood levels rapidly leads to coma and death. It is stored in the liver and the muscles in a polymerized form called GLYCOGEN. It is derived from carbohydrates in the diet, but in conditions of shortage can be synthesized from fats or proteins. The sugar is on the WHO official drug list.
How does glucose get into the body?
As you eat, food travels down your esophagus to your stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released. It goes into your intestines where it's absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to your cells.
Where is glucose stored in the body?
After your body has used the energy it needs, the leftover glucose is stored in little bundles called glycogen in the liver and muscles. Your body can store enough to fuel you for about a day. After you haven't eaten for a few hours, your blood glucose level drops.
What is the blood sugar level between meals?
Between meals, your blood sugar should be less than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). This is called your fasting blood sugar level. There are two types of diabetes: In type 1 diabetes, your body doesn't have enough insulin. The immune system attacks and destroys cells of the pancreas, where insulin is made.
What cells are responsible for regulating blood sugar?
Beta cells in your pancreas monitor your blood sugar level every few seconds. When your blood glucose rises after you eat, the beta cells release insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts like a key, unlocking muscle, fat, and liver cells so glucose can get inside them.
What hormone moves glucose from the blood to the cells?
Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose from your blood into the cells for energy and storage. People with diabetes have higher-than-normal levels of glucose in their blood. Either they don't have enough insulin to move it through or their cells don't respond to insulin as well as they should.
Why does the pancreas need insulin?
The immune system attacks and destroys cells of the pancreas, where insulin is made. In type 2 diabetes, the cells don't respond to insulin like they should. So the pancreas needs to make more and more insulin to move glucose into the cells. Eventually, the pancreas is damaged and can't make enough insulin to meet the body's needs.
What happens if you have too much glucose in your blood?
Too much glucose in your bloodstream for a long period of time can damage the vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to your organs. High blood sugar can increase your risk for: Heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. Kidney disease. Nerve damage.
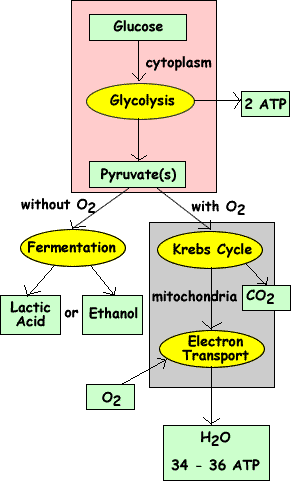
Glucose's Role in Cellular Respiration
Glucose represents a monosaccharide, or simple sugar, with the chemical formula C6H12O6. In the human body, glucose constitutes the primary source of energy for the brain and is used as the main substrate for energy production via cellular respiration.
What Happens to Glucose During Cellular Respiration?
What is glucose used for? In living organisms that consume food for energy, glucose is acquired through a variety of sources. For example, humans eat fruits, vegetables, and grain products that provide significant amounts of carbohydrates to the diet.
Cellular Respiration Steps
What happens to glucose during cellular respiration? Cellular respiration starts with glycolysis, in which glucose molecules are broken down to form two molecules of pyruvate. The major processes associated with glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm of the cell, where two main stages are involved in the conversion of glucose into pyruvate.
Overview
Biochemical properties
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide. Glucose is also the most widely used aldohexose in most living organisms. One possible explanation for this is that glucose has a lower tendency than other aldohexoses to react nonspecifically with the amine groups of proteins. This reaction—glycation—impairs or destroys the function of many proteins, e.g. in glycated hemoglobin. …
History
Glucose was first isolated from raisins in 1747 by the German chemist Andreas Marggraf. Glucose was discovered in grapes by another German chemist – Johann Tobias Lowitz – in 1792, and distinguished as being different from cane sugar (sucrose). Glucose is the term coined by Jean Baptiste Dumas in 1838, which has prevailed in the chemical literature. Friedrich August Kekulé proposed the term dextrose (from the Latin dexter, meaning "right"), because in aqueous solution …
Chemical properties
Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highly soluble in water and acetic acid but poorly soluble in methanol and ethanol. They melt at 146 °C (295 °F) (α) and 150 °C (302 °F) (β), and decompose starting at 188 °C (370 °F) with release of various volatile products, ultimately leaving a residue of carbon. Glucose has a dissociation exponent (pK) of 12.16 at 25 °C (77 °F) in methanol and water.
Pathology
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where the body is unable to regulate levels of glucose in the blood either because of a lack of insulin in the body or the failure, by cells in the body, to respond properly to insulin. Each of these situations can be caused by persistently high elevations of blood glucose levels, through pancreatic burnout and insulin resistance. The pancreas is the organ responsibl…
Sources
Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey. Glucose is extremely abundant and has been isolated from a variety of natural sources across the w…
Commercial production
Glucose is produced industrially from starch by enzymatic hydrolysis using glucose amylase or by the use of acids. The enzymatic hydrolysis has largely displaced the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. The result is glucose syrup (enzymatically with more than 90% glucose in the dry matter) with an annual worldwide production volume of 20 million tonnes (as of 2011). This is the reason for the former common name "starch sugar". The amylases most often come from Bacillus licheniformis
Commercial usage
Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. In foods, it is used as a sweetener, humectant, to increase the volume and to create a softer mouthfeel. Various sources of glucose, such as grape juice (for wine) or malt (for beer), are used for fermentation to ethanol during the production of alcoholic beverages. Most soft drinks in the US use HFCS-55 (wit…