Gradually Varied Flow In gradually varied flow, the flow depth and velocity vary slowly, and the free surface is stable. This makes it possible to formulate the variation of flow depth along the channel on the basis of the conservation of mass and energy principles and to obtain relations for the profile of the free surface.
What is meant by gradually varied flow?
Explanation: Gradually varied flow is steady non-uniform because the velocity of water remains constant at a specified point, but it changes from one point to another point. The terms steady and uniform are used frequently in engineering, and thus it is important to have a clear understanding of their meanings.
What is varied flow?
Used to describe nonuniform flow conditions in open channels and conduits, with changing cross section or slope with distance. When discharge is constant, the velocity changes with changes in slope and cross section.
What is meant by rapidly varied flow?
If water depth or velocity change abruptly over a short distance and the pressure distribution is not hydrostatic, the water surface profile is characterized as Rapidly Varying Flow (RVF). The occurrence of RVF is usually a local phenomenon.
What is the equation of gradually varied flow?
The basic governing equation of the steady GVF in open channels is given by [22], [23](1) dy dx = S 0 - S f 1 - F 2 where y = depth of flow (m), x = distance along the channel, measured positive in the downstream direction (m), dy/dx = slope of the free surface at any location x, S0 = longitudinal slope of the channel ...
What are the 3 types of flows?
The different types of fluid flow are: Steady and Unsteady Flow. Uniform and Non-Uniform Flow. Laminar and Turbulent Flow.
What is difference between gradually varied flow and rapidly varied flow?
Rapidly varied flow (RVF) occurs over a short distance near the obstacle. Gradually varied flow (GVF) occurs over larger distances and usually connects UF and RVF.
What are the four types of flow?
Laminar FlowUnidirectional laminar flow.Pulsatile laminar flow.Oscillatory laminar flow.
What are two types of flow patterns?
There are mainly two kinds of flow, such as:Laminar flow - Laminar flow would be the continuous movement of flowing fluid that follows or respects streamlines. ... Turbulent flow - Turbulent flow is characterized by erratic property modifications in the flow.
What are the different types of flow patterns?
Its flow pattern can be divided into bubbly flow, intermittent flow including slug flow and plug flow, stratified flow, annular flow (Taitel and Duckler, 1976).
What is steady flow formula?
The steady flow energy equation for the WHB is(9.11)Mf2hf0+HP4=λ′D+HP′S,where 4 and S are the entry and exit states, P refers to products entering (i.e. at exit from the turbine), P′ refers to products after the supplementary combustion and Mf2hf0 is the enthalpy flux of the entering fuel.
What is meant by prismatic channel?
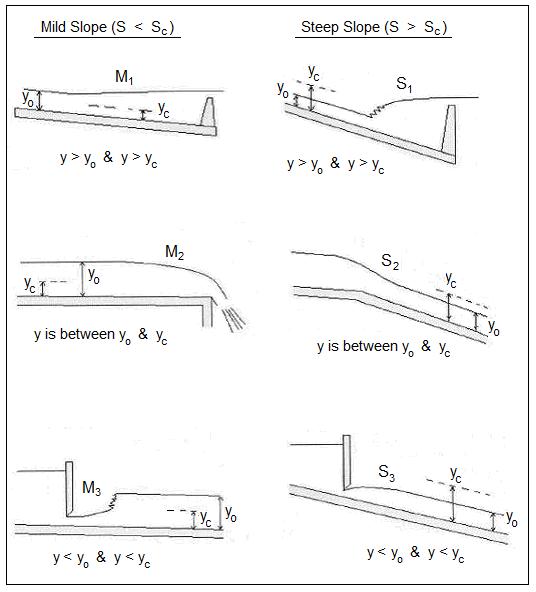
Prismatic chan- nels are those channels having a straight alignment and constant bot- tom slope, Manning's coefficient of roughness and cross section. Varied flows in a prismatic channel are classified to give some percep- tion of the water surface profile (WSP).
What is steady and unsteady flow?
steady: A steady flow is one in which the conditions (velocity, pressure and cross- section) may differ from point to point but DO NOT change with time. • unsteady: If at any point in the fluid, the conditions change with time, the flow is described as unsteady.
What are the four types of flow?
Laminar FlowUnidirectional laminar flow.Pulsatile laminar flow.Oscillatory laminar flow.
What are two types of flow patterns?
There are mainly two kinds of flow, such as:Laminar flow - Laminar flow would be the continuous movement of flowing fluid that follows or respects streamlines. ... Turbulent flow - Turbulent flow is characterized by erratic property modifications in the flow.
What's the difference between slow flow and Variflow?
A: Yes, apparently the Vari Flow changes the flow based on the infants sucking whereas the slow/medium/fast flows are an actual hole size difference. Vari Flow nipples were made to help breast milk fed babies with combating nipple confusion and transition between the bottle and breast easier. Hope this helps!
What are the 5 flows?
From the perspective of the channel manager, there are five important flows.Product flow.Negotiation flow.Ownership flow.Information flow.Promotion flow.
What is a nonuniform flow?
Nonuniform flows for which the changes in depth and velocity are so abrupt that radial accelerations distort the vertical distribution of fluid pressure from the hydrostatic condition are called rapidly varied flows. Flow over a sharp-crested dam or weir, and flow under a sluice gate, are good examples. Such flows are difficult to deal with analytically, and I will not pursue them here, although they are important in many engineering applications.
How far upstream is the backwater effect?
For big rivers flowing well below the critical condition, the backwater effect is felt not just for kilometers but for tens of kilometers upstream, and the superelevation of the actual water surface above the hypothetical point of intersection between the uniform flow and the reservoir level can be many meters. You can imagine the importance of being able to predict the magnitude of this superelevation at all points upstream, when you are worrying about how many homes and farms and businesses you are going to be flooding when you build that dam.
What is the energy gradient in equation 5.7.2?
The term on the left side of Equation 5.7.2 is the rate of change in total energy in the downstream direction. This is always negative, because energy is inevitably lost by friction. Think in terms of the downward slope of the line formed by plotting E w as a function of downstream distance. This slope, denoted by S e, is what was called the energy slope, or the energy gradient, or the slope of the energy line earlier in this chapter. By convention, such a negative slope is considered to be positive S e, so we replace d E w / d x in Equation 5.7.2 by − S e.
Is friction loss in nonuniform flow well studied?
Friction loss in nonuniform flow is not well studied, but to get somewhere just in a qualitative way we can assume that the friction loss in slightly to moderately nonuniform flow is not greatly different from what it would be in uniform flow—and we have already dealt with that satisfactorily in Chapter 4. Remember the Chézy coefficient I introduced back then? According to Equation 4.6.3, repeated here as Equation 5.7.3,
What happens if a portion of a culvert becomes pressurized?
If only a portion of the culvert becomes pressurized, FishXing will switch between the GVF and full flow equations.
What is constant j?
j = Constant equal to 1.49 for English units and 1.00 for SI units.
What is the GVF equation?
The GVF equations account for gravitational and frictional forces acting on the water, and are used to calculate water depths throughout the culvert. A GVF profile is also known as a water depth profile and applies to steady-state, or constant flow, conditions.
What method does FishXing use?
FishXing primarily uses the Standard Step Method of numerical integration. The following form of the equation is used:
How does FishXing work?
Therefore, FishXing uses numerical integration to generate a water surface profile. Numerical integration is a technique of dividing the channel, or culvert, into numerous short reaches and then performing the computations from one end of the reach to the other.
What is a steady non-uniform flow in a prismatic channel with gradual changes in its water-?
steady non-uniform flow in a prismatic channel with gradual changes in its water-surface elevation is termed as gradually-varied flow (GVF). The back water produced by a dam or weir across a river and the drawdown produced at a sudden drop in a channel are few typical examples of GVF. In a GVF , the velocity varies along the channel and consequently the bed slope, water surface slope, and energy slope will all differ from each other. Regions of high curvature are excluded in the analysis of this flow.
What is the process of identification of possible profiles as a prelude to quantitative computation?
The process of identification of possible profiles as a prelude to quantitative computation is known as analysis of flow profiles. A channel carrying a GVF can in general contain different prismoidal-channel sections of varing hydraulic properties. There can be a number of control sections at a various locations. To determine the resulting water-surface profile in a given case, one should be in a position to analyse the effect of various channel sections and controls connected in series.
