Full Answer
What is Graham’s law?
According to Graham’s Law, at constant pressure and temperature, molecules or atoms with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than the higher molecular mass molecules or atoms. Thomas even found out the rate at which they escape through diffusion.
What is Graham’s Law of the diffusion of gases?
In1829, Thomas Graham, a Scottish Chemist formulated the Graham’s Law of the Diffusion and Effusion of Gases. According to this Law, the rate of Diffusion of different gases, at a constant temperature, is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
How does Graham's Law relate to molar mass?
Graham's law states that the rate at which a gas will effuse or diffuse is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar masses of the gas. This means light gasses effuse/diffuse quickly and heavier gases effuse/diffuse slowly. This example problem uses Graham's law to find how much faster one gas effuses than another.
What did Thomas Graham discover about the rate of diffusion?
Graham’s Law Graham's law of diffusion was one of the breakthroughs in the field of chemistry. Thomas graham discovered this law in 1848, and it is also known as the graham's law of Effusion. His experimentation with the rate of effusion process unveiled that gas with heavier molecules travels slower than gas with lighter particles.

What does Graham's law explain?
Graham's law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely propertional to the square root of the density of the gas.
What is an example of Graham's law?
When the particles of a material are in an area of low concentration, they tend to move to the content with a high area of concentration. A straightforward example of this process is when we use perfume or a scented spray in one part of the room, and then we can smell it in the entire room.
What is Graham's law of effusion formula?
Graham's law is used to calculate the rate of diffusion or effusion and molar mass of gases. The equation of Graham's law is written as: rate 1 / rate 2 = √ (mass 2 / mass 1) rate 1 and rate 2 - Rates of effusion or diffusion of Gas 1 and 2, respectively.
Which of the following is Graham's Law?
Graham's Law refers to gaseous diffusion. The spontaneous mixing of gases against gravitational forces to form homogeneous mixture is known as the gaseous diffusion. The distance travelled by gas molecules per unit time is known as the rate of diffusion (r) of the gas.
How is Graham's law applied in real life?
The gases with different densities can be separated using Graham's law. It is also helpful in determining the molar mass of unknown gases by comparing the rate of diffusion of unknown gas to known gas. We can separate the isotopes of an element using Graham's law. A common example is enriching uranium from its isotope.
How was Graham's law discovered?
This result is known as Graham's law of diffusion after Thomas Graham (1805 to 1869), a Scottish chemist, who discovered it by observing effusion of gases through a thin plug of plaster of paris.
How does Graham's law explain why we smell odor?
It states that gas particles are constantly moving in random, rapid motion. So, if you have enough particles (or in this case, cookie smell molecules) in one central location, they will eventually spread out because they are moving randomly and rapidly.
What are the applications of Graham's law?
It helps in the separation of gases having different densities. It helps in the separation of isotopes of certain elements. It helps in determining the molecular weight of an unknown gas by using the rates of diffusion/effusion.
What are the constants in Graham's law of diffusion?
Graham's Law formula Let at constant temperature and pressure, r1 and r2 are the rates of diffusion or effusion of two gases having densities d1 and d2. According to Graham's law, r1 = 1/√d1 and r2 = 1/√d2.
What is gas hole in chemistry?
It is a defect in the casting that occurs due to trapped gases and dirty materials.
1. Why is Thomas Graham famous ?
Thomas Graham (1805-1869) is known as the author of colloidal chemistry and for his abecedarian exploration on the nature of phosphoric acid and ph...
2. What is the history of Graham ?
Graham's exploration on the prolixity of feasts was started by his reading about the observation of German druggist Johann Döbereiner that hydrogen...
3. State some examples of Graham’s Law ?
Graham’s law of effusion or prolixity is generally used to calculate the effusion or prolixity rate of a particular gas. It also helps to compare t...
4. How does Graham's Law help in construction of chimneys ?
The engineers and masterminds make use of Graham’s law to estimate the proper height of the artificial and domestic chimneys. The bank and poisonou...
5. What is Uranium Enrichment ?
Another practical operation of Graham's law is uranium enrichment. Natural uranium consists of an admixture of isotopes with slightly different mil...
6. Are there any Applications of Graham's Law in Real Life?
As we know, today, Graham's law has several uses in daily life. The main application of graham's law is in the separation process. We can separate...
7. What are the Limitations of Graham's Law?
Graham's law has a significant limitation that everyone should be aware of today. This law holds for Effusion, but in case of diffusion, we only ta...
How does Graham's law work?
As we know, today, Graham's law has several uses in daily life. The main application of graham's law is in the separation process. We can separate multiple gases with varying density using this law. Using the formula of Graham's law, we can compare the rates of diffusion and calculator molar masses of an unknown gas using given gas. Furthermore, we can even separate the isotopes of a given gas utilising this law. The typical example of this process is the isotopes of uranium. We mainly use the heavy and light isotopes of uranium that are we get from the natural uranium found on the planet.
What is Graham's law?
Graham’s Law. Graham's law of diffusion was one of the breakthroughs in the field of chemistry. Thomas graham discovered this law in 1848, and it is also known as the graham's law of Effusion. His experimentation with the rate of effusion process unveiled that gas with heavier molecules travels slower than gas with lighter particles.
Why does diffusion increase with time?
The main reason behind this phenomenon is that the velocity of atoms or molecules directly affects the rates of diffusion. Due to high temperatures, the speed of molecules increases, as a result of this increasing the diffusion rates with time.
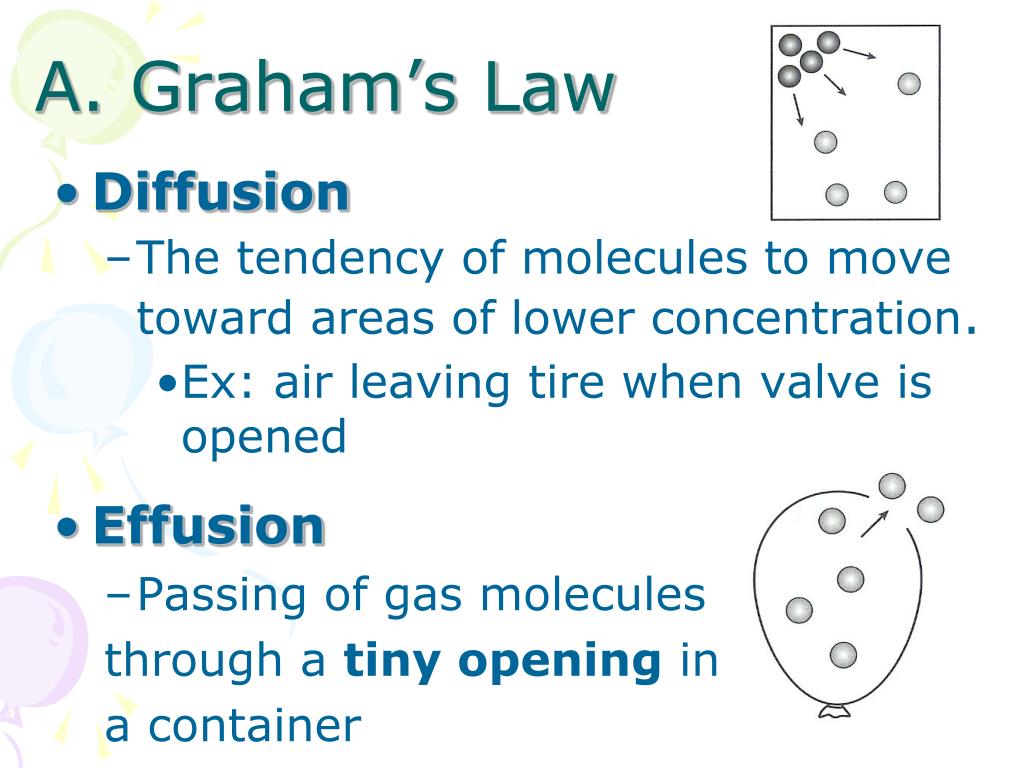
What is the process through which particles from one gas move to another gas?
The process through which the particles from one gas move to another gas is diffusion. It causes significant disorder in the entire system. We can also observe diffusion at slower rates in liquids as well as solids. The leading cause of this phenomenon is the concentration levels.
What is the process of a gaseous particle moving into a vacuum called?
When the gaseous particles move from a tiny opening into the vacuum of space or open container, then the process is called Effusion. This space can be a vacuum, any other gas or atmosphere. In this process, the molecules of material try to escape from a closed container through the aperture.
How to determine the mass of a gas?
According to the Universal or Ideal Gas Law, the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature for a fixed mass (quantity) of gas is as follows: 1 If temperature and pressure are kept constant, then the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas. 2 If the temperature and volume remain constant, then the pressure of the gas changes directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas present. 3 If the number of gas molecules and the temperature remain constant, then the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. 4 If the temperature changes and the number of gas molecules are kept constant, then either pressure or volume (or both) will change in direct proportion to the temperature.
How does the pressure of a gas change?
If the temperature and volume remain constant, then the pressure of the gas changes directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas present. If the number of gas molecules and the temperature remain constant, then the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. If the temperature changes and the number of gas molecules are kept ...
What is the ideal gas law?
What is the Ideal or Universal Gas Law? According to the Universal or Ideal Gas Law, the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature for a fixed mass (quantity) of gas is as follows : If temperature and pressure are kept constant, then the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the number of molecules of gas.
What does M mean in chemistry?
M = molar mass. The Molar Mass tells you the number of grams per mole of a compound. The units for molar mass is grams/mole. It indicates the number of atoms, ions, molecules, or formula units present in a particular chemical.
Does colliding with each other decrease energy?
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory : Collisions of molecules with each other or the walls of the container do not decrease the energy of the system. The temperature of a gas depends on its average kinetic energy, that is, the energy of an ideal gas is entirely kinetic.
Who created the Graham's law?
In1829, Thomas Graham, a Scottish Chemist formulated the Graham’s Law of the Diffusion and Effusion of Gases. According to this Law, the rate of Diffusion of different gases, at a constant temperature, is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
What is the law of effluence?
Graham's law states that the rate at which a gas will effuse or diffuse is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar masses of the gas. This means light gasses effuse/diffuse quickly and heavier gases effuse/diffuse slowly.
What is Graham's law?
Updated July 03, 2019. Graham's law is a gas law which relates the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas to its molar mass. Diffusion is the process of slowly mixing two gases together. Effusion is the process that occurs when a gas is permitted to escape its container through a small opening.
When does the gas law break down?
The law breaks down, like other gas laws, when the concentration of gases becomes very high. The gas laws were written for ideal gases, which are at low temperatures and pressures. As you increase the temperature or pressure, you can expect the predicted behavior to deviate from experimental measurements.
Who is Todd Helmenstine?
Todd Helmenstine is a science writer and illustrator who has taught physics and math at the college level. He holds bachelor's degrees in both physics and mathematics. Graham's law is a gas law which relates the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas to its molar mass. Diffusion is the process of slowly mixing two gases together.
How many gases were removed from balloons using Graham's law?
Using the apparatus shown and Graham's Law syringe needles, remove 25 mL of different gases from their balloons. Then, measure the time it takes for the gases to effuse from the syringe. Three gases were used: hydrogen, oxygen, and difluorodichlormethane.
What is the law of effusion?
Graham's law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely propertional to the square root of the density of the gas. Since equal volumes of gas at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of gas molecules, the rate of effusion is also inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight of the gas.
Which gas had the slowest rate of effusion?
Three gases were used: hydrogen, oxygen, and difluorodichlormethane. The hydrogen went the fastest, the oxygen was in the middle, and the difluorodichloromethane had the slowest rate of effusion.
