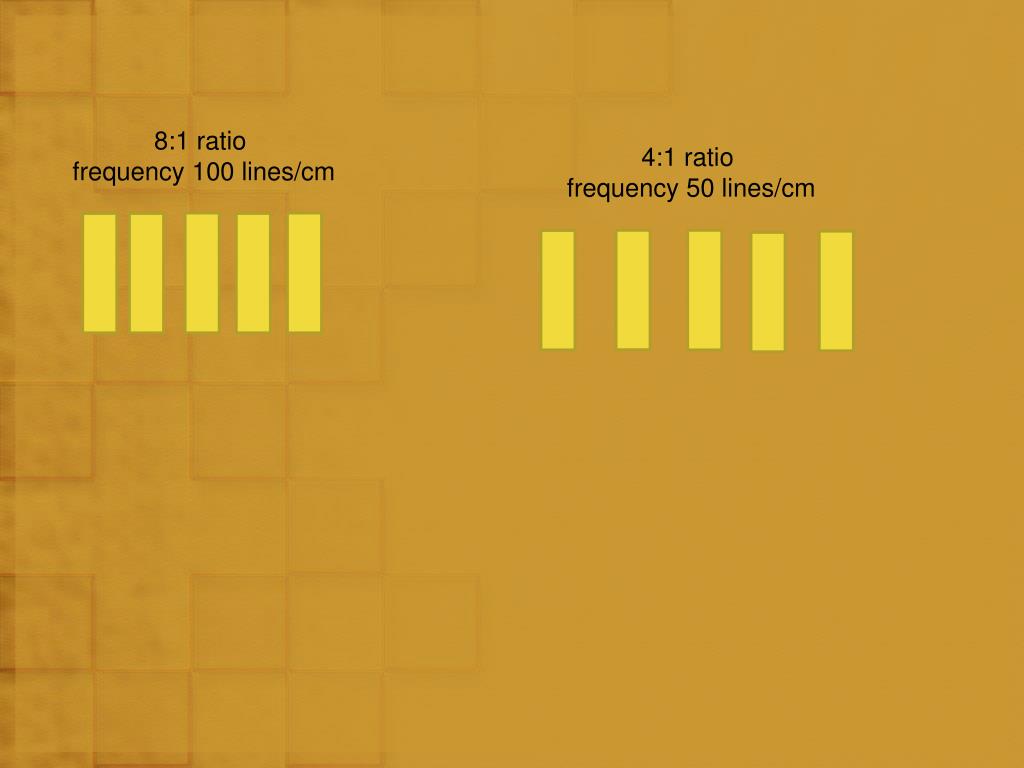
The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6). Thickness of the lead strip refers to that dimension of the lead which is at right angles to the primary radiation reaching the grid (Fig. 1). There are several qualities which determine the effectiveness of a grid.
What is a grid ratio?
The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6). Thickness of the lead strip refers to that dimension of the lead which is at right angles to the primary radiation reaching the grid (Fig. 1). There are several qualities which determine the effectiveness of a grid.
What is grid ratio in LED lighting?
The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6). Thickness of the lead strip refers to that dimension of the lead which is at right angles to the primary radiation reaching the grid (Fig. 1).
Do grids of different ratios produce different radiographs?
The present report describes an attempt to evaluate grids of different ratio with respect to their relative ability to produce good diagnostic radiographs and to correlate clinical and laboratory results. The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6).
What is a grid in radiology?
"A grid is a device that has very thin lead strips with radiolucent interspaces, intended to absorb scatter emitted from the patient." Ideally, grids would only absorb scattered photons and allow diagnostic photons to pass through.

What is grid in radiography?
The antiscatter grid plays an important role for enhancing image quality in projection radiography by transmitting a majority of primary radiation and selectively rejecting scattered radiation.
What is the best grid ratio?
In general, a 16:1 ratio grid will do the most good with equipment which can be used at kilovoltages above 100 KVP.
What is a high ratio grid?
Generally speaking, the higher the ratio of a grid, the more scattered radiation is absorbed (see Diagram). As grid ratio increases, the necessity of having the focused grid exactly centered and perfectly level under the x-ray tube becomes more and more important.
How do you find grid ratio?
GRD = HLS / DSWhere GRD is the Grid Ratio.HLS is the height of lead strips (in)DS is the distance between strips (in)
What does grid ratio mean?
The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6). Thickness of the lead strip refers to that dimension of the lead which is at right angles to the primary radiation reaching the grid (Fig.
What are the types of grid?
6 Examples of Grid SystemsBaseline Grid. A baseline grid is a dense grid of equally spaced horizontal lines that determine where text will sit. ... Column Grid. This is the most common type of grid used by designers. ... Modular Grid. ... Manuscript Grid. ... Pixel Grid. ... Hierarchical Grid.
What is the common range of grid ratios?
The grid ratio is the ratio of the height to the width of the interspaces (not the grid bars) in the grid. Grid ratios of 8:1, 10:1, and 12:1 are most. A 5:1 grid is most common for mammography. The grid is essentially a one-dimensional Collimator and increasing the grid ratio increases the degree of collimation.
How does a higher grid ratio affect density?
Using a grid removes much of the scatter radiation from reaching the screens and film. Because less x-ray photons reach the film, some density is lost (the film will be less dense, or lighter).
How does grid ratio affect exposure?
Image contrast can be improved by increasing the grid ratio by increasing the height of the lead strips or reducing the interspace. However, this leads to increased x-ray tube loading and radiation exposure to the patient.
What is the use of a grid?
Grids have so many uses, from helping to align and balance your designs, to helping you achieve cool effects like diagonal typography. They're really so much more than just some lines on a page, they structure, guide, and shape your design in a way that helps you to achieve your desired end result.
What is grid radius in radiology?
Grid-Radius is an NGDC term for a method for qualifying the data in grids. The method involves omitting grid cell data where the distance to actual data values is more than a specific distance, know as the Grid-Radius value.
What is air gap technique?
Air gap technique is a well-known method to reduce the amount of scattered x-ray radiation reaching the detector, thus reducing noise and improving image contrast. 1. It is rather commonly utilized instead of a conventional grid in plain radiography.
When should a grid be used in radiography?
Generally, grid use is recommended when the anatomy to be x-rayed exceeds 12 cm in thickness or if exposure settings exceed 70 kVp. There are two types of antiscatter grids: aluminum-interspaced, aluminum-covered grids and fiber-interspaced, carbon-covered grids.
Why are grids used in radiography?
Grids are placed between the patient and the x-ray film to reduce the scattered radiation reaching the detector (produced mainly by the Compton effect) and thus improve image contrast.
What is parallel grid?
Parallel Type Grids. A grid where the absorbing strips are parallel to each other in their longitudinal axis. Most linear grids are also focused (i.e. the strips are slightly tilted, converging at a line in space (the convergent line).
What is grid ratio?
The term grid ratio is defined as the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (6). Thickness of the lead strip refers to that dimension of the lead which is at right angles to the primary radiation reaching the grid (Fig. 1).
What determines the effectiveness of a grid?
There are several qualities which determine the effectiveness of a grid. The most important of these is the “cleanup”—the amount of secondary radiation removed—which should be high for maximum effectiveness.
What is the primary factor responsible for grid effectiveness?
One of the primary factors responsible for grid effectiveness is grid ratio , and it is with this factor that we are concerned here. The effect of different grid ratios on the quantity of secondary radiation reaching the film has been investigated in the laboratory with phantoms (2, 3, 5). We know of no investigation of grid ratios , however, based on an entirely clinical approach. The present report describes an attempt to evaluate grids of different ratio with respect to their relative ability to produce good diagnostic radiographs and to correlate clinical and laboratory results.
Who invented the radiographic grid?
Grids. "The radiographic grid was invented in 1913 by Gustave Bucky and continues to be the most effective means for limiting the amount of scatter radiation that reaches the IR.". "A grid is a device that has very thin lead strips with radiolucent interspaces, intended to absorb scatter emitted from the patient.".
Why do grids decrease density?
Grids decrease density because their lead strips absorb the scatter radiation which would otherwise reach the image. Grids increase contrast because their lead strips absorb the scatter radiation that creates a "fog" on the image. This allows for a more crisp image with higher contrast differences.
Do grids reduce noise?
Grids decrease noise. Fog or scatter radiation is a type of noise, and the lead strips clean up (absorb) that scatter radiation allowing for an image with less noise.
Do grids absorb photons?
Ideally, grids would only absorb scattered photons and allow diagnostic photons to pass through. However, this isn't the case and an increased technique, specifically mAs, is required when using grids. The amount of increase depends on the grid ratio. The multiplication of increase is also called the bucky factor.
What is the grid ratio?
GRID RATIO: The ratio of a grid is defined as the relation of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them. The higher the ratio of a grid the more scattered radiation is absorbed. As grid ratio increases, the necessity of having the focused grid exactly centered and perfectly level under the x-ray tube becomes more and more important. Also becomes more necessary to use the grid at its focal distance from the tube, instead of being able to use it through a range of distances.
What is a focused grid?
FOCUSED: a focused grid is one in which the lead strips are tilted progressively as they move away from center. Lines through each of these strips would converge at a point known as the grid focus.
