Groundwater overdraft is a specific condition in which extraction greatly exceeds the influxes of water (mainly recharge). This produces an unsustainable condition characterized by sustained declining water levels. Much like overdraft of a bank account, groundwater
Groundwater
Groundwater (or ground water) is the water present beneath Earth's surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fra…
What is groundwater overdraft and how can you avoid it?
Groundwater overdraft is a specific condition in which extraction greatly exceeds the influxes of water (mainly recharge). This produces an unsustainable condition characterized by sustained declining water levels. Much like overdraft of a bank account, groundwater overdraft is not a desirable state of affairs.
What is overdraft?
Overdraft. Overdraft occurs when, over a period of years, more water is pumped from a groundwater basin than is replaced from all sources – such as rainfall, irrigation water, streams fed by mountain runoff and intentional recharge. [See also Hydrologic Cycle .] While many of its individual aquifers are not overdrafted,...
What is a critically overdrafted basin?
Critically Overdrafted Basins. Overdraft occurs where the average annual amount of groundwater extraction exceeds the long-term average annual supply of water to the basin. Effects of overdraft result can include seawater intrusion, land subsidence, groundwater depletion, and/or chronic lowering of groundwater levels.
What are the effects of overdraft in California?
Effects of overdraft can include seawater intrusion, land subsidence, groundwater depletion, and/or chronic lowering of groundwater levels. In 2015, DWR evaluated California’s groundwater basins for conditions of critical overdraft.
What is groundwater overdraft?
Groundwater overdraft is a specific condition in which extraction greatly exceeds the influxes of water (mainly recharge). This produces an unsustainable condition characterized by sustained declining water levels. Much like overdraft of a bank account, groundwater overdraft is not a desirable state of affairs. Not only is it unsustainable in terms of management of the groundwater resource, but it also leads to long-lasting damages (a lot like what happens to your credit rating if your bank account is overdrafted!).
What happens when a groundwater aquifer is depressed?
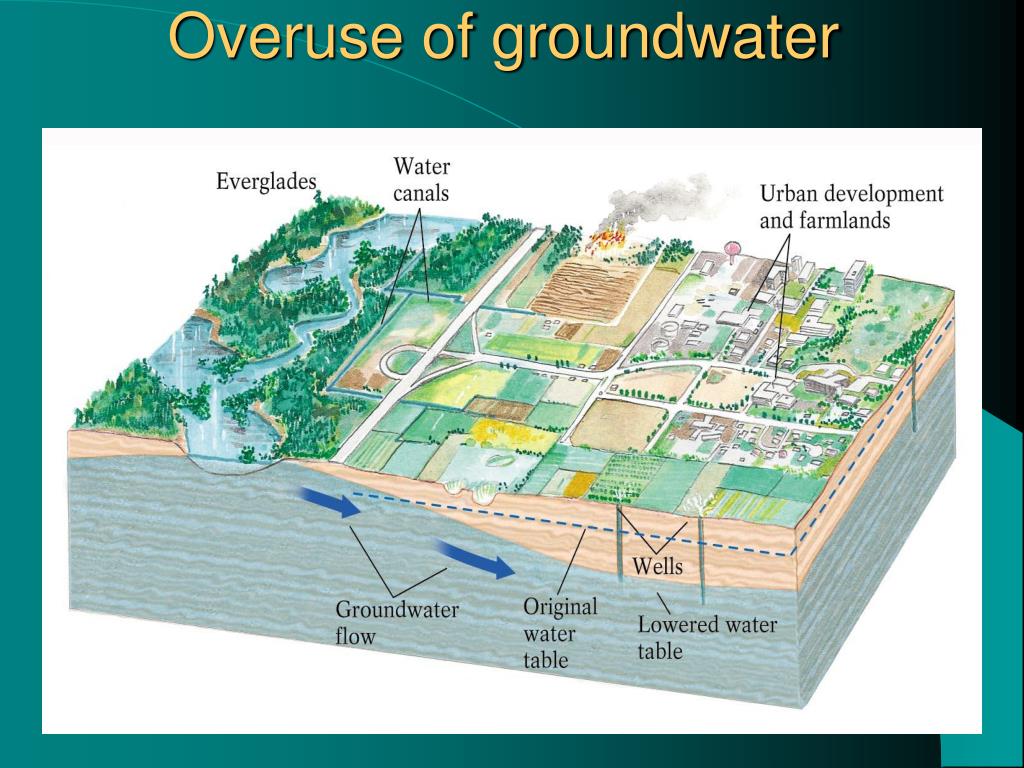
Depressurization of the aquifer, if large enough, may cause irreversible collapse and compaction. This reduces both storage (porosity) .and hydraulic conductivity. It can also lead to land subsidence, especially in cases where the magnitude of overdraft is large and the aquifer units are thick and highly compressible, as is common for unconsolidated or uncemented sedimentary aquifers. One well-known example of groundwater overdraft is the Central Valley of California (Figure 41). Another is the Ogallala aquifer, a major groundwater system spanning across eight states in the American Midwest (Figure 43; see The High Plains Aquifer section). Substantial overdraft and subsidence also occur in widespread areas of the southeastern U.S., the Gulf Coast, and parts of Arizona and Las Vegas (Figure 44).
What is overdraft in water?
Overdraft occurs when, over a period of years, more water is pumped from a groundwater basin than is replaced from all sources – such as rainfall, irrigation water, streams fed by mountain runoff and intentional recharge. [See also Hydrologic Cycle .]
Where does overdrafting occur?
Much of the overdrafting has occurred in the agricultural Central and San Joaquin valleys. As a result, overdrafting aquifers can have long-lasting consequences that are not resolved by a cloudburst or a flash flood.
How much water is recharged in California?
On average, California uses about 2 million acre-feet of groundwater more than is naturally or artificially recharged.
What are the effects of overdrafts?
Another less visible effect of overdraft and chronic declining groundwater levels is that many streams and rivers in the state have become disconnected from the underlying groundwater. This groundwater disconnection can result in the loss of wetlands and riparian habitat and can cause these streams and rivers to go dry periodically.
How much groundwater was lost in the Central Valley in 2010?
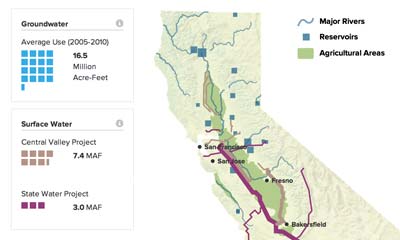
Elsewhere, the University of California Center for Hydrologic Modeling at the University of California, Irvine, estimated in 2011 that the groundwater loss in the Central Valley between October 2003 and March 2010 was 16.5 million acre-feet (20.3 cubic kilometers), which is more than half the size of Lake Mead – the nation’s largest reservoir with a 28.5 million acre-feet capacity – the third largest decline in 50 years.
How much water is pumped into the ground each year?
Some 15 million acre-feet of water is pumped each year on average. About 6.5 million acre-feet of water seeps back into the ground as irrigation water is spread onto fields or run through irrigation canals. An additional 7 million acre-feet of water is naturally recharged by rain and runoff percolating into the ground, ...
When does groundwater pumping go up?
In dry years, when there is less natural recharge and less surface water available, groundwater pumping typically goes up. In wet years, when more recharge occurs and more surface water is available, less groundwater pumping is needed.
What are the negative effects of groundwater overdraft?
Negative effects could include land subsidence, loss of groundwater quality, loss or decline of streamflows and riparian habitat, higher pumping costs and seawater intrusion.
What is it called when groundwater is pumping in excess of the rate of natural replenishment?
Pumping groundwater in excess of the rate of natural replenishment lowers the water table. Spread over a number of years without recovery, this is called “overdraft” – or “O.D.”
What is groundwater mining?
In fact, “groundwater mining” is exactly what experts call nonrenewable groundwater use, where farmers “mine” water to grow almonds, alfalfa or grapes. You could even say they are “mining” those commodities themselves.
How much groundwater was pumped in 2014?
In fact, 5 million acre feet of additional groundwater will be pumped in the Central Valley alone to make up for the 6.5 million acre feet in surface water reductions for agriculture in 2014. Even so, the economic loss for the Central Valley from this drought is expected to be $1.7 billion. Acre-Feet.
What happens to groundwater during drought?
During droughts, surface water availability can be sharply reduced, leaving water users to pump water from local wells. At times like these, groundwater can surge closer to 60% of water used statewide, and even higher in agricultural areas like the Central Valley.
Why is groundwater used?
Generally, though, groundwater is used alongside surface water to meet the state’s needs, which range from urban and industrial uses to irrigating roughly half the fruits and vegetables grown in the United States.
How much of the water is groundwater?
In normal and wet years, groundwater provides 30 to 40% of the water supply. It supplements surface water that is collected from snowmelt and rainfall then is stored and conveyed by a vast system of state and federal dams, reservoirs, and aqueducts. Click for an expanded view.
What is overdrafting in water?
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of the aquifer . Groundwater is the fresh water that can be found underground; it is also one of the largest sources. Groundwater depletion can be comparable to "money in a bank", The primary cause of groundwater depletion is pumping or the excessive pulling up ...
What happens when water is overdrafted?
The deeper the water is extracted from the worse the quality of the water becomes, which increases the cost of filtration. Saltwater intrusion is another consequence of overdrafting, leading to a reduction in water quality.
What happens when aquifers overdraw?
Some aquifers require a very long time to recharge and thus the process of overdrafting can have consequences of effectively drying up certain sub-surface water supplies. Subsidence occurs when excessive groundwater is extracted from rocks that support more weight when saturated.
How does groundwater affect the water table?
When drafting of water continues the cone of depression increases in width . The increase in width leads to the negative impacts caused by overdrafting, such as drop of the water table, land subsidence, and loss of surface water reaching the streams. In extreme cases the supply of water to naturally recharge the aquifers is pulled directly from streams and rivers, leading to depletion of water levels in streams and rivers. The depletion of water in rivers and streams has an effect on wildlife, as well as humans who might be using the water for other purposes.
How does aquifer recharge work?
Natural process of recharge is done through percolation of surface water. Artificial process of recharging the aquifer is through means of pumping reclaimed water from wastewater management projects directly into the aquifer. An example is the Orange County Water District in the State of California. This organization take waste water, treats it to a proper level, and then systematically pumps it back into the aquifers for artificial recharge.
How does aquifer drawdown affect sea level?
Aquifer drawdown or overdrafting and the pumping of fossil water may be a contributing factor to sea-level rise. By increasing the amount of moisture available to fall as precipitation, severe weather events are more likely to occur. To some extent moisture in the atmosphere accelerates the probability of a global warming event. The correlation coefficient is not yet scientifically determined.
What are the two types of aquifers?
There are two types of aquifers: confined and unconfined. In confined aquifers, there is an overbearing layer called aquitard, which contains impermeable materials through which groundwater cannot be extracted. In unconfined aquifers, there is no aquitard, and groundwater can be freely extracted from the surface.
What is the purpose of the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act?
The Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) directs the Department of Water Resources (DWR) to identify groundwater basins and subbasins in conditions of critical overdraft. As defined by SGMA, "A basin is subject to critical overdraft when continuation of present water management practices would probably result in significant adverse ...
What is SGMA data viewer?
The SGMA Data Viewer provides access to groundwater-related datasets, including the boundaries for critically overdrafted basins.
What are the effects of overdraft?
Effects of overdraft can include seawater intrusion, land subsidence, groundwater depletion, and/or chronic lowering of groundwater levels.
How much water was replenished by the Colorado Aqueduct?
During the first 35 years, the two agencies replenished more than 2 million acre-feet of water.
What was the name of the waterway that was built in 1928?
Bringing imported water to the region required a massive waterway that did not yet exist. In 1928, the Boulder Canyon Act authorized construction of Hoover Dam , Lake Mead, Imperial Dam, All-American Canal and the 123-mile Coachella Branch of the All-American Canal.
How much water has been replenished by the DWA?
CVWD and DWA's groundwater replenishment program has percolated billion gallons of water back into the aquifer. This has been possible thanks to a supply of imported water from the Sacramento Bay Delta and the Colorado River, as well as entitlements to captured snow melt from the San Gorgonio Mountains.
When was the Coachella Valley aquifer replenished?
The Coachella Valley’s earliest groundwater replenishment efforts in the 1910s involved capturing fast-moving flood waters during storms and using that flow to replenish the valley’s western aquifer at Windy Point, northwest of Palm Springs.
When did CVWD get irrigation water?
In 1919 , CVWD's directors approved contracts with the federal government for importation of Colorado River water into Coachella Valley for farm irrigation.
Is Coachella Valley in overdraft?
Consequently, the Coachella Valley groundwater basin is in overdraft;