
Full Answer
Is Hadoop the best big data tool?
- Hadoop Market Insights
- Hadoop Market Size and Forecast by Type
- Hadoop Market Size and Forecast, by Component
- Hadoop Market Size and Forecast, by Environment
- Hadoop Market Size and Forecast, by End-User
- Hadoop Market Size and Forecast, by Region
What is Hadoop and why it matters?
Hadoop What it is and why it matters. Hadoop is an open-source software framework for storing data and running applications on clusters of commodity hardware. It provides massive storage for any kind of data, enormous processing power and the ability to handle virtually limitless concurrent tasks or jobs.
How to collect big data into Hadoop?
- Hadoop is used for:
- Machine learning
- Processing of text documents
- Image processing
- Processing of XML messages
- Web crawling
- Data analysis
- Analysis in the marketing field
- Study of statistical data
How does Hadoop handle big data?
How does Hadoop handle Big Data? HDFS is made for handling large files by dividing them into blocks, replicating them, and storing them in the different cluster nodes. Thus, its ability to be highly fault-tolerant and reliable. HDFS is designed to store large datasets in the range of gigabytes or terabytes, or even petabytes.
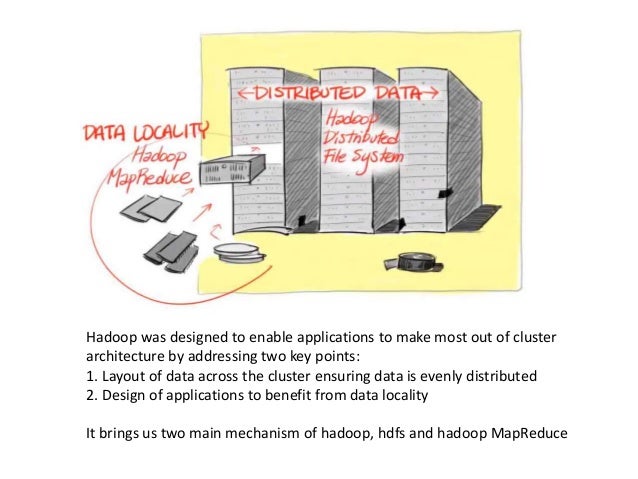
What is Hadoop database?
Hadoop is not a type of database, but rather a software ecosystem that allows for massively parallel computing. It is an enabler of certain types NoSQL distributed databases (such as HBase), which can allow for data to be spread across thousands of servers with little reduction in performance.
What is Hadoop stand for?
High Availability Distributed Object Oriented Platform.
What is difference between Hadoop and big data?
Big Data is treated like an asset, which can be valuable, whereas Hadoop is treated like a program to bring out the value from the asset, which is the main difference between Big Data and Hadoop. Big Data is unsorted and raw, whereas Hadoop is designed to manage and handle complicated and sophisticated Big Data.
Why Hadoop is used for big data?
Instead of relying on expensive, and different systems to store and process data, Hadoop enables distributed parallel processing of huge amounts of data across inexpensive, industry-standard servers that both store and process the data. With Hadoop, no data is too big data.
What are 3 main Vs of big data?
Dubbed the three Vs; volume, velocity, and variety, these are key to understanding how we can measure big data and just how very different 'big data' is to old fashioned data.
What is Hadoop example?
Examples of Hadoop Retailers use it to help analyze structured and unstructured data to better understand and serve their customers. In the asset-intensive energy industry Hadoop-powered analytics are used for predictive maintenance, with input from Internet of Things (IoT) devices feeding data into big data programs.
What are examples of big data?
Big data also encompasses a wide variety of data types, including the following:structured data, such as transactions and financial records;unstructured data, such as text, documents and multimedia files; and.semistructured data, such as web server logs and streaming data from sensors.
What type of data is big data?
Put simply, big data is larger, more complex data sets, especially from new data sources. These data sets are so voluminous that traditional data processing software just can't manage them. But these massive volumes of data can be used to address business problems you wouldn't have been able to tackle before.
What is the difference between Hadoop and Apache?
Apache Spark is an open-source distributed general-purpose cluster-computing framework. Spark provides an interface for programming entire clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance....Hadoop vs Apache Spark.FeaturesHadoopApache SparkMemory usageHadoop is disk-boundSpark uses large amounts of RAM8 more rows•Nov 23, 2021
Where is data stored in Hadoop?
Hadoop stores data in HDFS- Hadoop Distributed FileSystem. HDFS is the primary storage system of Hadoop which stores very large files running on the cluster of commodity hardware.
Is Hadoop a cloud?
The three different cloud computing architecture are : Public Cloud – operated by third-party cloud providers for example google cloud....Hadoop:S.No.Cloud ComputingHadoop7Computing behaviour like Performance, scalability are analysed.Processed data will be analysed and stored.7 more rows•May 5, 2020
What is the benefit of Hadoop?
Means Hadoop provides us 2 main benefits with the cost one is it's open-source means free to use and the other is that it uses commodity hardware which is also inexpensive. Hadoop is a highly scalable model. A large amount of data is divided into multiple inexpensive machines in a cluster which is processed parallelly.
What is Hadoop and how does it work?
Hadoop is an Apache open source framework written in java that allows distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. The Hadoop framework application works in an environment that provides distributed storage and computation across clusters of computers.
Is Hadoop is a programming language?
Hadoop is not a programming language. The term "Big Data Hadoop" is commonly used for all ecosystem which runs on HDFS. Hadoop [which includes Distributed File system[HDFS] and a processing engine [Map reduce/YARN] ] and its ecosystem are a set of tools which helps its large data processing.
What is Apache spark vs Hadoop?
Apache Spark — which is also open source — is a data processing engine for big data sets. Like Hadoop, Spark splits up large tasks across different nodes. However, it tends to perform faster than Hadoop and it uses random access memory (RAM) to cache and process data instead of a file system.
Is Hadoop a data warehouse?
Hadoop boasts of a similar architecture as MPP data warehouses, but with some obvious differences. Unlike Data warehouse which defines a parallel architecture, hadoop's architecture comprises of processors who are loosely coupled across a Hadoop cluster. Each cluster can work on different data sources.
Why is Hadoop useful?
The modest cost of commodity hardware makes Hadoop useful for storing and combining data such as transactional, social media, sensor, machine, scientific, click streams, etc. The low-cost storage lets you keep information that is not deemed currently critical but that you might want to analyze later.
How to get data into Hadoop?
Getting data into Hadoop 1 Use third-party vendor connectors (like SAS/ACCESS ® or SAS Data Loader for Hadoop ). 2 Use Sqoop to import structured data from a relational database to HDFS, Hive and HBase. It can also extract data from Hadoop and export it to relational databases and data warehouses. 3 Use Flume to continuously load data from logs into Hadoop. 4 Load files to the system using simple Java commands. 5 Create a cron job to scan a directory for new files and “put” them in HDFS as they show up. This is useful for things like downloading email at regular intervals. 6 Mount HDFS as a file system and copy or write files there.
Why is Hadoop used for analytics?
Because Hadoop was designed to deal with volumes of data in a variety of shapes and forms, it can run analytical algorithms. Big data analytics on Hadoop can help your organization operate more efficiently, uncover new opportunities and derive next-level competitive advantage. The sandbox approach provides an opportunity to innovate with minimal investment.
How does Hadoop help the IoT?
At the core of the IoT is a streaming, always on torrent of data. Hadoop is often used as the data store for millions or billions of transactions. Massive storage and processing capabilities also allow you to use Hadoop as a sandbox for discovery and definition of patterns to be monitored for prescriptive instruction. You can then continuously improve these instructions, because Hadoop is constantly being updated with new data that doesn’t match previously defined patterns.
What is Bloor Group's report on Hadoop?
That’s how the Bloor Group introduces the Hadoop ecosystem in this report that explores the evolution of and deployment options for Hadoop. It includes a detailed history and tips on how to choose a distribution for your needs.
What is Hadoop's most popular analytical use?
Building a recommendation engine in Hadoop. One of the most popular analytical uses by some of Hadoop's largest adopters is for web-based recommendation systems. Facebook – people you may know. LinkedIn – jobs you may be interested in. Netflix, eBay, Hulu – items you may want.
What is data lake?
Data lakes support storing data in its original or exact format. The goal is to offer a raw or unrefined view of data to data scientists and analysts for discovery and analytics. It helps them ask new or difficult questions without constraints. Data lakes are not a replacement for data warehouses.
What is Hadoop used for?
Analytics and big data. A wide variety of companies and organizations use Hadoop for research, production data processing, and analytics that require processing terabytes or petabytes of big data, storing diverse datasets, and data parallel processing.
What industries use Hadoop?
Companies in myriad industries—including technology, education, healthcare, and financial services —rely on Hadoop for tasks that share a common theme of high variety, volume, and velocity of structured and unstructured data.
Why is Apache Hadoop important?
Apache Hadoop was born out of a need to more quickly and reliably process an avalanche of big data. Hadoop enables an entire ecosystem of open source software that data-driven companies are increasingly deploying to store and parse big data.
How does Hadoop control costs?
Hadoop controls costs by storing data more affordably per terabyte than other platforms. Instead of thousands to tens of thousands of dollars per terabyte being spent on hardware, Hadoop delivers compute and storage on affordable standard commodity hardware for hundreds of dollars per terabyte.
Why is Hadoop data replicated across clusters?
In the Hadoop ecosystem, even if individual nodes experience high rates of failure when running jobs on a large cluster, data is replicated across a cluster so that it can be recovered easily should disk, node, or rack failures occur.
What is Hadoop Data File System?
Hadoop uses the HDFS (Hadoop Data File System) to divide the massive data amounts into manageable smaller pieces, then saved on clusters of community servers. This offers scalability and economy.
What are the components of Hadoop?
It is the most commonly used software to handle Big Data. There are three components of Hadoop. Hadoop HDFS - Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is the storage unit of Hadoop.
What is the name of the HDFS cluster?
Master and slave nodes form the HDFS cluster. The name node is called the master, and the data nodes are called the slaves. The name node is responsible for the workings of the data nodes. It also stores the metadata. The data nodes read, write, process, and replicate the data.
What is MapReduce in Hadoop?
Hadoop MapReduce is the processing unit of Hadoop. In the MapReduce approach, the processing is done at the slave nodes, and the final result is sent to the master node.
How is data stored in HDFS?
Data is stored in a distributed manner in HDFS. There are two components of HDFS - name node and data node. While there is only one name node, there can be multiple data nodes. HDFS is specially designed for storing huge datasets in commodity hardware.
What is the main element of big data?
Big Data refers to the massive amount of data that cannot be stored, processed, and analyzed using traditional ways. The main elements of Big Data are: Volume - There is a massive amount of data generated every second. Velocity - The speed at which data is generated, collected, and analyzed.
Is MapReduce a good program?
MapReduce is limited. Yes, it’s a great programming model, but MapReduce uses a file-intensive approach that isn’t ideal for real-time interactive iterative tasks or data analytics. Security is an issue. There is a lot of data out there, and much of it is sensitive.
Why is Hadoop useful?
The explosion of Big Data and data-collecting devices throughout business operations offers companies significant opportunities to innovate and succeed.
How was Hadoop developed?
Hadoop was born out of a need to process increasingly large volumes of Big Data and was inspired by Google’s MapReduce, a programming model that divides an application into smaller components to run on different server nodes.
What are the benefits of Hadoop?
Hadoop has five significant advantages that make it particularly useful for Big Data projects. Hadoop is:
HDFS
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) allows massive amounts of data to be stored in various formats and distributed across a Hadoop cluster. It provides high throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications that have large data sets.
MapReduce
The MapReduce module is both a programming model and a Big Data processing engine used for the parallel processing of large data sets. With MapReduce, the processing logic is sent to various slave nodes, and then the data is processed in parallel across these different nodes.
How is Hadoop used?
Companies in a range of industries ae using Hadoop for Big Data analytics to drive many benefits to their organizations.
HPE solutions for Hadoop
The HPE Elastic Platform for Big Data Analytics (EPA) is designed as a modular infrastructure foundation to address the need for a scalable multi-tenant platform. It does this by enabling independent scaling of compute and storage through infrastructure building blocks that are optimized for density and workloads.
What is Hadoop ecosystem?
The term Hadoop is a general term that may refer to any of the following: The overall Hadoop ecosystem, which encompasses both the core modules and related sub-modules. The core Hadoop modules, including Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS™), Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN), MapReduce, and Hadoop Common (discussed below).
What is Apache Hadoop?
What is Hadoop? Apache Hadoop is an open source, Java-based software platform that manages data processing and storage for big data applications. Hadoop works by distributing large data sets and analytics jobs across nodes in a computing cluster, breaking them down into smaller workloads that can be run in parallel.
What is the language used in Hadoop?
Other popular packages that are not strictly a part of the core Hadoop modules but that are frequently used in conjunction with them include: Apache Hive is data warehouse software that runs on Hadoop and enables users to work with data in HDFS using a SQL-like query language called HiveQL.
What are the challenges of Hadoop?
What are the challenges with Hadoop architectures? Complexity — Hadoop is a low-level, Java-based framework that can be overly complex and difficult for end-users to work with. Hadoop architectures can also require significant expertise and resources to set up, maintain, and upgrade.
When did Doug Cutting start Hadoop?
Inspired by Google’s MapReduce, a programming model that divides an application into small fractions to run on different nodes, Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella started Hadoop in 2002 while working on the Apache Nutch project. According to a New York Times article, Doug named Hadoop after his son's toy elephant.
Is Hadoop a philosophy?
Furthermore, in 2020, a leading Hadoop provider shifted its product set away from being Hadoop-centric, as Hadoop is now thought of as “ more of a philosophy than a technology .”. Lastly, 2021 has been a year of interesting changes.
Is Hadoop scalable?
Scalability — Unlike traditional systems that limit data storage, Hadoop is scalable as it operates in a distributed environment. This allowed data architects to build early data lakes on Hadoop. Learn more about the history and evolution of data lakes.

Purpose
- Hadoop is an open-source software framework for storing data and running applications on clusters of commodity hardware. It provides massive storage for any kind of data, enormous processing power and the ability to handle virtually limitless concurrent tasks or jobs.
Development
- As the World Wide Web grew in the late 1900s and early 2000s, search engines and indexes were created to help locate relevant information amid the text-based content. In the early years, search results were returned by humans. But as the web grew from dozens to millions of pages, automation was needed. Web crawlers were created, many as university-led research projects, a…
Projects
- One such project was an open-source web search engine called Nutch the brainchild of Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella. They wanted to return web search results faster by distributing data and calculations across different computers so multiple tasks could be accomplished simultaneously. During this time, another search engine project called Google was in progress. I…
Criticism
- MapReduce programming is not a good match for all problems. Its good for simple information requests and problems that can be divided into independent units, but it's not efficient for iterative and interactive analytic tasks. MapReduce is file-intensive. Because the nodes dont intercommunicate except through sorts and shuffles, iterative algorithms require multiple map-s…
Security
- Data security. Another challenge centers around the fragmented data security issues, though new tools and technologies are surfacing. The Kerberos authentication protocol is a great step toward making Hadoop environments secure.
Software
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) the Java-based scalable system that stores data across multiple machines without prior organization. Other software components that can run on top of or alongside Hadoop and have achieved top-level Apache project status include: Open-source software is created and maintained by a network of developers from around the world. It's free t…
Resources
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) provides resource management for the processes running on Hadoop.
Example
- MapReduce a parallel processing software framework. It is comprised of two steps. Map step is a master node that takes inputs and partitions them into smaller subproblems and then distributes them to worker nodes. After the map step has taken place, the master node takes the answers to all of the subproblems and combines them to produce output.
Goals
- SAS support for big data implementations, including Hadoop, centers on a singular goal helping you know more, faster, so you can make better decisions. Regardless of how you use the technology, every project should go through an iterative and continuous improvement cycle. And that includes data preparation and management, data visualization and exploration, analytical m…
Results
- And remember, the success of any project is determined by the value it brings. So metrics built around revenue generation, margins, risk reduction and process improvements will help pilot projects gain wider acceptance and garner more interest from other departments. We've found that many organizations are looking at how they can implement a project or two in Hadoop, wit…