What is HBs positive?
A positive HBsAg test result means that you are infected and can spread the hepatitis B virus to others through your blood. anti-HBs or HBsAb (Hepatitis B surface antibody) - A "positive" or "reactive" anti-HBs (or HBsAb) test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus.
Can HBs be cured?
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading the virus to others.
What does hep B virus do?
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It is a major global health problem. It can cause chronic infection and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Is hepatitis B virus life threatening?
It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Can I get hep B from my husband?
Anyone who lives with or is close to someone who has been diagnosed with chronic Hepatitis B should get tested. Hepatitis B can be a serious illness, and the virus can be spread from an infected person to other family and household members, caregivers, and sexual partners.
Can you live a long life with hepatitis B?
The most important thing to remember is that hepatitis B is a chronic medical condition (such as diabetes and high blood pressure) that can be successfully managed if you take good care of your health and your liver. You should expect to live a long, full life.
What is the main cause of hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Hepatitis B is spread when blood, semen, or other body fluids from a person infected with the virus enters the body of someone who is not infected.
What is the fastest way to cure hepatitis B?
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include: Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medicines — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth.
How does hepatitis B get transmitted?
You can get infected through contact with an infected person's blood or body fluids. The hepatitis B virus can be spread in the following ways: unprotected vaginal or anal sex. living in a household with a person with chronic (life-long) HBV infection.
Why hepatitis B is called silent killer?
It's pretty contagious and can be transmitted by blood or bodily fluids, so through things like sharing razors and toothbrushes. It's been called the silent killer because it is asymptomatic—you might have the virus but not know until it manifests itself until much later.
What should hepatitis B patients avoid?
Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking since both will hurt your liver, which is already being injured by the hepatitis B virus. Talk to your provider before starting any herbal remedies or vitamin supplements because some could interfere with your prescribed hepatitis B drugs or even damage your liver.
Who is at risk for hepatitis B?
Who Is Most Affected? In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
Can hepatitis B go away on its own?
If your provider determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your provider might recommend rest, proper nutrition, plenty of fluids and close monitoring while your body fights the infection.
Is cure for hepatitis B coming soon?
The future of treatment Dr Tavis says the cure to HBV is coming. “The feeling within the scientific community is that major improvements will happen somewhere in the next five to 10 years… [but] it isn't going to be one optimal combination at first.”
What is the fastest way to cure hepatitis B?
There is no cure or medication that totally eliminates the virus or makes HBsAg negative, but there is hope. There are approved therapies for hepatitis B and many in development. First-line therapies in the U.S. and globally are entecavir, tenofovir (TDF) and tenofovir (TAF), which are antivirals.
Can hepatitis B become negative?
About half of patients will no longer be infectious by 7 weeks after onset of symptoms, and all patients who do not remain chronically infected will be HBsAg-negative by 15 weeks after onset of symptoms (12).
How is HBV transmitted?
Sharing of needles : HBV is easily transmitted through needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
What is HBsAg?
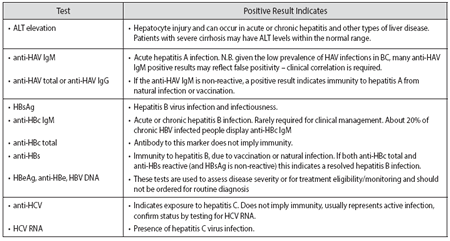
Hepatitis B. Symptoms. Causes. HBsAg. Screening Tests. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is a blood test ordered to determine if someone is infected with the hepatitis B virus. If it is found, along with specific antibodies, it means the person has a hepatitis B infection. If your blood is positive for HBsAg, ...
What does a hepatitis B test show?
The test can diagnose hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in the mother so steps can be taken to avoid infecting the baby during delivery. Being infected during infancy raises the likelihood that a child will develop chronic HBV and increases the risk of long-term illness or death. 6
What is the center of hepatitis B?
At the center of the hepatitis B virus is DNA , which contains the genes the virus uses to replicate itself.
What blood test is used to test for HBV?
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. 5 The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
How long does it take for hepatitis B to show symptoms?
Signs and symptoms of hepatitis B, ranging from mild to severe, usually appear about one to four months after you've been infected. 3 They may include:
How long does hepatitis B last?
For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosis—a condition that causes permanent scarring of the liver. 1 .
What Does Anti HBS Positive Mean?
When the anti-HBS result is obtained by laboratory test, a negative value means that there is no immunity against Hepatitis B virus in the body. The frequently asked question is “What does anti-HBS negative mean?”, can be answered in this way. It is quite normal for people who have not had hepatitis B vaccine to have anti-HBS. However, the fact that the negative Anti-HBS result does not mean that the person is not suffering from hepatitis B and is not affected by infection. In order to understand this condition, the level of HBsAg known as Hepatitis B surface antigen test should be checked. The negative value obtained by the anti-HBS level at 5.0 mIU/ml indicates that the body does not produce antibodies against the antigen identified as HBsAG on the surface of the Hepatitis B virus in the presence of Hepatitis B due to acute or chronic hepatitis. It is recommended that the person be vaccinated in case of anti-HBS negative value, which is an indication that the person has not been exposed to hepatitis B virus or had not been vaccinated before. Hepatitis B, which has a worldwide prevalence of 5%, can lead to fatal diseases such as liver cancer, and the patient is reminded that he can easily gain protection through vaccination.
What does a negative anti-HBS mean?
When the anti-HBS result is obtained by laboratory test, a negative value means that there is no immunity against Hepatitis B virus in the body. The frequently asked question is “What does anti-HBS negative mean?”, can be answered in this way.
What is the purpose of anti-HBS test?
The purpose of the Anti-HBS test is to determine whether if the person has been previously infected with or vaccinated for ...
What is anti-HBA?
Anti-HBA is a product of the body’s fight against Hepatitis B virus and heralds that the infection is completely cleared. These antibodies also ensure permanent immunity in the body. The body is then ready to produce antibodies against antigens present on the surface of the virus when it encounters the Hepatitis B virus.
What is the HBC IGG?
The Anti HBC IGG value, which does not give information about the recovery or chronicity of the disease, therefore has no meaning alone. These antibodies, which are developed by the body and form a defence mechanism, are called Anti-HBS. Anti-HBA is a product of the body’s fight against Hepatitis B virus and heralds that ...
What does it mean when you have HBsAG?
When the person encounters the hepatitis B virus, the immune system tries to detect and destroy the virus. To do this, it produces antibodies against the antigen identified as HBsAG on the surface of the Hepatitis B virus. The anti-HBC IGG positive value indicates that life-long immunity is achieved by the antibodies produced after ...
Is jaundice a type of hepatitis?
Hepatitis B or in another word jaundice is a type of virus sourced, liver disease. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) can transmit via blood, sexual intercourse or it can pass onto baby in mothers’ womb it can develop as acute or chronic.
How does HBV spread?
Sharing of needles. HBV easily spreads through needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood. Sharing IV drug paraphernalia puts you at high risk of hepatitis B. Accidental needle sticks.
What are the complications of HBV?
Complications. Having a chronic HBV infection can lead to serious complications, such as: Scarring of the liver (cirrho sis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. Liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B go undetected?
Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
How to avoid HBV?
Other ways to reduce your risk of HBV include: Know the HBV status of any sexual partner. Don't engage in unprotected sex unless you're absolutely certain your partner isn't infected with HBV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
What to do if you think you have hepatitis B?
If you think you have signs or symptoms of hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
Can hepatitis B be recovered?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
What is HBsAb in medical terms?
He was the founding editor and co-editor in chief of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. The hepatitis B surface antibody test (HBsAb), looks for antibodies that your immune system makes in response to the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B surface antibody is also referred to as anti-HBs and should not be confused with HBsAg, ...
What is HBsAb antibody?
The hepatitis B surface antibody test (HBsAb), looks for antibodies that your immune system makes in response to the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B surface antibody is also referred to as anti-HBs and should not be confused with HBsAg, which stands for hepatitis B surface antigen .
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody?
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity (called acquired immunity) is disease-specific.
What does it mean when HBsAb is positive?
When HBsAb is positive (antibodies are present) it usually means that you have recovered from a hepatitis B infection and have some immunity, or that you once received the hepatitis B vaccination and are immune. 2
Why do we do HBsAb?
Purpose of Test. This HBsAb test may be done to look for prior exposure to hepatitis B or whether your vaccination was successful. It may also be done if you have hepatitis B to see if you are recovering. While it is standard (since 1991) to vaccinate babies and children for hepatitis B, many adults were not vaccinated as children ...
What happens if you have a negative HBsAb?
If your HBsAb test is negative but other hepatitis tests are positive, your healthcare provider will need to evaluate you further. It could be that you have an active infection, which should be monitored closely, or that you have now developed a chronic hepatitis B infection.
How is HBsAb done?
How the Test Is Done. The HBsAb test is done by drawing a blood sample, which is sent to the lab for analysis. Your doctor will receive the results and evaluate them in light of your vaccination history, exposure risk, symptoms, and the results of other hepatitis tests.
What does a positive anti-HBs test mean?
A positive anti-HBs (or HBsAb) test result means you are “immune” and protected against the hepatitis B virus and cannot be infected. You are not infected and cannot spread hepatitis B to others.
What does HBsAg mean in blood work?
HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen) - A "positive" or "reactive" HBsAg test result means that the person is infected with hepatitis B.
What does it mean when you have a positive HBsAg?
A positive HBsAg test result means that you are infected and can spread the hepatitis B virus to others through your blood. anti-HBs or HBsAb (Hepatitis B surface antibody) - A "positive" or "reactive" anti-HBs (or HBsAb) test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus. This protection can be the result of receiving ...
Does the core antibody protect against hepatitis B?
The core antibody does not provide any protection against the hepatitis B virus (unlike the surface antibody described above). This test can only be fully understood by knowing the results of the first two tests (HBsAg and anti-HBs).
What is HBsAg?
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the body’s immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
How long does it take for HBsAg to appear in blood?
HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks. Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the body’s immune system to fight HBsAg.
What is a hepatitis B surface antibody test?
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
What is the purpose of a hepatitis B test?
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
What do hepatitis B test results mean?
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
What is the antibody for HBEAg?
Hepatitis B e-antibody (anti-HBe): Anti-HBe is an antibody to HBeAg. Lack of HBeAg and presence of anti-HBe in the serum is called seroconversion and may be an indication of resolving infection, but anti-HBe does not protect against HBeAg negative mutant viruses.
What is an IgG anti-HBC?
Hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg): HBeAg is a protein produced in the core or in the region near the core of the HB virus. A positive HBeAg result indicates active viral replication and infectivity.
What is hepatitis B?
Thus, “hepatitis B” refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
How to detect HBsAg?
The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus. The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or "HBcAg," which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
How many people have hepatitis B?
It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks and injures the liver. Two billion people (or 1 in 3) have been infected and about 300 million people are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection.
What is the function of hepatitis?
Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries. Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection. Releases a substance called "bile" to help digest food and absorb important nutrients. The word “hepatitis” actually means “inflammation” of the liver.
Where does the virus enter the cell?
The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), which serves as a template for viral replication (creation of new hepatitis B virus).

Overview
Prevention
- Most people infected with hepatitis B as adults recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have it. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading HBV to others.
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of hepatitis B, ranging from mild to severe, usually appear about one to four months after you've been infected. They may include:
Causes
- If you are positive for HBsAg, your blood and body fluids contain the virus and you can transmit it to others. Your body can produce antibodies to any of these antigens once you are exposed to the virus. These antibodies develop at different stages of the infection.
Diagnosis
- HBsAg is cleared within four to six months in self-limited infections (infections that resolve by themselves). It can be detected in the blood during both acute infections (infections that come on suddenly) and chronic infections (infections that last for longer than six months). In addition to the signs and symptoms that a patient has, additional antibodies can be tested to distinguish betwe…
Pathophysiology
- At the center of the hepatitis B virus is DNA, which contains the genes the virus uses to replicate itself. Surrounding the DNA is a protein called hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAG), which cannot be detected with blood tests. Surrounding this is HBsAg, which is actually part of the \"envelope\" that protects the virus from attack by the body's immune system. However, the immune system is go…