How many protons and neutrons does helium have?
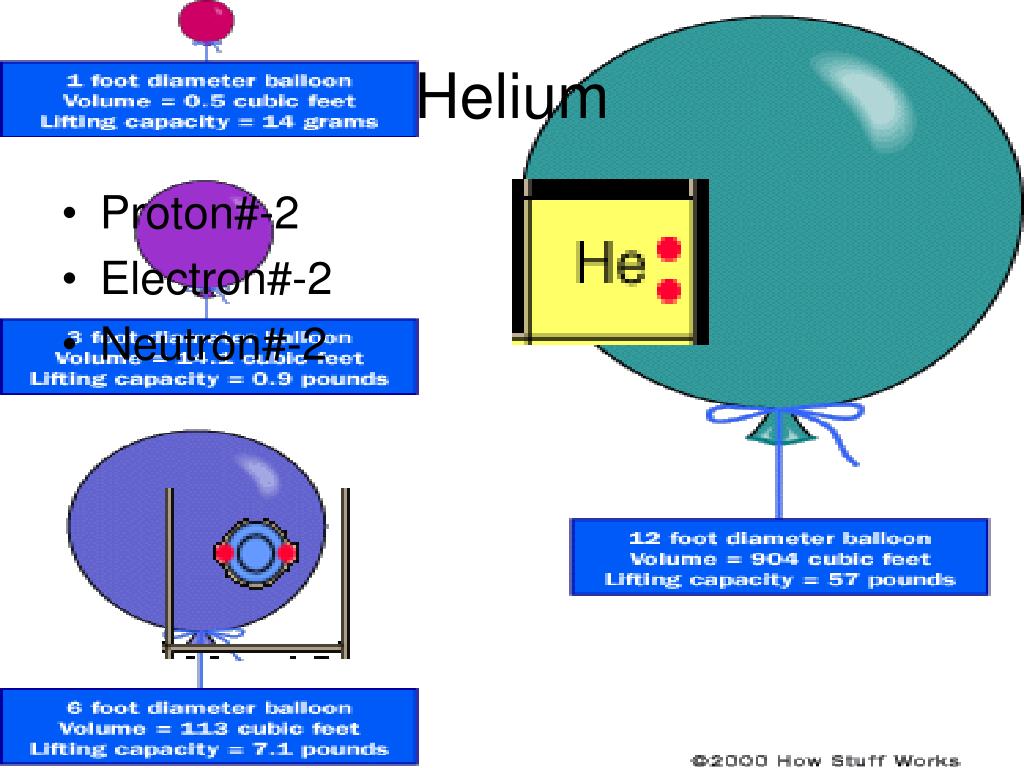
Most common helium isotope (helium 4) contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons in its nucleus. Every helium isotope has two protons (Z = 2) and A-Z neutrons.For example: helium-6 has 2 protons (otherwise it wouldn't be helium) and 6-2=4 neutrons. Why does a sodium atom have 12 neutrons?
Does helium have protons and neutrons in its nucleus?
The helium atom, in its most abundant form, is made of a nucleus comprised of two protons and two neutrons surrounded by two electrons. The electrons have a negative electric charge, while the protons are positive. Neutrons have no electric charge but are key to keep the protons from repelling each other.
What are the quantum numbers of helium?
Helium in its ground state has two electron, so with the same n, l and m(l) as hydrogen, it will have BOTH s = + 1/2 and s = - 1/2 spin quantum numbers. Z = 3 (Lithium): The n = 0 shell is filled the same way as Helium.
Does helium represent an atom or a molecule?
While the basic unit of an element is an atom, the basic unit of a compound is a molecule. The best-known example of a molecule is water, H 2 O, meaning that a molecule of water consists of two atoms of hydrogen bonded to a single atom of oxygen. The molecule in question here is helium hydride, HeH +. The plus sign indicates that this molecule is a positive ion, a molecule with a net positive charge.

What is helium neutron number?
Helium is composed of two electrons, two protons, and usually two neutrons. It is a colorless, odorless, inert gas.
What is the number of proton and neutron in helium?
NameHeliumNumber of Protons2Number of Neutrons2Number of Electrons2Melting Point-272° C9 more rows
Is helium a proton or neutron?
For hydrogen, the atomic mass is 1 because there is one proton and no neutrons. For helium, it is 4: two protons and two neutrons....2.1 Electrons, Protons, Neutrons, and Atoms.ElementHeliumSymbolHeAtomic No.2Number of Electrons in Each ShellFirst229 more columns
Does helium always have 4 protons?
The total spin of the helium-4 nucleus is an integer (zero), and therefore it is a boson (as are neutral atoms of helium-4)....Helium-4.GeneralNameshelium-4, He-4Protons (Z)2Neutrons (N)2Nuclide data7 more rows
What is the proton and electron of helium?
Helium is composed of two electrons, two protons, and usually two neutrons. It is a colorless, odorless, inert gas.
Does helium have 2 electrons?
In its neutral state, Helium has two electrons in orbit about the nucleus. Model of a helium atom's nucleus with two protons and two neutrons. Helium is a relatively inert element, which when in its neutral state is quite unreactive due to a filled outer shell of electrons.
Why does helium have a 2+ charge?
Helium has two protons and two neutrons in the nucleus. It has two electrons orbiting the nucleus. Here the charge of the protons is balanced by the charge of the electrons. There are two positive charges for the protons and two negative charges for the electrons.
How many protons are in an element?
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, let's use oxygen. According to the periodic table, oxygen has the atomic number eight. The atomic number is located above the element's symbol.
What's the charge of helium?
A helium nucleus has a charge +2. It has a big mass. Now we can see structure. A helium nucleus is made of two protons and two neutrons.
What has 4 protons and 5 neutrons?
BerylliumAtomic NumberNameProtonsNeutronsLithium34Beryllium45Boron56Carbon662 more rows•Sep 3, 2019
What has 5 protons and 5 neutrons?
BoronNameBoronNumber of Protons5Number of Neutrons6Number of Electrons5Melting Point2300.0° C9 more rows
What ion has 4 protons and 2 electrons?
berylliumFirst of all, beryllium has total how much electrons and protons, four electrons and four protons. And beryllium has two electrons in its outermost shell.
What element has 24 electrons 24 protons and 28 neutrons?
Chromium atomsChromium atoms have 24 electrons and 24 protons with the most abundant isotope having 28 neutrons.
How many protons does helium 7 have?
2 protonsProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons 7. A helium atom has 2 protons and 2 neutrons in the nucleus.
How do you find protons neutrons and electrons?
To calculate the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom, use its atomic number and mass number: number of protons = atomic number. number of electrons = atomic number. number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number.
Is the mass of a proton 1?
Protons are found in the nucleus of the atom. This is a tiny, dense region at the center of the atom. Protons have a positive electrical charge of one (+1) and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is about 1.67×10−27 kilograms.
How many protons does helium have?
Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He.
How many protons does nitrogen have?
Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 which means there are 7 protons and 7 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Nitrogen is N.
How many electrons does neon have?
Neon is a chemical element with atomic number 10 which means there are 10 protons and 10 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Neon is Ne.
How are atoms determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
What is the most common type of boron?
There are over 100 different borate minerals, but the most common are: borax , kernite, ulexite etc. Natural boron consists primarily of two stable isotopes, 11B (80.1%) and 10B (19.9%). In nuclear industry boron is commonly used as a neutron absorber due to the high neutron cross-section of isotope 10B.
Where is beryllium found?
Beryllium is a hard, grayish metal naturally found in mineral rocks, coal, soil, and volcanic dust . The commercial use of beryllium requires the use of appropriate dust control equipment and industrial controls at all times because of the toxicity of inhaled beryllium-containing dusts that can cause a chronic life-threatening allergic disease in some people called berylliosis.
How many protons does helium have?
Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He.
What is the mass number of helium?
Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Helium are 3; 4.
How many electrons does neon have?
Neon is a chemical element with atomic number 10 which means there are 10 protons and 10 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Neon is Ne.
How many protons and electrons are in hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H.
How many protons does nitrogen have?
Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 which means there are 7 protons and 7 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Nitrogen is N.
How are atomic nuclei determined?
Properties of atomic nuclei (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). It must be noted, especially nuclear cross-sections may vary by many orders from nuclide with the neutron number N to nuclide with the neutron number N+1. For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable.
What is the atomic mass of an atom?
The atomic mass is the mass of an atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance.
How many electrons are in helium?
In the perspective of quantum mechanics, helium is the second simplest atom to model, following the hydrogen atom. Helium is composed of two electrons in atomic orbitals surrounding a nucleus containing two protons and (usually) two neutrons. As in Newtonian mechanics, no system that consists of more than two particles can be solved with an exact analytical mathematical approach (see 3-body problem) and helium is no exception. Thus, numerical mathematical methods are required, even to solve the system of one nucleus and two electrons. Such computational chemistry methods have been used to create a quantum mechanical picture of helium electron binding which is accurate to within < 2% of the correct value, in a few computational steps. Such models show that each electron in helium partly screens the nucleus from the other, so that the effective nuclear charge Z which each electron sees, is about 1.69 units, not the 2 charges of a classic "bare" helium nucleus.
What is the element helium?
edit. | references. Helium (from Greek: ἥλιος, romanized : helios, lit. 'sun') is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas, the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table.
What is the nucleus of helium 4?
The helium atom. Depicted are the nucleus (pink) and the electron cloud distribution (black). The nucleus (upper right) in helium-4 is in reality spherically symmetric and closely resembles the electron cloud, although for more complicated nuclei this is not always the case.
Why is helium used in diving?
Helium as a breathing gas has no narcotic properties, so helium mixtures such as trimix, heliox and heliair are used for deep diving to reduce the effects of narcosis, which worsen with increasing depth. As pressure increases with depth, the density of the breathing gas also increases, and the low molecular weight of helium is found to considerably reduce the effort of breathing by lowering the density of the mixture. This reduces the Reynolds number of flow, leading to a reduction of turbulent flow and an increase in laminar flow, which requires less work of breathing. At depths below 150 metres (490 ft) divers breathing helium–oxygen mixtures begin to experience tremors and a decrease in psychomotor function, symptoms of high-pressure nervous syndrome. This effect may be countered to some extent by adding an amount of narcotic gas such as hydrogen or nitrogen to a helium–oxygen mixture.
How many units does each electron see in helium?
Such models show that each electron in helium partly screens the nucleus from the other, so that the effective nuclear charge Z which each electron sees, is about 1.69 units, not the 2 charges of a classic "bare" helium nucleus.
What are the two phases of helium?
In scientific research, the behavior of the two fluid phases of helium-4 (helium I and helium II ) is important to researchers studying quantum mechanics (in particular the property of superfluidity) and to those looking at the phenomena, such as superconductivity, produced in matter near absolute zero .
Why is helium used in chromatography?
Because of its inertness, thermally and calorically perfect nature, high speed of sound, and high value of the heat capacity ratio, it is also useful in supersonic wind tunnels and impulse facilities.
What is the mass of helium?
Everyone learns about Helium in school. It is the second element in the periodic table having 2 protons, 2 neutrons and 2 electrons - having an atomic mass of 4. But another form of Helium has been in the news lately and it is called Helium-3. Helium-3, also written as 3 He, is a light isotope of helium having 2 protons but only one neutron and an atomic mass of 3. The existence of Helium-3 was first proposed in 1934 by the Australian nuclear physicist Mark Oliphant. Helium-3 was originally thought to be a radioactive isotope until it was found in samples of natural helium,, taken both from the terrestrial atmosphere and from natural gas wells. Other than 1H, helium-3 is the only stable isotope of any element with more protons than neutrons. Its presence is rare on Earth, it is sought after for use in nuclear fusion research, and it is abundant in the moon's soil.
How much Helium-3 is on the moon?
Some estimates suggest there are at least 1.1 million metric tons of helium-3 on the lunar surface, enough to power human energy needs for up to 10,000 years.
What is the reality of using Helium 3?
The reality is not so clear-cut. The most advanced fusion programs in the world are inertial confinement fusion (such as National Ignition Facility and magnetic confinement fusion (such as ITER and other. In the case of the former, there is no solid roadmap to power generation. In the case of the latter, commercial power generation is not expected until around 2050. In both cases, the type of fusion discussed is the simplest: Deuterium-Tritium fusion. The reason for this is the very low Coulomb barrier for this reaction; for D+3He, the barrier is much higher, and it is even higher for 3He–3He. The immense cost of reactors like ITER and National Ignition Facility are largely due to their immense size, yet to scale up to higher plasma temperatures would require reactors far larger still. The 14.7 MeV proton and 3.6 MeV alpha particle from D–3He fusion, plus the higher conversion efficiency, means that more electricity is obtained per kilogram than with D-T fusion (17.6 MeV), but not that much more. As a further downside, the rates of reaction for helium-3 fusion reactions are not particularly high, requiring a reactor that is larger still or more reactors to produce the same amount of electricity.
What is nuclear fusion?
Nuclear fusion makes use of the same energy source that fuels the Sun and other stars. Unlike nuclear fission it does not produce the radioactivity and nuclear waste that is the by-product of current nuclear fission power generation.
How much energy is generated by fission?
The fission of one atom of U-235 generates 202.5 MeV = 3.24 × 10 −11 J, which translates to 19.54 TJ/mol , or 83.14 TJ/kg. This is around 2.5 million times more than the energy released from burning coal. When 23592 U nuclides are bombarded with neutrons, one of the many fission reactions that it can undergo is the following.
What reaction did Uranium 235 undergo?
FISSION REACTION OF URANIUM 235 BOMBRADED BY NEUTRONS:
When was helium 3 discovered?
The existence of Helium-3 was first proposed in 1934 by the Australian nuclear physicist Mark Oliphant. Helium-3 was originally thought to be a radioactive isotope until it was found in samples of natural helium,, taken both from the terrestrial atmosphere and from natural gas wells.
