
What's the difference between heparin and warfarin?
Summary of difference between Heparin and Warfarin Heparin and warfarin are both used as anticoagulants, in order to decrease the development of blood clots. Heparin is a direct anticoagulant. ... Warfarin is an indirect anticoagulant. ... The low dose of both anticoagulants can cause thrombosis, while overdose causes hemorrhages. More items...
Why is heparin and warfarin given together?
Warfarin and heparin are used together because it takes 5 to 7 days for the effect of warfarin to manifest. Heparin is fast-acting. Once the warfarin because active, heparin is discontinued. Warfarin often comes in the form of tablets, while heparin comes in the form of injectable, which is injected intramuscularly. Patients receiving heparin must be closely monitored, and it is only used in the inpatient settings.
Is there a safe dose of warfarin?
Well yes there is a safe dose of warfarin, zero mg is safe. Just like anything in life there are consequences of our actions. Instead of looking at the safe doses we start out in the scientific field by looking at the lethal doses in rats/mice and other non-human subjects.
What painkillers to take with warfarin?
When you are taking warfarin, paracetamol is the best painkiller to take. You should not experience a significant effect from paracetamol when you take it occasionally. Can You Take Tylenol Or Ibuprofen With Warfarin? It is generally considered safe to use acetaminophen and warfarin together.

Why do we give heparin with warfarin?
Warfarin works by slowing down the process in the liver that uses vitamin K to make certain proteins (clotting factors) that cause clotting. Because it may take several days before warfarin becomes completely effective, heparin or LMWH is given until the warfarin is working.
What is heparin used for?
Heparin is used to prevent or treat certain blood vessel, heart, and lung conditions. Heparin is also used to prevent blood clotting during open-heart surgery, bypass surgery, kidney dialysis, and blood transfusions.
Are heparin and warfarin blood thinners?
There are different types of blood thinners: Anticoagulants, such as heparin or warfarin (also called Coumadin), slow down your body's process of making clots.
What is the function of warfarin?
Warfarin is used to prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger in your blood and blood vessels. It is prescribed for people with certain types of irregular heartbeat, people with prosthetic (replacement or mechanical) heart valves, and people who have suffered a heart attack.
Is heparin a blood thinner?
Heparin is in a class of medications called anticoagulants ('blood thinners'). It works by decreasing the clotting ability of the blood.
Is heparin a strong blood thinner?
Heparin. Heparin is a strong, fast-acting anticoagulant (blood thinner). Heparin is given through a needle inserted in a vein (IV), but can also be given by injection under the skin. IV heparin works within minutes, and is usually given in the hospital.
What is the safest blood thinner to use?
For instance, apixaban was associated with the lowest risk of major bleeding in a 2016 study published in the journal Chest, and the lowest risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in elderly adults compared with dabigatran and rivaroxaban in a study published in the journal Gastroenterology in 2017.
Can heparin cause blood clots?
For some people, heparin triggers their immune system and causes a reaction where antibodies form and activate platelets -- tiny blood cells that clump together to form clots and stop bleeds in your body. That can make blood clots more likely.
What are the side effects of heparin?
Side EffectsAbdominal or stomach pain or swelling.back pain or backaches.bleeding from the gums when brushing teeth.blood in the urine.coughing up blood.headaches, severe or continuing.heavy bleeding or oozing from cuts or wounds.joint pain, stiffness, or swelling.More items...•
What are warfarin side effects?
What are the side effects of warfarin?Severe bleeding, including heavier than usual menstrual bleeding.Red or brown urine.Black or bloody stool.Severe headache or stomach pain.Joint pain, discomfort or swelling, especially after an injury.Vomiting of blood or material that looks like coffee grounds.Coughing up blood.More items...
What foods affect warfarin?
Avoid or drink only small amounts of these when taking warfarin: Cranberry juice. Grapefruit juice. Alcohol....Vitamin K-rich foods include:Kale.Spinach.Brussels sprouts.Collard greens.Mustard green.Turnip greens.Swiss chard.Broccoli.More items...
How long can you be on warfarin?
If you take warfarin to reduce your risk of having a blood clot in future or because you keep getting blood clots, it's likely your treatment will be for longer than 6 months, maybe even for the rest of your life.
Will heparin dissolve blood clots?
Heparin thins the blood, but newer drugs that actively break up the clots (thrombolytics) may act more quickly and may be more effective. These newer drugs include streptokinase, urokinase, and recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. The major complication of this treatment is bleeding.
Why is heparin given in hospital setting?
Use in the Hospital To prevent the formation of the blood clots that can form as a complication of staying in bed for prolonged periods of time: A low daily dose of heparin is typically injected under the skin to help prevent the formation of deep venous thromboses (DVT) in the veins of the legs, thighs, and pelvis.
What's the most common side effect of heparin?
The more common side effects of this drug include: bruising more easily. bleeding that takes longer to stop. irritation, pain, redness, or sores at the injection site.
What type of drug is heparin?
GlycosaminoglycanHeparin / ClassificationGlycosaminoglycans or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. Wikipedia
Heparin vs Warfarin
The main difference between Heparin and Warfarin is the process of intake if both medications differ from each other. The Heparin drugs are taken through the veins of the patient, with the help of an injection. And on the other hand, the Warfarin medications are directly taken orally.
What is Heparin?
Heparin is one of the leading anticoagulants that is used for thinning the blood when an abnormality or any disease is detected in a human body. Generally, Heparin is considered to be a direct anticoagulant. It is termed a direct anticoagulant because it is absorbed by the body directly from the veins, which makes the process quick and easy.
What is Warfarin?
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that is used to stop the blood from clogging that is caused by various diseases. The chemical formula that represents Warfarin is C¹⁹H¹⁶O⁴. It has both advantages as well as many disadvantages. Even though Warfarin is widely used in many cases but it is restricted in some specific cases such as pregnancy.
Main Differences Between Heparin and Warfarin
Generally, Heparin is considered to be a direct anticoagulant. On the other hand, generally, Warfarin is considered to be an indirect anticoagulant.
Conclusion
Some medications are widely used for thinning the blood, because of certain diseases or abnormal symptoms that can cause strokes and these medications are known as anticoagulants. Here, Heparin and Warfarin are two variants of anticoagulants.
What is indirect thrombin inhibitor?
Family Name: indirect thrombin inhibitors. Enhances the activity of antithrombin III, which will inhibit thrombin and the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Work on intrinsic pathway of coagulation: this pathway is normally activated by internal vascular trauma. Onset: Fast.
How long does it take for a vitamin K antagonist to work?
Since it’s a Vitamin K antagonist, it will work to inhibit clotting factors from using Vitamin K. Works on extrinsic pathway of coagulation: this pathway is normally activated by external trauma. Onset: Slow (takes about 3-5 days for patient to become therapeutic) Duration: Long…stays in the system for days.
Can you take both heparin and heparin at the same time?
A patient can be on both of these medications at the same time until the patient’s INR level becomes therapeutic….then the Heparin will be discontinued.
Is heparin weight based?
It’s weight-based (always obtain a current and accurate weight for proper dosing). Here are some Heparin drip calculations for practice.
Can you drink alcohol while taking Warfarin?
NO alcoholic beverage because this interferes with Warfarin.
Does heparin increase osteoclast activity?
Osteoporosis with long term/high doses of Heparin….because Heparin increases osteoclast activity and decreases osteoblast activity.
What is the use of warfarin and heparin?
Heparin and warfarin: use of anticoagulants in the prevention and treatment of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
How long after stopping heparin can you take warfarin?
After stopping heparin, oral anticoagulation with warfarin should be continued for six weeks. Then, in the absence of a previous history of venous thromboembolism or a known predisposing condition, it is safe to abruptly discontinue anticoagulation in most patients.
How long does heparin last?
Heparin is generally continued for seven to ten days. During this time warfarin is generally begun, and it is important to continue the patient on warfarin for five to seven days while the patient is receiving intravenous heparin therapy.
Is heparin effective for pulmonary embolism?
It has been shown that in many cases, low-dose heparin is effective in the prevention of both venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. However, once venous thrombosis has already occurred, it is necessary to use full-dose heparin, preferably by the continuous intravenous route, with maintenance of the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) ...
What is heparin used for?
Heparin can be used for things such as a stroke, a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a pulmonary embolism (PE) or other thromboembolic disorders that require fast anticoagulation. It is also used to prevent blood clotting during open-heart surgery, bypass surgery, kidney dialysis and blood transfusions.
How does heparin work?
Heparin works by activating antithrombin, which is a naturally occurring protein in the bloodstream that prevents us from clotting too much. It blocks our blood clotting mechanism by inactivating the major clotting protein thrombin. It prevents new clots from forming and existing clots from getting any bigger, but it will not break down clots.
What are the two medications that prevent blood clots?
In this article, we cover two important cardiovascular medications - heparin and warfarin, both of which are used to treat and prevent blood clots from forming in the body. The Nursing Pharmacology video series follows along with our Pharmacology Flashcards, which are intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI, and NCLEX.
What is the antidote for heparin?
Antidote for heparin. Protamine sulfate is a medication used to reverse and counteract the effects of heparin. Protamine sulfate is a basic protein derived from fish sperm that binds to heparin to form a stable salt.
How is heparin administered?
Heparin is a drug that can be administered through an IV or through a subcutaneous injection. A subcutaneous injection is a shot given directly into the fat layer between the skin and muscle and allows a drug to be absorbed slowly over a period of time.
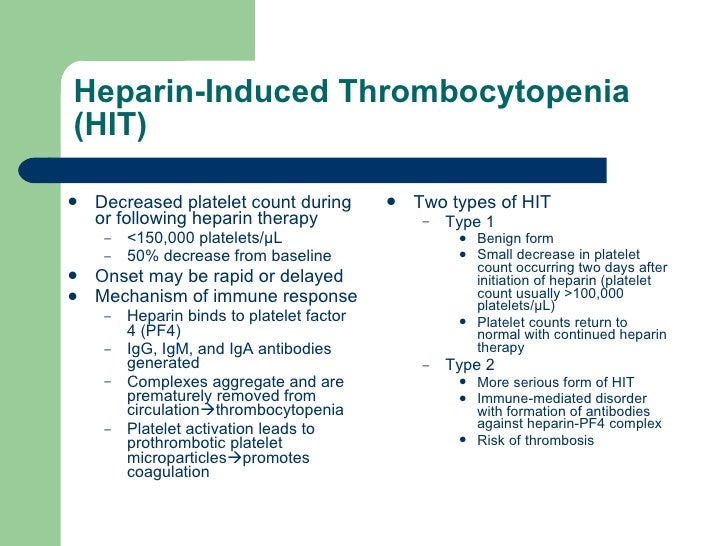
Does heparin cause platelet count to decrease?
Heparin can also cause something called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) which leads to decreased platelet counts. HIT is marked by a 50%+ reduction of platelets from the patient's baseline, so we need to monitor their thrombocyte count closely. HIT is a very serious complication where a patient forms microclots.
Does heparin therapy need to be monitored?
A patient receiving heparin therapy will need to be monitored for bleeding.
Why is heparin given in combination with warfarin?
Heparin is administered in combination with warfarin the first week, because haparin potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin, in order to protect the patient against the increased risk of thrombosis, induced by the effect of warfarin on protein C. Cite. 9th May, 2018. Omer Iqbal.
Why is heparin given in DVT?
in acute DVT heparin is given to prevent propagation of the clot. In the acute settings the patient is usually admitted in the hospital and heparin is given intravenously for immediate action under nursing supervision. When the patient is discharged from the hospital warfarin is given for convenience since it could be given orally. Furthermore, warfarin requires time for initiation of its action And hence should be given while the patient is still in the hospital And is under heparinization.
What is LMWH in medicine?
If for any reason the patient or the physician decides not to use warfarin, then the patient receives heparin while in the hospital and when the patient is discharged, the physician prescribes LMWH (Low Molecular Weight Heparins) to be given subcutaneously. There are at least 4 different LMWHs which are approved by the United States FDA.
How long does it take for warfarin to take effect?
warfarin takes a few days for its effect to take effect (which is why it’s bridged with heparin), it must be monitored with INR regularly bc its pharmacodynamics vary by diet/comorbidities, and it can be reversed with pcc (prothrombin complex concentrate) or vitamin k. Cite. 2 Recommendations. 10th May, 2018.
How long does it take for vitamin K to be reduced after warfarin?
Steady state conditions regarding the plasma concentration of all vitamin K dependent proteins are achieved after approximately one week of warfarin treatment.
Is Vit K dependent coagulation variable?
Johannes is absolutely right. The half life of Vit K dependent coagulation is variable. For example factors II (100hrs), FVII (5 Hrs), FIX (20 Hrs), FX (65 Hrs) and inhibitory proteins, Protein C (6 Hrs) and protein S (60 Hrs). Since the half life of protein C and FVII are relatively shorter it takes at least a week's time to achieve steady state concentrations. Thus Heparin should be given first because it is given intravenously and has an immediate effect. Heparin is a conventional anticoagulant drug. Heparin augments the activity of antithrombin 1000 folds and helps in the prevention of the propagation of the clot and also prevents future formation of the clot. As long as the patient is in the hospital the patient continues to receive heparin. Before the patient needs to be discharged and while still in the hospital the patient receives heparin and warfarin together and when the INR is therapeutic the patient is discharged and then continues warfarin.
Is warfarin cheaper than heparin?
I believe warfarin needs time to build up in system to therepeutic dose while heparin is pretty quick. Warfarin is much cheaper then heparin (especially low molecular weight varieties).
How to reduce the effect of warfarin?
One nutrient that can lessen warfarin's effectiveness is vitamin K. It's important to be consistent in how much vitamin K you get daily. The adequate intake level of vitamin K for adult men is 120 micrograms (mcg). For adult women, it's 90 mcg. While eating small amounts of foods that are rich in vitamin K shouldn't cause a problem, avoid consuming large amounts of certain foods or drinks, including: 1 Kale 2 Spinach 3 Brussels sprouts 4 Collards 5 Mustard greens 6 Chard 7 Broccoli 8 Asparagus 9 Green tea
What is the best vitamin to take while taking warfarin?
It's important to pay attention to what you eat while taking warfarin. One nutrient that can lessen warfarin's effectiveness is vitamin K. It's important to be consistent in how much vitamin K you get daily. The adequate intake level of vitamin K for adult men is 120 micrograms (mcg). For adult women, it's 90 mcg.
Is there a diet for warfarin?
Warfarin is a blood-thinning medication that helps treat and prevent blood clots. There is no specific warfarin diet. However, certain foods and beverages can make warfarin less effective in preventing blood clots. It's important to pay attention to what you eat while taking warfarin.
Anticoagulant Overview
Therapeutic Uses
- These medications prevent or treat blood clots in those with DVTs (Deep Vein Thrombosis), PEs (Pulmonary Embolisms), and A-fib, which is a dysrhythmia that causes blood to accumulate in the heart's chambers, causing blood clots. It also helps prevent clots such as DVTs and PEs postoperatively, meaning clients who just got out of really long surgeries are at increased risk fo…
Medication Names
- All right. Let's dive into the medication names. The brand name for Warfarin is Coumadin. Heparin is a little bit more difficult because it's available as Heparin sodium and something else called Low Molecular Weight Heparin. You'll see it written as LMWH, also called fractionated Heparin. An example of a Low Molecular Weight Heparin is enoxaparin, brand name Lovenox. Low molecula…
Key Differences Between Heparin and Warfarin
- Let's dive into the key differences between these two medications. Heparin can be given intravenously or subcutaneously. However, Heparin can not be given orally because Heparin is inactivated by gastric acids in the stomach. Warfarin can be given orally or intravenously, but it's most commonly given orally. The onset of these medications are very ...
Monitoring
- Now for monitoring of these medications. So many students get confused with this topic, but I'm going to break it down into simple terms. Heparin is measured with something called aPTT, and Warfarin is measured with something called INR. You can remember Heparin is measured with aPTT because Heparin has a P in it, and Warfarin does not. aPTT stands for Activated Partial Th…
Antidotes
- Each medication has an antidote. You would give this antidote if aPTT or INR exceeds the therapeutic level or if there's evidence of bleeding. The antidote for Heparin is protamine sulfate. You can remember this by the 💡memory trick: You will need HELP from a PRO to stop bleeding out. The antidote for Warfarin is Vitamin K. You can remember this by the 💡memory trick: During WAR…
Patient Teaching
- Let's talk about some patient teaching while a patient is on Warfarin, you want to educate your patient to be consistent with their Vitamin K intake. Vitamin K foods include green leafy vegetables like kale, spinach, and liver. Think about this: I just said the antidote for Warfarin was Vitamin K. So if the patient consumes too much Vitamin K, it's like they're consuming the antidot…
Review
- OK, let's review the key differences. Heparin is given IV or SubQ, It cannot be given PO. Warfarin is most commonly given PO. Heparin is safe to give during pregnancy while Warfarin is teratogenic and should be avoided during pregnancy. Heparin’s onset is rapid while Warfarin’s onset is slow. Heparin is monitored with aPTT and Warfarin is monitored with INR. The antidote for Heparin is …