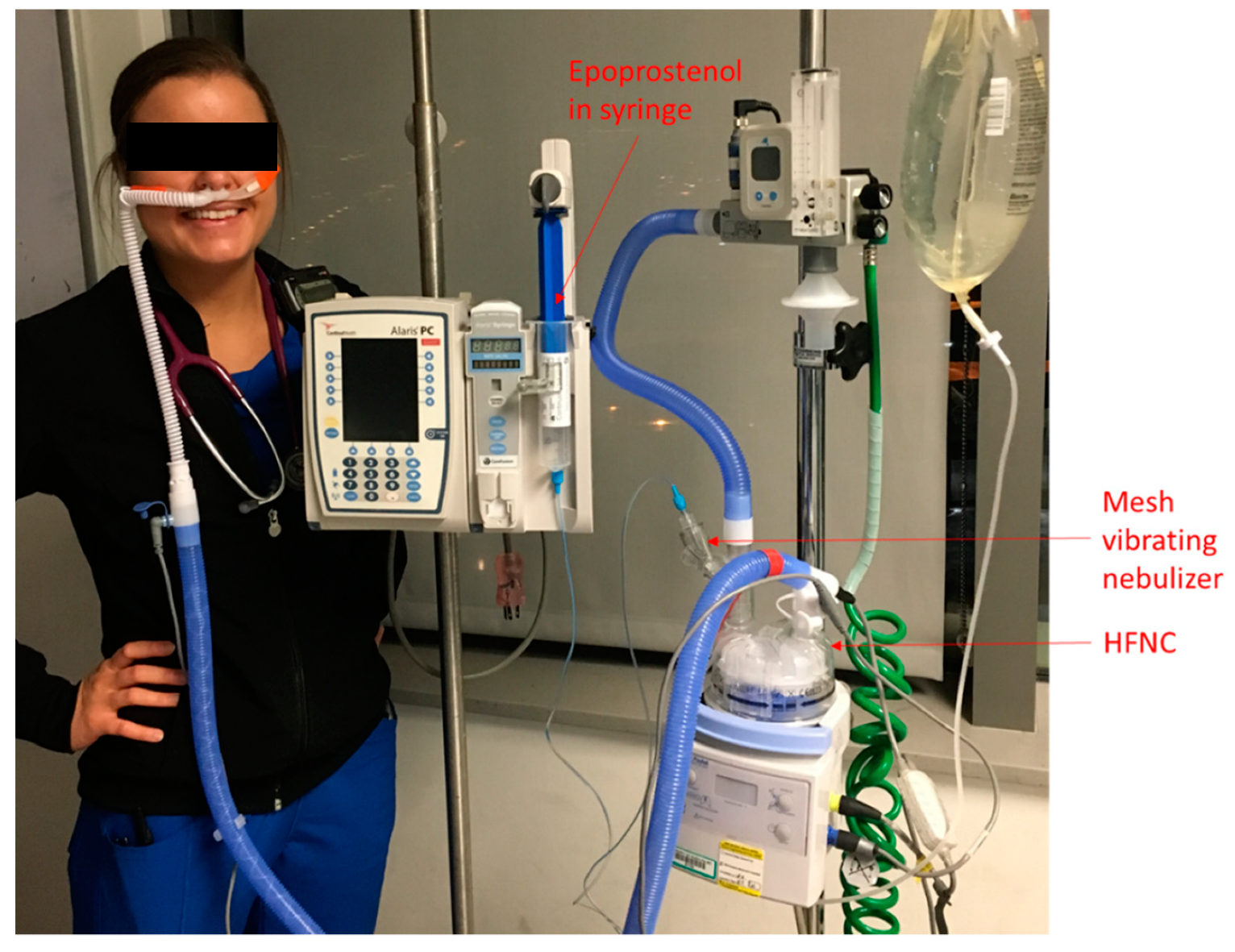
The AcuCare High Flow Nasal Cannula provides high flow oxygen therapy for adult patients with acute respiratory failure. It is designed to deliver continuous oxygen therapy up to a maximum flow of 60 L/min. The AcuCare High Flow Nasal Cannula is for single-patient use (maximum seven days) in the hospital/clinical environment.
Full Answer
What is high flow oxygen rate?
It is usually defined as the administration of gas flow above 6-15 liters per minute. High-flow systems refer to the second group of oxygen delivery devices that are capable of delivering at least 40 liters per minute of conditioned gas, providing an accurate FiO 2 regardless of the patient’s breathing pattern.
How much oxygen can you put through nasal cannula?
The nasal cannula carries 1 to 5 liters of oxygen per minute. There are also infant or neonatal nasal cannulas which carry less than one liter per minute. (These also have smaller prongs.) The oxygen percentage provided to the patient ranges roughly from 24 to 35 percent, or the cannula may merely supply humidified air.
What is HFNC oxygen?
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy is an oxygen supply system capable of delivering up to 100% humidified and heated oxygen at a flow rate of up to 60 liters per minute. All settings are controlled independently, allowing for greater confidence in the delivery of supplemental oxygen as well as better outcomes when used.
How does nasal cannula help in delivering oxygen therapy?
When high-flow nasal cannula, or HFNC, is used to deliver oxygen, the flow rates are much higher than can be achieved with traditional nasal cannula. This results in a greater delivery of prescribed oxygen into the lungs, and less entrainment of room air. The oxygen you want to deliver to your patients is not prone to the same effect of dilution!

What is the difference between nasal cannula and high-flow nasal cannula?
When high-flow nasal cannula, or HFNC, is used to deliver oxygen, the flow rates are much higher than can be achieved with traditional nasal cannula. This results in a greater delivery of prescribed oxygen into the lungs, and less entrainment of room air.
What does high-flow nasal cannula do?
A high-flow nasal cannula accomplishes a reduction of nasopharyngeal airway resistance, leading to improved ventilation and oxygenation through the application of a positive pressure environment.
When do you use a high-flow nasal cannula?
The indications for the use of HFNC in adults include community-acquired pneumonia, post-extubation (even in low-risk patients), pre-oxygenation prior to intubation, DNI patients with respiratory failure, and perhaps in patients with cardiogenic pulmonary edema when NIPPV is not tolerated.
How many liters can high-flow nasal cannula?
(A) The high-flow nasal cannula circuit consists of a flow meter and oxygen–air blender connected to a humidifier. Flow rates up to 60 liters per minute are delivered to the nasal cannula via a heated circuit.
What is the difference between high flow and regular oxygen?
When compared to traditional oxygen therapy, delivered through a face mask, high flow continuous oxygen therapy offers: Better clearance of fluids (secretions) due to humidified air. Better tolerated and more comfortable. Easier to communicate during therapy.
How many liters is considered high flow?
Heat and humidified high flow nasal cannula or as most call it, Hi Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC), isn't just a standard nasal cannula cranked up to very high flow rates. It actually takes gas and can heat it to 37 o C with a 100% relative humidity and can deliver 0.21 – 1.00% fi02 at flow rates of up to 60 liters/min.
What does it mean to be on 3 liters of oxygen?
With each LPM of supplemental oxygen, the patient receives an additional 3-4% of oxygen, so a patient receiving 3 LPM during oxygen therapy would be breathing air that is approximately 30-33% oxygen.
What are the disadvantages of nasal cannula?
Several drawbacks are associated with these devices, which may limit efficacy and tolerance of oxygen delivery. Usually, oxygen is not humidified at low flow, and complaints, especially dry nose, dry throat, and nasal pain, are common.
What is the minimum flow rate for high-flow nasal cannula?
HFNC is best applied in a monitored setting such as the intensive care unit, intermediate care floor, or emergency department. Oxygen is delivered to the patient through wide bore nasal cannulae (picture 1). We prefer to set the flow rate first, typically at 20 to 35 L/minute (range 5 to 60 L/minute).
What is the highest level of oxygen you can be on?
Usual target SpO2 ranges The best target for most adults is 92 to 96% SpO2. The best target for most children is 90 to 95% SpO2. Your best target range may differ if you have certain types of lung disease. For example, if you have COPD, your best target range may be 88 to 92% SpO2.
Is being on 4 liters of oxygen a lot?
Rates of 4 liters/minute or greater are considered higher oxygen flow. As more scarring develops in the lungs, they become less efficient in delivering the necessary oxygen the body needs.
How many liters of oxygen is normal?
The normal flow rate of oxygen is usually six to 10 litres per minute and provides a concentration of oxygen between 40-60%. This is why they are often referred to as MC (medium concentration) masks, as 40%-60% is considered to be a medium concentration of oxygen.
Why is high flow oxygen used?
How does high flow nasal oxygen work? In physiological terms, HFNO improves the fraction of inspired oxygen, washes and reduces dead space, generates positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and provides more comfort than cold and dry oxygen.
Does high flow nasal cannula provide peep?
A high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) demonstrably generates PEEP in neonatal and adult populations at lower flows (eg, 2-8 L/min) and higher flows (eg, ≥ 60 L/min). Few studies have demonstrated PEEP generation at the moderate flows (eg, 8-50 L/min) that are used commonly in pediatric patients.
What is the FIO2 of a high flow nasal cannula?
Figure 1. High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) systems use specialized nasal cannulas that allow oxygen to be delivered at an FIO2 of 21–100% with high flow rates of 20–60 L / min. Heating the circuit to body temperature and humidifying the air allows these high flow rates to be well tolerated by the patient.
How much oxygen can a nasal cannula deliver?
Let’s take a moment to remember the traditional nasal cannula. When connected to wall oxygen, this cannula can deliver oxygen at flow rates from 1 to 6 L / min for extended periods of time. Higher flow rates are not well tolerated due to nasal irritation and discomfort.
What is HFNC in medical terms?
What is high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC)? High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC), also referred to as nasal high flow (NHF), is a therapy that has gained traction in the past decade and is sometimes lumped together with the use of noninvasive ventilation (NIV). Since it differs from noninvasive ventilation, it will be important to highlight differences ...
How does HFNC differ from NIV?
HFNC differs to NIV in that it provides less ventilatory support. You set a flow rate instead of setting inspiratory and expiratory pressures. Therefore, the pressure produced from HFNC flow rates is much lower in comparison to NIV.
What is HFNC used for?
This makes it easier to cough up or remove. Keeps the airway open during sleep. HFNC can be used to manage obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA is usually treated with a continuous positive air pressure (CPAP) machine.
How does HFNC work?
HFNC is used to give oxygen at a high rate. The oxygen is delivered through small prongs that sit in the nostrils. The high flow rate makes breathing easier. The lungs do not have to work as hard to get air in and out. It also helps clear carbon dioxide from the airway.
Why may HFNC be needed?
This can cause a condition called apnea of prematurity (AOP). AOP causes the baby to stop breathing for 15 to 20 seconds or to pause for several seconds. HFNC can help the baby breathe more regularly.
What do I need to know about HFNC use at home?
Healthcare providers will show you how to set up and use the device at home. You will get information on how to clean the parts and how much extra oxygen to keep as a backup. You will also get instructions for using oxygen safely. This includes checking your blood oxygen level regularly with a pulse oximeter.
Is a CPAP mask more comfortable than a CPAP?
A CPAP mask may be difficult to wear during sleep. HFNC does not use a mask, so it may be more comfortable than CPAP. Prevents breathing problems before and after a procedure or surgery. For example, breathing problems can develop during intubation.
HOW DOES HIGH FLOW NASAL CANNULA WORK?
HFNC can warm (to 98.6 o F or 37 o C) and humidify gas, which can decrease airway inflammation, maintain mucociliary function, improve mucous clearance and reduce the caloric expenditure in acute respiratory failure.
How much air flow does a nasal cannula deliver?
Traditional nasal cannula delivers flow rates of 2–6 L / min. However, patients with respiratory distress can have much higher peak inspiratory flow rates which can cause the patient to entrain room air into the lungs. This can result into an oxygen dilution, and the patient will not receive the precise amount of oxygen that is desired. ...
What is HFNC in respiratory?
HFNC can warm (to 98.6oF or 37oC) and humidify gas, which can decrease airway inflammation, maintain mucociliary function, improve mucous clearance and reduce the caloric expenditure in acute respiratory failure .
What happens when you use HFNC?
Lastly, when HFNC is applied, the constant high flow of oxygen provides a washout of the anatomical dead space of the oropharynx and proximal tracheobronchial tree, which results in more efficient breathing.
Is HFNC oxygen delivery effective?
HFNC oxygen delivery has already proved its value as an effective mode of noninvasive ventilatory support and has been gaining attention as a simple and well-tolerated alternative means of respiratory support for critically ill patients .
How much oxygen does a nasal cannula provide?
Let’s start by defining the flow in the different oxygen devices. Regular nasal cannula provides between 1-6 liters of flow.
How much flow can a face mask give?
A simple face mask can get you flows between 6-10L/min. Venti masks, aka Venturi masks can get you flow rates between 4-8L/min. The best you can potentially do with a non-high flow device is the non-rebreather which can generate a flow rate of 10-15L/min.
Why use a high flow nasal cannula?
Compared to traditional nasal cannula, the use of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) results in more efficient breathing due to a washout of anatomical dead space in the oropharynx and proximal tracheobronchial tree . That’s it for now.
How much air flow can a nasal cannula deliver?
Traditional nasal cannula delivers flow rates of 2–6 L / min. But patients with respiratory distress can have much higher peak inspiratory flow rates. If the inspiratory flow rate of the patient is greater than what is being provided by the cannula, the patient will entrain room air into the lungs.
What is HFNC in medical terms?
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) is a heated and humidified system that allows prescribed fraction of inspired oxygen (F I O 2) levels to be delivered at very high flow rates. Let’s now consider how HFNC can help our patients improve their respiratory disease.
What happens when you use HFNC?
Lastly, when HFNC is applied, the constant high flow of oxygen provides a washout of the anatomical dead space of the oropharynx and proximal tracheobronchial tree, which results in more efficient breathing.
What is HFNC in a cannula?
When high-flow nasal cannula, or HFNC, is used to deliver oxygen, the flow rates are much higher than can be achieved with traditional nasal cannula. This results in a greater delivery of prescribed oxygen into the lungs, and less entrainment of room air. The oxygen you want to deliver to your patients is not prone to the same effect of dilution!
How much does functional residual capacity increase when HFNC is applied?
Despite this discrepancy, studies show that the functional residual capacity (FRC) increases by about 25% when HFNC is applied.
How does HFNC exert its effect?
HFNC also exerts its effect by providing some variable positive pressure.
How much fio2 does a nasal cannula deliver?
I was taught on my ICU rotation as an intern that every 1 liter of nasal cannula will deliver ~4% fiO2 above room air (21%). So 1 liter/min via the NC should deliver ~ 25% fi02, and 2 liters/min should deliver 29% fiO2 (see Table 1 below). I believed this “1:4 rule” was true for years, but let’s see if it makes sense for a patient in acute respiratory distress
What is HFNC in medical terms?
Heat and humidified high flow nasal cannula or as most call it, Hi Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC), isn’t just a standard nasal cannula cranked up to very high flow rates. It actually takes gas and can heat it to 37 o C with a 100% relative humidity and can deliver 0.21 – 1.00% fi02 at flow rates of up to 60 liters/min. The flow rate and fi02 can be independently titrated based on your patient’s flow and fi02 requirements.
How much PEEP does HFNC deliver?
HFNC has been shown to deliver up to 1 mm of Hg of PEEP for every 10L/min of flow delivered with closed mouth breathing. (4-5)
What is HFNC in bronchiolitis?
The use of heated and humidified high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) has become increasingly popular in the treatment of patients with acute respiratory failure through all age groups. I first started using it as a pediatric intensive care fellow, but had little knowledge of how it actually worked. I noticed a few years after using it successfully in children, mainly with severe bronchiolitis, that we began to use it in the adult intensive care unit as well. It seems over the past several years many studies have come out reviewing the mechanisms of action as well as its use in a variety of conditions. In this part we will summarize how it works and for part 2 we will discuss the main indications for its use in adult and pediatric patients.
How hot can HFNC be?
HFNC can warm (to 37 o C ) and humidify gas, which can decrease airway inflammation, maintain mucociliary function, improve mucous clearance and reduce the caloric expenditure in acute respiratory failure (1-2). One obvious benefit, but worth mentioning is that high flow can give you a very high flow of gas.
What is the peak inspiratory flow of a tachypneic patient?
This is important as patients in acute respiratory failure can be extremely tachypneic, and therefore their peak inspiratory flows, which may normally be 30L/min – 60L/min, can reach up to 120 L/min (3). So if you place your tachypneic patient with PIF rate of 120L/min and minute volume >20L/min on a 15L/min NRB mask, you may not be helping them as much as you think. I am going to get into this point a bit later on in this review when we discuss the concept of oxygen dilution.
Why do patients prefer HFNC?
Patients often prefer the use of HFNC to that of non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (CPAP or BPAP) because the tight fitting mask can be uncomfortable to some patients. They may even prefer it to standard NC because the warmed, humidified gases won’t dry their mucosa like standard oxygen therapy (5). This may lead to higher compliance with HFNC and perhaps an improvement in your patient’s oxygenation and work of breathing.
High Flow Oxygen vs. Low Flow Oxygen
HFNC is the medical abbreviation for a high-flow nasal cannula. These devices blow humidified, heated oxygen into the nostrils. They can deliver up to 60 liters of oxygen per minute.
Nasal Cannula Uses
Your doctor may recommend a nasal cannula if you are having trouble breathing or if you do not have enough oxygen in your blood. Reasons you might use a nasal cannula include:
Nasal Cannulas and COVID-19
In the earliest days of the COVID-19 pandemic, people with severe cases were intubated. During this procedure, doctors put a tube down a patient's throat, allowing a mechanical device to breath for the patient.
Using a Nasal Cannula at Home
While nasal cannulas are used to provide supplemental oxygen in ICUs and hospital wards, people with certain conditions like COPD or pulmonary fibrosis may use one at home.
What is nasal high flow?
Our preferred generic descriptor is nasal high flow (NHF) because it’ s really all about Nasal delivery of High Flows of humidified air.
What sets NHF apart from COT devices and bi-level NIV?
7. What sets NHF apart from COT devices and bi-level NIV is that it is delivered via a nasal cannula (sometimes a tracheotomy). This means a mask seal is not required, making setup a simpler process. This results in several benefits to patients, including (and most importantly) granting them better communication with caregivers and loved ones.
Does oxygen alone increase alveolar ventilation?
2. It can deliver high levels of oxygen but it is significantly more sophisticated than that – the higher rates of flow (independent of oxygen) confer benefits that oxygen alone cannot, i.e. reduction of deadspace and dynamic positive airway pressure both which are capable of increasing alveolar ventilation.
How does a high flow nasal cannula work?
High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) blends oxygen and air to deliver a constant FiO2 to a patient. It also utilizes heated tubing combined with humidification connected to a two-prong nasal cannula to deliver a heated humidified gas mixture to the patient. HFNC works by filling the patient’s oropharynx with a reservoir of a controlled gas mixture. On inspiration, the patient inhales the gas, washing away anatomical dead space in the oropharynx and upper airways, delivering this gas to the lungs, which improves gas exchange. This improvement in gas exchange improves the work of breathing. The humidified gases delivered to the patient by the high flow cannula can decrease airway inflammation, maintain mucociliary function, and improve airway clearance.
What is HFNC in respiratory?
In the late 1990s, clinicians developed a clinical approach in treating hypoxic respiratory failure with the creation of High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC). Up until then, hypoxic respiratory failure was being treated with a non-rebreather mask, BiPAP, and/or intubation. As much as these interventions brought about the necessary changes, there wasn’t always a severe enough need for intubation and not every patient could tolerate BiPAP. These patients were the ideal patients for the use of HFNC. With the advancement in technology, new high-flow devices can produce flows similar to that of a ventilator and provide a way to avoid intubation or slow the process of intubation with more patient compliance. Two high flow devices to consider are those that utilize primarily small-bore cannulas (Vapotherm) and those that utilize large-bore cannulas (Airvo2).
What is a large bore HFNC?
Large-bore HFNC distinguishes itself from small-bore HFNC by delivering flows from 2 to 60 L/min on the same unit without having to change cartridges. The FiO2 is adjustable from 21% to 100%. Note, however, the upper O2 alarm is automatically set at 100%, which will cause the device to alarm if the delivered FiO2 is set at 100%. You can fix this by setting the delivered FiO2 at 99%. Unlike common small-bore devices, large-bore devices come with one medical gas cord (oxygen) that makes it easier to use when access to medical air is limited. This device comes with the unit itself, water chamber, o2 tubing, flow meter, O2 analyzer, and nasal cannulae varying in sizes specific to the patient population. This device utilizes entrained room air blending with dialed in oxygen by an attached flowmeter to create a delivered FIO2. This device uses the passover humidity system to humidify the delivered gas which also acts as a way to not transport contaminated viruses that can be carried with water droplets. The manufacturer prides itself on the better use of patient compliance with their device as flows are less forceful through their large bore tubing. This device also notes patient compliance since it is quieter and easier to tolerate. Also, the device can be used in the home setting since it can be connected to an oxygen concentrator.
Why do patients need higher flow rates?
The higher flow rates help patients in distress because they have much higher peak inspiratory flow rate demands. A patient in distress can easily pull 40 L/min. A patient in distress with an increase in demand on a low-flow nasal cannula will entrain room air into the lungs, resulting in oxygen dilution.
Does HFNC work?
According to Hyzy, HFNC has been shown in studies to produce a “PEEP effect.” It helps by decreasing work of breathing , improves oxygenation in patients with alveolar filling diseases, and unloads auto-PEEP. By increasing the airway pressure in the nasopharynx with increasing flow rates, the pressure at the end of expiration increases, similar to CPAP. While closed mouth breathing leads to approximately 0.8-1 of PEEP, open mouth breathing only produces about 0.4 of PEEP for each 10 L/min of flow. This result is limited and only provides mild PEEP at best.
Can you extubate to HFNC?
Some studies note, patients with comorbidities and/or patients with an increased length of ventilator days may benefit from extubation directly to HFNC. Patients must be extubated directly to high flow and flow rate settings must start high.
