What temperature to pasteurize?
ing is pasteurized, a temperature of 82° to 85° C. (180° to 185° F.) is used, but in this country the cream is frequently heated to not more than 63° C. (145° F.), and rarely above 77° C. (170° F.). It is obvious that it is desirable to determine the most effective
What are the dangers of pasteurized milk?
“Pasteurisation denatures the fragile and nutritious milk proteins and enzymes, and it reduces the vitamin content. In addition, contamination can occur after pasteurisation and lead to outbreaks of serious infection. Pasteurisation also negates the reduction in childhood asthma and atopy associated with the consumption of raw milk.
What temperature is milk pasteurized?
Pasteurization of milk, widely practiced in several countries, notably the United States, requires temperatures of about 63 °C (145 °F) maintained for 30 minutes or, alternatively, heating to a higher temperature, 72 °C (162 °F), and holding for 15 seconds (and yet higher temperatures for shorter periods of time).
When did pasteurization start?
Pasteurization is the process of heating a liquid to below the boiling point to destroy microorganisms. It was developed by Louis Pasteur in 1864 to improve the keeping qualities of wine. Commercial pasteurization of milk began in the late 1800s in Europe and in the early 1900s in the United States.

What is high temperature short time processing?
Also known as high-temperature–short-time (HTST) processing, aseptic canning is a process whereby presterilized containers are filled with a sterilized and cooled product and sealed in a sterile atmosphere with a sterile cover.
What is higher heat shorter time pasteurization?
Higher heat shorter time (HHST) treatment of fluid milk and milk products is the application of heat to a continuously flowing product using high temperatures, generally above 100°C, for such time to extend the shelf-life of the product under refrigerated conditions.
What is the difference between high temperature short time pasteurization and ultra high temperature pasteurization?
HTST pasteurization heats the milk to 161 degrees Fahrenheit for 15 seconds and then rapidly cools it to 39 degrees. For UHT, raw milk is heated to approximately 280 degrees Fahrenheit for just 2 seconds and is then rapidly chilled back to 39 degrees. Both methods result in milk that is 99.9% free of bacteria.
What are the 3 types of pasteurization?
Different Types of Thermal Processing MethodsThermization: Heat the milk to between 57°C to 68°C and hold for 15 minutes. ... Batch pasteurization: Also known as low-temperature long time (LTLT) pasteurization. ... Flash pasteurization: Also known as high-temperature short time (HTST) pasteurization.More items...•
What are the two high temperature techniques?
The use of high temperatures to preserve food is based on their destructive effects on microorganisms. By high temperatures are meant any and all temperatures above ambient. With respect to food preservation, there are two temperature categories in common use: pasteurization and sterilization.
What is the difference between Pasteurised and UHT milk?
Pasteurization is a low-temperature sterilization method invented in 1865 by a French named Pasteur. Pasteurized milk is sterilized by heating at 72-85°C for 10-15 seconds. UHT: Ultra High Temperature. Milk is heated by ultra-high temperature of 135-145°C and kept for 2-4 seconds for sterilization.
Is UHT milk better than fresh milk?
The nutritional value of UHT milk and fresh milk are the same when it comes to the main nutrients in milk, such as protein, calcium and Vitamin D. UHT treatment may reduce the level of some heat sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C, but milk is not the main source of these nutrients in the first place.
What is the main advantage of UHT pasteurized milk?
1. UHT-Pasteurized Products Last Longer: UHT pasteurization extends a product's shelf-life by months, making it an extremely cost-effective option. 2. UHT-Pasteurized Products Contain Less Bacteria: The high heat required during UHT pasteurization results in milk that is up to 99.9% bacteria-free.
What is the difference between UHT milk and fresh milk?
The difference between fresh and long-life milk is the method of processing. Fresh (pasteurised) milk is heated to 74°C for 15 seconds. Long-life milk is heated to 140°C for two seconds and then packaged aseptically.
What are the two methods of pasteurization?
Top 4 Methods of Milk PasteurizationHigh Temperature Short Time. In the United States, the most common method of pasteurization is High Temperature Short Time (HTST). ... Higher Heat Shorter Time. ... Ultra High Temperature. ... Ultra Pasteurized.
Which method is best for milk pasteurization?
Pasteurization Type The most common method of pasteurization in the United States today is High Temperature Short Time (HTST) pasteurization, which uses metal plates and hot water to raise milk temperatures to at least 161° F for not less than 15 seconds, followed by rapid cooling.
What temperature do you pasteurize milk?
Keep the milk at the right temperature. Heat the milk to 63°C (150°F) for at least 30 minutes or 72°C (162°F) for at least 15 seconds. If the temperature falls lower than the one you're using, you have to start timing again.
What is the advantage of high temperature short time pasteurization HTST compared with sterilization?
HTST Pasteurization is Effective in Reducing Bacteria: Although not as effective as UHT-pasteurization in reducing bacteria and other microorganisms, HTST pasteurization strikes a great balance between food safety, long shelf-life and uncompromised flavor.
What temperature is pasteurization?
Pasteurization of milk, widely practiced in several countries, notably the United States, requires temperatures of about 63 °C (145 °F) maintained for 30 minutes or, alternatively, heating to a higher temperature, 72 °C (162 °F), and holding for 15 seconds (and yet higher temperatures for shorter periods of time).
What is high temperature food preservation?
Temperature preservation Sterilized food is heated to a moderately high temperature, for example 112 °C for an hour, or a slightly higher temperature, for example 121 °C for 3 minutes. This treatment eliminates all pathogenic bacteria in the food.
When milk is high temperature short time HTST pasteurized each particle of milk has to be heated to?
This method involves heating milk rapidly to 72°C, keeping it for a few seconds (usually 15 s), and cooling it down immediately.
What are the factors that affect pasteurization?
Temperature and time are critical factors required to achieve pasteurization. Failure to achieve pasteurization could result in a microbiological hazard in the dairy products. The following are the generally accepted pasteurization schedules for dairy products produced by HTST pasteurization.
What is a CLT in pasteurization?
The constant level tank (CLT) is a reservoir for a supply, at atmospheric pressure, of raw or recirculated product to the pasteurizer to permit continuous operation of the HTST pasteurization system. It is located at the start of the pasteurization system. It controls the milk level and provides a uniform head pressure to the product leaving the tank.
Why do we need a stuffing pump?
The stuffing pump is necessary in large homogenizers where it will enable the product to be under positive pressure at the homogenizer suction intake manifold.
How long to process frozen milk?
Frozen dairy product mixes and egg nog: Process at 80°C for 25 seconds or at 83°C for 15 seconds (unless the milk ingredients going into the mix for the frozen dairy product are already pasteurized and all other components being added to the mix are microbiologically safe and ready to eat). Other:
When to use culinary quality steam?
Use culinary quality steam if it comes in contact with product.
Can liquids cross contaminate pasteurization plates?
Since the physical distance between the various liquids in the pasteurization plates is extremely small, the liquids have the potential to move through the plates and cross-contaminate the product if pin holes exist.
Can air be drawn into pasteurizer?
Ensure the design and capacity of the tank does not permit air to be drawn into the pasteurizer with the product when operating at the maximum sealed capacity of the flow control device.
What temperature is HTST?
…the continuous high-temperature short-time (HTST) method (72 °C or 161 °F for 15 seconds or above). The HTST method is conducted in a series of stainless steel plates and tubes, with the hot pasteurized milk on one side of the plate being cooled by the incoming raw milk on…
What is HTST in food preservation?
In food preservation: Commercial sterility. …process uses the high-temperature–short-time (HTST) method in which foods are heated at a high temperature for a short period of time. The time and temperature conditions depend on several factors, such as size, shape, and type of food.
What is aseptic canning?
Also known as high-temperature–short-time (HTST) processing, aseptic canning is a process whereby presterilized containers are filled with a sterilized and cooled product and sealed in a sterile atmosphere with a sterile cover. The process avoids the slow heat penetration inherent in ...
What is HTST pasteurization?
In high-temperature short-time (HTST) pasteurization, also known as Flash pasteurization, the product is heated to the minimum temperature and held continuously at or above that temperature for at least the minimum time required. This thermal treatment extends the shelf life of product by eliminating vegetative and pathogenic microorganisms.
Why is pasteurization important?
Products that can be completely pasteurized are beer, canned food, milk and milk product, eggs, juices, low alcoholic beverages, syrups, vinegar, water, wines, nuts, etc. It is important to handle the pasteurized product in refrigerated condition after pasteurization to prevent the recontamination of product.
How does a HTST process work?
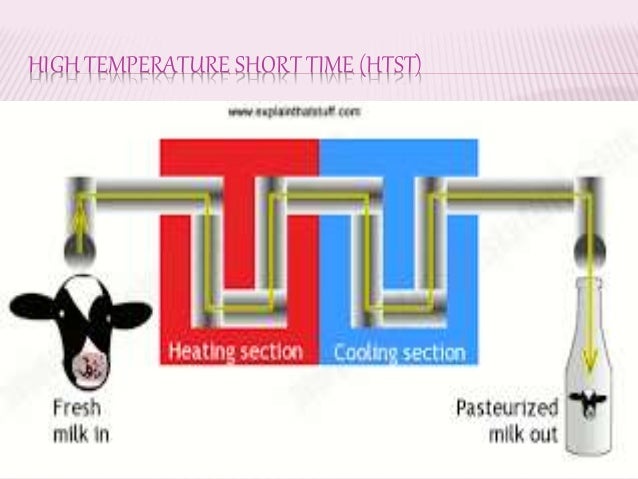
Stepwise flow of process in HTST starts with product entering the balance tank and is drawn under reduced pressure to the regenerator section. In the regenerator section, the product is pre-warmed by hot product flowing through regenerator plates. The product is then drawn through the timing pump to the heating section. The now-hot product flows through the holding tube. The product contacts the indicating thermometer and the recording thermometer. If it has not reached the minimum required temperature, it is returned back to the constant level tank via the diversion port. If the product is at or above the minimum required temperature, it passes through the regenerator plates (on the pasteurized side) and then to the cooling section. The product exits the cooling section and rises to an elevation of at least 12 inches above any raw product. Finally, the product passes to a storage tank for packaging.
Why is it important to keep pasteurized products refrigerated?
It is important to handle the pasteurized product in refrigerated condition after pasteurization to prevent the recontamination of product . Temperature and time for process is set on the basis of product and targeted microorganism of the product. Effectiveness of pasteurized product can be detected by various means.
Where is the timing pump located in a HTST?
Timing Pump: The timing pump controls the flow rate within the HTST system. It is located after the raw regenerator and before the holding tube. It draws raw milk through the raw regenerator and pushes it forward. The pasteurized product is always under greater pressure than the raw.
Is a tubular heat exchanger a PHE?
Tubular heat exchanger (THE): Unlike PHEs, THEs have no contact points in the product channel. THEs may have either a double-tube or triple-tube design. However, from the standpoint of heat transfer, the THE is less efficient than the PHE. The tubes within a THE have spiral or corrugated surfaces to increase turbulence and heat exchange.
What temperature is used for pasteurization?
In general, temperatures and times for HTST range from 161ºF for 15 sec used for pasteurization of milk to higher temperatures for shorter times. Use of temperatures above 280ºF is generally referred to as ultra-high-temperature (UHT) processing.
Why are high temperature processes used?
Because the products are exposed to high temperatures for short times, there is minimal degradation of the products.
What is the equipment used in aseptic processing?
There are lots of innovations in aseptic processing, he said, but traditional equipment is still being used, including scraped-surface heat exchangers and tubular heat exchangers. But tubular heat exchangers have changed dramatically. For example, helical heat exchangers provide a lot of turbulence, which improves heat transfer. Dimpled tubular heat exchangers change the flow pattern and provide quicker, more uniform heating.
How long does it take for a HTST to kill spores?
According to Meyer, an HTST process is one that provides a 12-log kill of Clostridium botulinum spores, e.g., 121ºC for 6 min. With high pressure (690 MPa or higher), sterility can be accomplished with an end temperature of 100–105ºC at each pulse peak, using two pulses (cycles). In the batch process, product is placed into the pressure chamber and heated uniformly to 90ºC at 690 MPa. Adiabatic heating raises the end temperature to 119ºC. The chamber is pressurized, then decompressed to ambient pressure, then repressurized and decompressed again. He said that it is necessary to pulse the system because, although high pressure protects the product from heat degradation, it also protects spores. If only one pulse is used and the product is held under pressure for even as long as 60 min, sterility is not achieved. It’s the pulsing that kills, he said, not the time at a certain temperature, unlike conventional thermal processing.
When was aseptic processing filed?
An aseptic process for a low-acid product containing particulates (potato soup) was filed with the Food and Drug Administration in 1997 by Tetra Pak, as a result of two workshops conducted in 1995–96 by CAPPS and the National Center for Food Safety and Technology (see article in the August 1997 issue of Food Technology ). Since then, Sastry said, no other such processes have been filed. Aseptic processing is being used for products containing particulates in Europe, but to the best of Sastry’s knowledge not in the United States.
What are the steps of thermal process?
In any thermal process, there are heating, holding, and cooling steps. In determining the lethality of the process, the heating and holding steps are the most important. Swartzel said that efforts are being made to get the heatup time shorter.
Why is it important to use high temperatures for short times?
Using high temperatures for short times improves the quality of liquid foods. The problem is to apply it to products that are solid or contain large solid particles. Since not all particles flow at the same rate, enough heat must be provided to sterilize the slowest-heating (i.e., fastest-moving) particle.
What temperature is milk pasteurized?
The most common method of pasteurization in the United States today is High Temperature Short Time (HTST) pasteurization, which uses metal plates and hot water to raise milk temperatures to at least 161° F for not less than 15 seconds, followed by rapid cooling.
How long does it take to pasteurize milk?
The original method of pasteurization was vat pasteurization, which heats milk or other liquid ingredients in a large tank for at least 30 minutes. It is now used primarily in the dairy industry for preparing milk for making starter cultures in the processing of cheese, yogurt, buttermilk and for pasteurizing some ice cream mixes.
What is aseptic processing?
Another method, aseptic processing, which is also known as Ultra High Temperature (UHT), involves heating the milk using commercially sterile equipment and filling it under aseptic conditions into hermetically sealed packaging. The product is termed "shelf stable" and does not need refrigeration until opened. All aseptic operations are required to file their processes with the Food and Drug Administration's "Process Authority." There is no set time or temperature for aseptic processing; the Process Authority establishes and validates the proper time and temperature based on the equipment used and the products being processed.
What is the process of heating milk?
Pasteurization. Pasteurization is a process, named after scientist Louis Pasteur, that applies heat to destroy pathogens in foods. For the dairy industry, the terms "pasteurization," "pasteurized" and similar terms mean the process of heating every particle of milk or milk product, in properly designed and operated equipment, ...
What temperature does milk need to be to be pasteurized?
The standard US protocol for flash pasteurization of milk, 71.7 °C (161 °F) for 15 seconds in order to kill Coxiella burnetii (the most heat-resistant pathogenic germ found in raw milk), was introduced in 1933, and results in 5- log reduction (99.999%) or greater reduction in harmful bacteria.
Why do we need flash pasteurization?
Flash pasteurization is performed to kill spoilage microorganisms prior to filling containers, in order to make the products safer and to extend their shelf life compared to the unpasteurised foodstuff. For example, one manufacturer of flash pasteurizing machinery gives shelf life as "in excess of 12 months". It must be used in conjunction with sterile fill technology (similar to aseptic processing) to prevent post-pasteurization contamination.
When did Tropicana juice become pasteurized?
The juice company Odwalla switched from non-pasteurized to flash-pasteurized juices in 1996 after tainted unpasteurized apple juice containing E. coli O157:H7 sickened many children and killed one.
What is HTST in food?
Flash pasteurization, also called " high-temperature short-time " ( HTST) processing, is a method of heat pasteurization of perishable beverages like fruit and vegetable juices, beer, wine, and some dairy products such as milk. Compared with other pasteurization processes, it maintains color and flavor better, but some cheeses were found to have varying responses to the process.
Why is HTST Pasteurization the Preferred Method?
High temperature short time pasteurization is a continuous process that efficiently and effectively destroys microorganisms in milk products. An HTST pasteurization system is a modular unit that includes a plate-and-frame heat exchanger, stainless steel balance tank, pumps, holding tube, valves piping and controls. Vat pasteurization, or the holding method, is the oldest method for pasteurizing food products. However, over the years HTST has gained favor in the food industry for multiple reasons:
Why is HTST used in food?
However, over the years HTST has gained favor in the food industry for multiple reasons: Large equipment capacity allows large volumes at one time. Continuous process allows for bottling to begin when pasteurization begins. Highly energy efficient. Minimal chance of damage to milk product.
What is HTST in milk?
HTST, or high temperature short time pasteurization, has become one of the most common methods of pasteurization today. It is more frequently known as flash pasteurization, or the “continuous method”. Pasteurization destroys pathogenic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, molds and yeasts in milk products to reduce bacterial content ...
Is HTST pasteurization more expensive than holding method?
Since HTST pasteurization requires more components, it can be more expensive than the holding method .
