
It's called the homeostatic response. This is the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate the chemical processes that take place internally to maintain health and functioning regardless of outside conditions (ie. temperature). Neurologically, we do this by avoidance of discomfort both emotionally and physically.
What are the three mechanisms of homeostasis?
Things to Remember Based on Homeostasis
- Homeostasis can be defined as the maintenance of a stable internal body environment.
- Homeostasis can also be stated as resistance to the external environment in order to maintain a stable and constant environment.
- The regulation of Homeostasis depends on the three components- Receptor, Control center and Effector.
What are the stages of homeostasis?
What is Hemostasis | Its Mechanism in 4 Stages
- Vasoconstriction. In these stages, the injured blood vessel’s channel gets narrow so as to minimize the blood flow. ...
- Plug formation by platelets. The sticky platelets adhere to each and release adenosine diphosphate ( ADP ). ...
- Coagulation. In this stage, another layer of the cover is formed on the previous platelet plug formed. ...
- Fibrinolysis. ...
What are some examples of homeostatic mechanisms?
- Sweating . It consists of the secretion of liquid substances on the skin, whose evaporation cools it and makes it possible to alleviate the increase in interior temperature.
- Ammonia control . ...
- Lingual perspiration of dogs . ...
- The acceleration of breathing . ...
- The cellular homeostasis . ...
- Regulation of blood pH . ...
- The immune system . ...
What are the different types of homeostatic functions?
The regulation of homeostasis depends on three mechanisms:
- Effector.
- Receptor.
- Control Center.
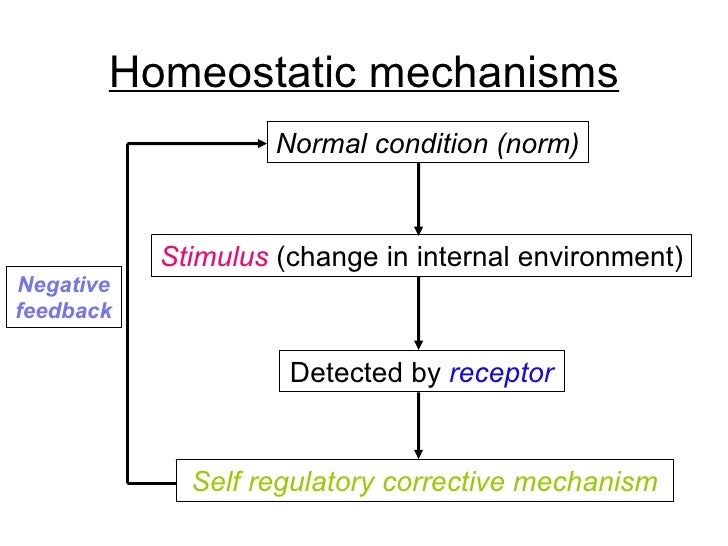
What is an example of a homeostatic response?
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example, your body shivers to maintain a relatively constant body temperature when the external environment gets colder.
What is a simple definition of homeostasis?
(HOH-mee-oh-STAY-sis) A state of balance among all the body systems needed for the body to survive and function correctly.
What are the steps of the homeostatic response?
Adjustment of physiological systems within the body is called homeostatic regulation, which involves three parts or mechanisms: (1) the receptor, (2) the control center, and (3) the effector. The receptor receives information that something in the environment is changing.
What is a homeostatic process?
Homeostasis: a Definition Homeostasis, as currently defined, is a self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions.
What are 5 examples of homeostasis?
Examples include thermoregulation, blood glucose regulation, baroreflex in blood pressure, calcium homeostasis, potassium homeostasis, and osmoregulation.
What is another word for homeostasis?
What is another word for homeostasis?equilibriumbalanceevennessstabilityequanimityequipoiseparityequitysymmetryequivalence39 more rows
Why homeostasis is important?
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action throughout the body, as well as all cell functions. It is the maintenance of a constant internal environment despite changes in internal and external conditions. In the human body, these include the control of: blood glucose concentration.
How do humans maintain homeostasis?
So how does your body maintain homeostasis? The regulation of your internal environment is done primarily through negative feedback. Negative feedback is a response to a stimulus that keeps a variable close to a set value (Figure below).
What are the types of homeostasis?
Generally, there are three types of homeostatic regulation in the body, which are:Thermoregulation. Thermoregulation is the process occurring inside the body that is responsible for maintaining the core temperature of the body. ... Osmoregulation. ... Chemical regulation.
What are the 4 steps of homeostasis?
The four components of homeostasis are a change, a receptor, a control center and an effector. A healthy cell or system maintains homeostasis, also commonly referred to as “being in balance.”
How does homeostasis affect the human body?
The tendency to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment is called homeostasis. The body maintains homeostasis for many factors in addition to temperature. For instance, the concentration of various ions in your blood must be kept steady, along with pH and the concentration of glucose.
What are the 3 components of homeostasis?
Components of homeostasis A system requires three components for homeostasis: - A receptor; - A control centre; - An effector.
What is homeostasis for kids?
Introduction. In biology, the term homeostasis refers to the ability of the body to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions.
Which is the most accurate definition of homeostasis?
the most accurate definition of homeostasis. The ability of an organism to maintain relatively constant internal conditions despite variability in external conditions.
What is the definition of homeostasis quizlet?
Homeostasis. Homeostasis then, by definition, is the ability of the body to maintain relatively stable internal conditions (internal environment) even though the outside world (external environment) is changing. The internal environment is defined as the fluid that surrounds the cells.
Why homeostasis is required short answer?
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action throughout the body, as well as all cell functions. It is the maintenance of a constant internal environment despite changes in internal and external conditions.
1. State homeostasis definition.
Homeostasis is the ability to maintain internal stability in an organism in response to the environmental changes. The internal temperature of the...
2. Which body systems help to maintain homeostasis?
The endocrine system and the nervous system are essential in maintaining the homeostasis of the body. However, other organs also play a role in mai...
3. How is homeostasis essential for our body?
Homeostasis is a self-regulating process that controls internal variables necessary to sustain life.
4. What are the main components of homeostasis?
Homeostasis involves three components- the receptor, the control centre, and the effector. The receptor receives information on the changing enviro...
5. What is the primary function of homeostasis?
The primary function of homeostasis is to maintain a balance within the body regarding its temperature, salt concentration, food intake and pH levels.
6. How does the cell maintain homeostasis in the body?
To maintain homeostasis in the body, the cells perform the following activities: Obtain and use energy, exchange materials, make new cells, and eli...
7. What role does liver play in homeostasis?
Our liver plays a vital role in blood glucose homeostasis. When the blood glucose level rises after a meal, the liver removes glucose from the bloo...
8. How does the skin help in maintaining homeostasis?
If the external temperature is high, the body tries to keep cool by producing sweat. Also, blood vessels near the skin surface dilate. This helps i...
What is Homeostasis?
Furthermore, homeostasis is a self-regulating process that regulates internal variables necessary to sustain life.
How does homeostasis work?
The body maintains homeostasis by controlling a host of variables ranging from body temperature, blood pH, blood glucose levels to fluid balance, sodium, potassium and calcium ion concentrations.
What does Bradford's homeostasis mean?
Bradford derived Homeostasis from the ancient Greek words ὅμοιος (pronounced: hómoios) and ἵστημι (pronounced: hístēmi). The combination of these words translates to “similar” and “standing still” respectively. Homeostasis Definition. Read on to explore what is homeostasis and its role in regulating internal body environment.
What is the role of the liver in homeostasis?
Our liver plays a vital role in blood glucose homeostasis. When the blood glucose level rises after a meal, the liver removes glucose from the blood and stores it in the form of glycogen. When the blood glucose levels are low, it converts the stored glycogen back to glucose.
What is the process of controlling internal variables necessary to sustain life?
Homeostasis is a self-regulating process that controls internal variables necessary to sustain life.
What are the causes of homeostasis breakdown?
The failure of homeostasis function in an internal environment will result in illnesses or diseases. In severe cases, it can even lead to death and disability. Many factors can affect homeostasis. The most common are: Genetics. Physical condition. Diet and nutrition. Venoms and toxins.
What are the activities of the cells that maintain homeostasis?
To maintain homeostasis in the body, the cells perform the following activities: Obtain and use energy, exchange materials, make new cells, and eliminate wastes.
What is homeostasis behavior?
Homeostasis involves both physiological and behavioral responses. 4 In terms of behavior, you might seek out warm clothes or a patch of sunlight if you start to feel chilly. You might also curl your body inward and keep your arms tucked in close to your body to keep in the heat.
What Is Homeostasis?
Homeostasis refers to the body's need to reach and maintain a certain state of equilibrium. The term was first coined by a physiologist named Walter Cannon in 1926. More specifically, homeostasis is the body's tendency to monitor and maintain internal states, such as temperature and blood sugar, at fairly constant and stable levels. 1
How does homeostasis work?
In the same way, if something is out of balance in your body, a physiological reaction will kick in until the set point is once again reached. Here's how the primary components of homeostasis work: 1 Stimulus: A stimulus from a change in the environment kicks something out of balance in the body. 2 Receptor: The receptor reacts to the change by informing the control unit. 3 Control unit: The control unit then communicates the change needed to bring the body back into balance. 4 Effector: The effector receives this information and acts on the change that is needed.
What is the body's need to maintain a certain state of equilibrium?
Homeostasis refers to the body's need to reach and maintain a certain state of equilibrium. The term was first coined by a psychologist named Walter Cannon in 1926. 1 More specifically, homeostasis is the body's tendency to monitor and maintain internal states, such as temperature and blood sugar, at fairly constant and stable levels.
What happens when the temperature drops in your house?
When the temperature drops in your house, your furnace will turn on and warm things up to the preset temperature. In the same way, if something is out of balance in your body, a physiological reaction will kick in until the set point is once again reached. Here's how the primary components of homeostasis work: ...
What is the function of homeostasis?
When the level is off (in either direction, too much or too little), homeostasis will work to correct it. For example, to regulate temperature, you will sweat when you get too hot or shiver when you get too cold.
What is the name of the system that regulates temperature?
Thermoregulation. When you think about homeostasis, temperature might come to mind first. It is one of the most important and obvious homeostatic systems. Regulating body temperature is called thermoregulation. All organisms, from large mammals to tiny bacteria, must maintain an ideal temperature in order to survive.
What is the set point of homeostasis?
A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates.
How does the body respond to a potential catastrophe?
The body responds to this potential catastrophe by releasing substances in the injured blood vessel wall that begin the process of blood clotting. As each step of clotting occurs, it stimulates the release of more clotting substances. This accelerates the processes of clotting and sealing off the damaged area.
What is the effector in a feedback system?
An effector is the component in a feedback system that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range. In a negative feedback loop, a stimulus—a deviation from a set point—is resisted through a physiological process that returns the body to homeostasis.
How do pancreatic beta cells respond to increased blood glucose levels?
These pancreatic beta cells respond to the increased level of blood glucose by releasing the hormone insulin into the bloodstream. The insulin signals skeletal muscle fibers, fat cells (adipocytes), and liver cells to take up the excess glucose, removing it from the bloodstream.
What is negative feedback?
Negative feedback is a mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point. Therefore, negative feedback maintains body parameters within their normal range.
What is the brain's temperature regulation center?
When the brain’s temperature regulation center receives data from the sensors indicating that the body’s temperature exceeds its normal range, it stimulates a cluster of brain cells referred to as the “heat-loss center.”. This stimulation has three major effects:
What is sensor in feedback?
A sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. This value is reported to the control center. The control center is the component in a feedback system that compares the value to the normal range.
What is the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate the chemical processes that take place internally?
The tendency of an organism or cell to regulate the chemical processes that take place internally so as to maintain health and functioning, regardless of outside conditions. The ability to maintain a steady body temperature is an example of homeostasis.
What is the state of equilibrium in the body?
A state of equilibrium, as in an organism or cell, maintained by self-regulating processes: The kidneys maintain homeostasis in the body by regulating the amount of salt and water excreted.
What is the tendency of a system?
the tendency of a system, esp. the physiological system of higher animals, to maintain internal stability, owing to the coordinated response of its parts to any situation or stimulus tending to disturb its normal condition or function.
What is homeostasis in the body?
Homeostasis is defined as a constant, steady environment despite external changes, such as exercise. Exercise affects your body temperature, blood oxygen levels, sugar levels and hydration – all properties necessary for your survival. Your body uses an automatic feedback system to preserve normal temperature and water levels, ...
How to maintain homeostasis?
Your body uses an automatic feedback system to preserve normal temperature and water levels, so you can keep exercising. Eat properly and drink plenty of fluids to help your body maintain homeostasis.
How does sweat help maintain homeostasis?
To maintain homeostasis, the blood vessels in your skin dilate to allow more blood flow to the surface of your body where it disperses the heat. You won't feel the vasodilation, but you certainly will feel yourself sweating. The evaporation of sweat and breathing out warm air also serve to help cool your body and thereby maintain a steady temperature.
Why do hormones increase blood pressure?
Hormones are released to signal your heart rate to increase so you can deliver more oxygenated blood and nutrients to where you need them most. As your blood vessels dilate, you will also experience an increase in blood pressure. Advertisement.
