What is the horizontal 2G welding position?
The horizontal 2G welding position is a welding position in which the weld face lies in an approximately vertical plane and the weld axis at the point of welding is approximately horizontal. In the horizontal welding position, the weld bead will have a slightly convex shape.
When do you use the vertical position in welding?
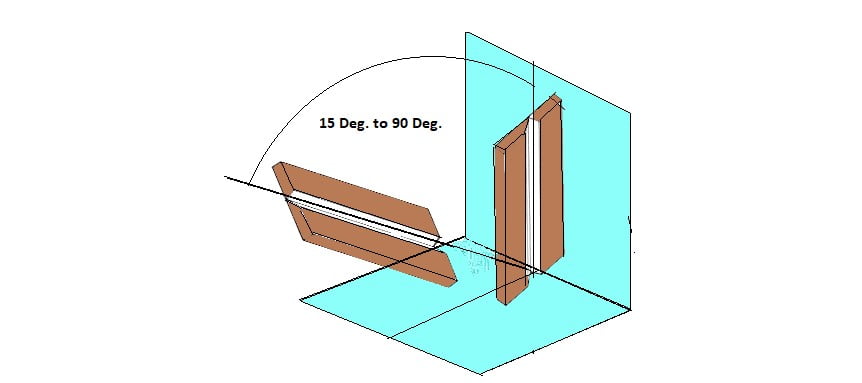
This welding position may be required when you’re working on a large weldment that cannot be easily moved into the flat or horizontal position. Moving up the plate for a vertical weld, the weld puddle will naturally want to sag out of the joint.
What are the different welding positions?
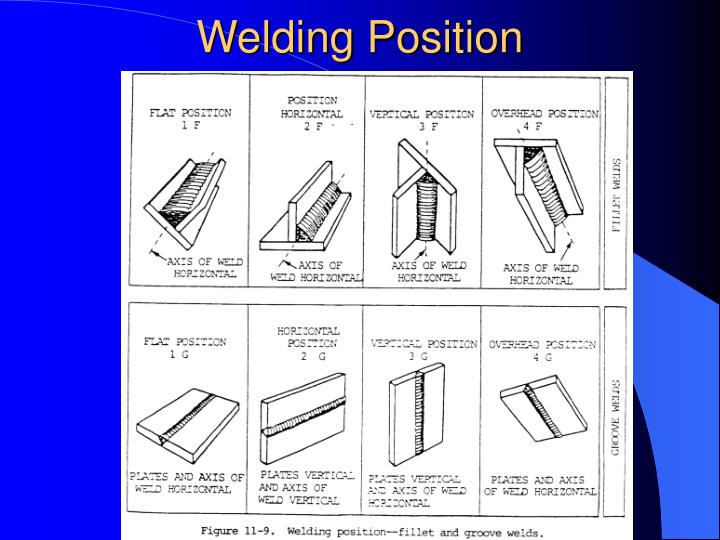
Generally, welding positions are the angles at which metals are joined. They usually fall into four categories: horizontal, vertical, flat, and overhead. Groove and fillet welds have become the most common type of weld. Welders can execute these two welds in any position.
What is the position of the weld axis?
The weld axis is horizontal. How the position is executed depends on the type of weld. For a fillet weld, the weld bead is placed where a vertical and a horizontal piece of metal meet at a 90-degree angle. When performing a groove weld, the weld face will be along a vertical plane. 1 3. Vertical Position
What is vertical and horizontal welding?
PB / 2F | Welding in horizontal-vertical position Fillet welding refers to the process of joining two pieces of metal perpendicular to each other or lap joints which are two pieces of metal that overlap and are welded at the edges.
What is flat and horizontal welding?
With the flat welding position, different metals are first placed flat on a surface, with an electric arc passed over them. In a horizontal direction, the electric arc moves over the workpiece, with the joint's top side simply welded together with the molten material moving downward into its edges.
What are the 4 welding positions?
What Are the Different Welding Positions?Flat position.Horizontal position.Vertical position.Overhead position.
How do you do horizontal welding?
1:389:40Horizontal Stick Welding E7018 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut if you really watch that puddle and make sure that it gets over and hits that other previousMoreBut if you really watch that puddle and make sure that it gets over and hits that other previous bead well you should be okay so let's go ahead and give it a shot and see how it. Goes.
What is flat position?
If you had no positions in the U.S. dollar or your long and short positions cancel each other out, you would be flat or have a flat book. The flat position is considered a positive position, given that although the trader is not making any profits by standing on the sidelines, they are also not making any losses.
What is 1F 2F 3F 4F welding?
An architect's blueprints would indicate the welding symbol. 1 refers to a flat position – either 1F or 1G. 2 refers to a horizontal position – either 2F or 2G. 3 is a vertical position – either 3F or 3G. 4 is an overhead position – either 4F or 4G.
What is a vertical weld?
When you place two pieces together in a way that one end faces downwards toward the ground, while the other points skywards, it is known as the vertical or upright welding position. Welding in such positions requires skills and experience.
What is 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G in welding?
The positions of groove welds are divided into 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G and 6G, respectively indicating flat welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding, overhead welding, horizontal fixed welding of pipeline and 45 °inclined fixed welding of pipeline.
What are the 6 welding positions?
What Are the Welding Symbols for the Different Positions?Welding SymbolWelding PositionWeld Type1 GFlat positionGroove weld2 FHorizontal positionFillet weld2 GHorizontal positionGroove weld3 FVertical positionFillet weld4 more rows
How do you weld vertical position?
11:2012:19Stick Welding Tips Vertical 7018 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSome of the best advice. I can give you for welding a vertical uphill joint like this is use enoughMoreSome of the best advice. I can give you for welding a vertical uphill joint like this is use enough amps that you can hold a tight arc without sticking the rod. Then hold a tight arc. Another.
How many welding positions are there?
Normally, there are four types of welding positions namely horizontal, flat, vertical, and overhead. And the most common types of welds are groove and fillet welds. Welders can perform these two welds in all four positions.
What is overhead position in welding?
The overhead position of welding is the most difficult position to work in. In this position, the welding is performed with the two pieces of metal above the welder and the welder needs to angle himself and the equipment to reach the joints.
How do you weld flat?
0:217:18Simple MIG Welding Technique - Flat, Horizontal, Vertical & OverheadYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo for the flat the one F and the horizontal two F I'm gonna be using a slight pull angle a dragMoreSo for the flat the one F and the horizontal two F I'm gonna be using a slight pull angle a drag angle.
What are types of welding?
There are four main types of welding. MIG – Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), TIG – Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Stick – Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) and Flux-cored – Flux-cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
What does 1G 2G 3G and 4G mean in welding?
The positions of groove welds are divided into 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G and 6G, respectively indicating flat welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding, overhead welding, horizontal fixed welding of pipeline and 45 °inclined fixed welding of pipeline.
What are the different types of welding position?
Normally, there are four types of welding positions namely horizontal, flat, vertical, and overhead. And the most common types of welds are groove and fillet welds. Welders can perform these two welds in all four positions.
What is welding position?
A welding position is a technique that allows a welder to join metals in the position in which they are found or the position in which a specific component will be used. 1. 1. Flat position.
What is flat position welding?
1. Flat position. Also referred to as a “downhand” position, the flat position weld is the easiest and often the first weld that new students learn. The metals to be joined are placed flat, and the welder passes the electric arc over them, moving across the workpiece in a horizontal direction.
Why Are There Different Welding Positions?
Those who’ve never taken welding classes or fused metal in the field might assume a welder simply sits at a workstation and fuses the metal components in front of them, moving freely around the table and repositioning the workpiece as needed.
What Are the Main Types of Welds?
Often considered the most popular type of weld, a fillet weld fuses two pieces of metal at an approximate right angle to each other. 4
What Are the Primary Types of Weld Joints?
When joints and welds are combined, you get weld joints. 4 The location where two or more pieces of metal are joined is what sets weld joints apart. Below are 5 common types of weld joints. 5
What Are the Welding Symbols for the Different Positions?
Let’s bring all of these concepts together so you know which welding position to use when reading the welding symbols on an architect’s blueprints:
What is fillet welding?
Often considered the most popular type of weld, a fillet weld fuses two pieces of metal at an approximate right angle to each other. 4
What position is the metal piece in a flat welder?
For flat welding, the metal piece is in the horizontal position and remains parallel to the welder’s torso as he welds it while he stands in front of the machine.
What are the four positions of welding?
Generally, welding positions are the angles at which metals are joined. They usually fall into four categories: horizontal, vertical, flat, and overhead.
Why is butt welding more complicated than flat welding?
The butt weld in the 2F/2f position may be somewhat more complicated than flat welding because the molten metal flows downward, and the torch is heated upward from the joint. Therefore, a uniform deposit is not possible at joints. Generally, welders should align the metals and secure the joint at both ends.
What is a F weld?
F-weld (F) – F-welding can be used to weld two separate parts of metal straight up or at a slight angle. Groove Welds (G)- Groove Welds (G) can be made in the groove if they can penetrate through the lower surface. This type of weld calls for full penetration to yield strong welds.
How many stages of welding 5G?
By doing so, welders are more productive and produce better welding results. When welding 5G, welders travel through three stages, beginning at flat, then horizontal, and concluding with overhead.
What is 5G welding?
Pipe welding is done in a 5G position in which the pipe axis does not turn or rotate horizontally. 5G stands for “ groove welding ” on the American Welding Society/American Society of Mechanical Engineer’s standard; ISO/EN standard calls it PF.
Where is tack weld used?
Fabrication or installation of pipe and pipelines most often takes place with a tack weld position commonly used in chemical plants, oil refineries, industrial plants, and any other similar businesses that use pipe and pipelines.
Pipe and Plate Weld Joint Positions
Normally there are six welding positions with certain numbers and letter i.e. 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G/6GR. All the positions are used in various angles and shapes while performing welding. Generally, the ways and ideas of welding are similar in different countries.
6G Welding Positions-
This is one of the hardest types of welding positions for welders to perform. The position is a pre-condition for getting certified. To some extent, this position is similar to 5G/PH/PJ but the pipe stands at 45° to the other one. Other names are 6G Uphill/H-L045 and 6G Downhill/J-L045 Position.
What is vertical position welding?
For verticals position welds, both the weld & the plate will be located vertically. One of the major problems when performing these welds is the molten metal flowing down and accumulating. Welding in a vertical position downhill or uphill can prevent this problem.
What Is a Welding Position?
Welding position is a technique that allows the welder to join metal in the position in which they are found or position in which specifics components would be used. Often this can be on the ceiling, in a corner, or on the floor.
Why Are There Different Welding Positions?
Those who have never taken a welding class or fielded fused metal may assume that a welder simply sits at a workstation and fuses metal components in front of them, moving freely around the table, and Restores the workpiece as needed.
What is the 1G 2G 5G 6G Pipe Welding Positions?
In the constructions phase of a project in the oil & gas industry, we often find welding activities on pipes or welding on tanks. In order to maintain the quality of welding, professional organizations (ASME, AWS, ISO, JWES) make rules and classifications of welding positions.
Why is welding important in 1G position?
Welding positions are important variables to determine weld quality. If welders have the qualification of 1G position, he is not allowed to perform welding in a more difficult condition such as 6G positions.
What is 1G welding?
The 1G welding position is a position where the pipe is in horizontal positions & the pipe can be rotated against the horizontals axis or the X-axis. The welder does the welding from the top of the pipe. The position of the welder does not change.
What angle should the torch be held at when welding?
This position can be used to obtain either a fillet or a groove weld. For a fillet weld, the torch will be held at a 45-degree angle. The weld axis is horizontal. How the positions are executed depends on the type of weld.
How to weld horizontally?
In horizontal welding, position the electrode so that it points upward at a 5- to 10-degree angle in conjunction with a 20-degre e travel angle (fig. 7-24). Use a narrow weaving motion in laying the bead. This weaving motion distributes the heat evenly, reducing the tendency of the molten puddle to sag. You should use the shortest are length possible, and when the force of the are undercuts the plate at the top of the bead, lower the electrode holder a little to increase the upward angle.
What is a chain intermittent weld?
Chain-intermittent or staggered-intermittent fillet welds, as shown in figure 7-29, are used on long tee joints. Fillet welds of these types are for joints where high weld strength is not required; however, the short welds are arranged so the finished joint is equal in
What is fillet weld?
A fillet weld is used in making the tee joint, and a short arc is necessary to provide good fusion at the root and along the legs of the weld (fig. 7-26, view A). Hold the electrode at an angle of 45 degrees to the two plate surfaces (fig. 7-26, view B) with an incline of approximately 15 degrees in the direction of welding.
How many passes to weld light plates?
When practical, weld light plates with a fillet weld in one pass with little or no weaving of the electrode. Welding of heavier plates may require two or more passes in which the second pass or layer is made with a semicircular weaving motion, as shown in figure 7-27. To ensure good fusion and the prevention of undercutting, you should make a slight pause at the end of each weave or oscillation.
How many degrees should you hold the electrode in lap joints?
In making lap joints on plates of different thickness, you should hold the electrode so that it forms an angle of between 20 and 30 degrees from the vertical
Is welding difficult in horizontal position?
An inexperienced welder usually finds the horizontal position of are welding difficult, at least until he has developed a fair degree of skill in applying the proper technique. The primary difficulty is that in this position you have no "shoulder" of previously deposit ed weld metal to hold the molten metal.
Can you weld in the flat position?
You will discover that it is impossible to weld all pieces in the flat position. Often the work must be done in the horizontal position. The horizontal position has two basic forms, depending upon whether it is used with a groove weld or a fillet weld. In a groove weld, the axis of the weld lies in a relative horizontal plane and the face of the weld is in a vertical plane (fig. 7-22). In a fillet weld, the welding is performed on the upper side of a relatively horizontal surface and against an approximately vertical plane (fig. 7-23).
What are the different welding positions?
The above-mentioned welding positions, i.e, flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead are the most basic types of welding positions used for plate welding. However, these do not completely describe pipe welding positions. As far as pipe welding is concerned, there are four types of piping welding positions. They are: 1 Horizontal Rolled Pipe Weld Position 1G 2 Vertical Position 2G 3 Horizontal Fixed Position 5G, and 4 Inclined Weld Position 6G
What is vertical welding?
In vertical position welding, the weld axis is almost vertical. Both the weld and the plate will lie vertically. For welding vertical surfaces, the molten metal runs downward by gravity and pile up. Welding in an upward or downhill vertical position can resolve this problem.
Why care about Pipe Welding Positions?
Welding position is one of the most important variables that determine weld quality. For each pipe weld position, welders need to undergo certification processes. If a welder is qualified to weld in a 1G position, he is not allowed to weld hard positions like the 6G position. But on the other hand, if the welder is certified for the hardest 6G position then he can work in the 1G position. So, expertise over each weld position levels up a welder’s skills and qualifications.
What is welding position 2F?
Welding position 2F is for a fillet weld where the welding is performed on the upper side of a horizontal surface and against an approximately vertical surface keeping to welding torch at a 45-degree angle.
Why is welding important?
The welding position is very important as it affects the flow of molten filler material. It’s desirable that the welding operator understands the types of welding positions to smoothly accomplish the task. Also, at a certain position of the welder different welding processes are performed. In this article, we will learn about ...
How to get rid of a high crown in welding?
In overhead welding positions, the metal deposited tends to drop or sag on the plate that results in a bead with a high crown. To get rid of this difficulty, the molten puddle should be kept small. When the puddle becomes too large, one can remove the flame momentarily for molten metal to cool.
What is flat welding?
The flat welding position is easier and faster and the molten metal is drawn downward. Flat welding position is also known as down hand welding position.
