
What does HUVs stand for?
Hypocomplementemic Vasculitis; McDuffie Syndrome Hypocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis Syndrome (HUVS) is a rare type of chronic autoimmune inflammation of small blood vessels and abnormally low levels of complement. HUVS is often associated with systemic diseases such as COPD, systemic lupus, and Sjögren syndrome.
What is the pathophysiology of human ultraviolet (HUV) infection?
HUV causes recurrent episodes of hives (urticaria) and painful skin lesions that itch or burn. Individuals with HUV may also have systemic, multiorgan involvement, causing arthritic joint pain; pulmonary (lung) disease; ocular (eye) inflammation; kidney inflammation; or various other symptoms.
What are the two criteria for a diagnosis of HUV?
Diagnosis Diagnosis. Listen. A diagnosis of HUV requires the presence of the two major criteria, as well as at least two minor criteria. The major criteria are hives (urticaria) for at least 6 months, and low levels of complement system proteins in the blood.
What is the pathophysiology of herpes simplex virus (HUV)?
It is thought to develop due to an abnormal immune system response involving specific proteins that work together to fight organisms that cause infections. In some cases HUV may be associated with an underlying infection or systemic diseases such as systemic lupus, Sjögren's syndrome, monoclonal gammopathy, or blood disorders.

How is HUVS diagnosed?
HUV is diagnosed where the patient has the main symptoms of Urticarial Vasculitis combined with lower than normal levels of C1q complements and raised levels of anti-C1q antibodies (antibodies that attack the C1q complements).
What triggers urticarial vasculitis?
In urticarial vasculitis, the inflammatory process may be set in motion by an infection or virus such as hepatitis, a drug reaction, or the existence of cancer or another autoimmune disorder such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis or Sjögren's syndrome.
What causes Hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis?
Both genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role in causing HUV. It generally occurs sporadically, but familial cases have been reported. It is thought to develop due to an abnormal immune system response involving specific proteins that work together to fight organisms that cause infections.
How rare is HUVS?
HUVS or McDuffie syndrome is an uncommon form of autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis that is characterized by urticaria and persistent hypocomplementemia. It is a rare disease with a reported incidence of 0.5/100,000 persons [5].
How do you get rid of urticarial vasculitis?
Cutaneous symptoms of urticarial vasculitis are treated with oral antihistamines and can also require non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, oral corticosteroids, colchicine, chloroquine and/or dapsone. Treatment is challenging due to the limited effect and side effects of current treatments.
What is the best treatment for urticarial vasculitis?
The skin manifestations of Urticarial Vasculitis may simply be treated with antihistamines and NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen. Hydroxychloroquine, an anti-malarial, dapsone and colchine can be tried especially for relapsing disease. Corticosteroids work well but relapse can occur on withdrawal and they are more toxic.
What does a vasculitis rash look like?
Common vasculitis skin lesions are: red or purple dots (petechiae), usually most numerous on the legs. larger spots, about the size of the end of a finger (purpura), some of which look like large bruises. Less common vasculitis lesions are hives, an itchy lumpy rash and painful or tender lumps.
What is the rarest form of vasculitis?
Microscopic polyangiitis is a rare and potentially serious long-term type of vasculitis that most often develops in middle-aged people. It can affect any organ, but particularly affects the lungs, kidneys and nerves. It can cause: a rash.
Is urticarial vasculitis a disability?
HUVS automatically qualifies you for social security disability benefits under the Social Security Administration's guidelines. If you or a loved one is diagnosed with HUVS, then you are considered disabled for at least 24 months from the date of diagnosis.
How can you tell the difference between urticaria and vasculitis?
Major difference between urticarial vasculitis and urticaria is the duration of lesions. Urticarial lesions regress in 24 hours, but UV lesions persist longer than 24 hours.
Is urticarial vasculitis life threatening?
Urticarial vasculitis associated with hypocomplementemia is associated with a greater incidence of coexisting disease (ie, angioedema, connective-tissue disease [primarily SLE], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Mortality is rare.
How do you test for urticarial vasculitis?
Perform skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of urticarial vasculitis. Recent lesions, less than 48 hours in onset, are the best for biopsy. Biopsy of a lesion of less than 24 hours' duration is best for direct immunofluorescence.
Do antihistamines help vasculitis?
Antihistamines may serve as an adjunctive agent to relieve the itching or burning associated with urticarial vasculitis. Given alone, they usually provide only symptomatic relief.
Is urticarial vasculitis contagious?
Vasculitis is not contagious. One cannot acquire vasculitis from contact with a vasculitis patient. In addition, despite the fact that genes probably play a role in susceptibility to some forms of vasculitis, it is unusual for vasculitis to occur in more than one member of the same family.
What are symptoms of autoimmune inflammatory vasculitis?
The symptoms of vasculitis are many because of the wide variety of body systems it can affect. Depending on the system involved there may be muscle pain, joint pain, fever, weight loss, loss of appetite (anorexia), headache, or generalized weakness.
Is vasculitis an autoimmune disease?
Vasculitis is thought to be an autoimmune disease, which means the body comes under attack by its own immune system. In vasculitis, the immune system attacks blood vessels. Some cases of vasculitis are caused by reactions to medicines.
Who are affected?
NUV is most common between the ages of 30-40 and is found in women more than men. HUV and HUVS are almost exclusively found in women.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptom is a recurring urticarial (“stinging nettle”) rash that lasts for longer than 24 hours and “burns” rather than “itches”, leaving marks behind on the skin when it clears.
What is the best treatment for urticarial vaculitis?
Milder cases of Urticarial Vasculitis may simply be treated with antihistamines and NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen. Corticosteroids such as Prednisolone might be used for more persistent cases. However for the more severe forms of Urticarial Vasculitis, steroids such as Prednisolone are usually prescribed to reduce inflammation as well as immunosuppressants such as Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide or Mycophenolate Mofetil (CellCept).
What is a HUV?
HUV is diagnosed where the patient has the main symptoms of Urticarial Vasculitis combined with lower than normal levels of C1q complements and raised levels of anti-C1q antibodies (antibodies that attack the C1q complements). HUV is a more severe form of Ur ticarial Vascul itis and is likely to include symptoms such as purple or dark red spots or rash on the skin (a typical vasculitic rash); arthritic joint pain; breathing difficulties such as asthma, and stomach pains. Some regard HUV as a form of SLE (Lupus), although HUV patients usually test Anti-Nuclear Antibody (ANA) negative instead of the normal positive result for Lupus patients.
What is NUV in a patient?
NUV is diagnosed where a patient has the main symptoms of Urticarial Vasculitis combined with normal levels of C1q complements. NUV is generally the least severe form of Urticarial Vasculitis. It is less likely to be associated with any other symptoms.
What is the prognosis for urticarial vaculitis?
The overall prognosis in Urticarial Vasculitis depends on the severity of the disease and the amount of damage that has been done to organs, especially the lungs. The main risk to patients appears to be Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
What are the three subtypes of urticarial vasculitis?
HUV, HUVS, and NUV are the three subtypes of Urticarial Vasculitis.
What is hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome?
Hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome is characterized as the chronic inflammation of blood vessels, with painful, itchy, burning skin lesions (urticarial), and may involve other organs.
What are the symptoms of hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis?
Reports may be affected by other conditions and/or medication side effects. We ask about general symptoms (anxious mood, depressed mood, fatigue, pain, and stress) regardless of condition.
Is lithium carbonate good for ALS?
Lithium carbonate wasn't helping ALS patients, and we learned it faster than the clinical trials did. Read about it in Nature .
What are the physical findings of HUVS?
Physical findings: HUVS usually involves the skin with painful urticaria (hives), and may cause inflammatory changes in joints, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, heart, and eyes.
What is a HUVS?
Hypocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis Syndrome (HUVS) is a rare type of chronic autoimmune inflammation of small blood vessels and abnormally low levels of complement. HUVS is often associated with systemic diseases such as COPD, systemic lupus, and Sjögren syndrome.
What is the treatment for HUVS?
The treatment of HUVS is determined by the organ involved and severity of the disease, and may include combinations of antihistamines, glucocorticoids and other immunosuppressive medications. COPD and cardiac valvular defects may require specific treatment.
Does smoking cause lung disease?
Lung disease results in significant morbidity and mortality, and is made worse by smoking. Kidney involvement with glomerulonephritis may ultimately result in end stage renal disease with need for kidney transplant. Death may also occur due to acute laryngeal edema. TREATMENT.
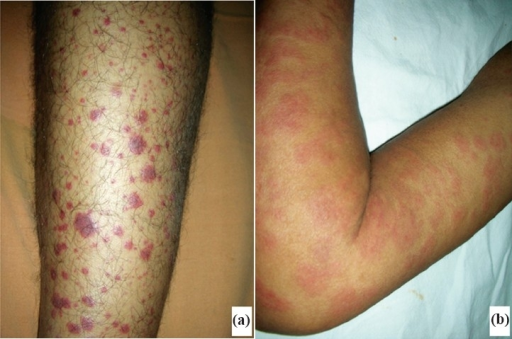
Normocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis
Hypocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis
- HUV is diagnosed where the patient has the main symptoms of Urticarial Vasculitis combined with lower than normal levels of C1q complements and raised levels of anti-C1q antibodies (antibodies that attack the C1q complements). HUV is a more severe form of Urticarial Vasculitis and is likely to include symptoms such as purple or dark red spots or rash on the skin (a typical …
Hypocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis Syndrome
- HUVS is a very rare and severe form of Urticarial Vasculitis. HUVS patients have more extensive complement abnormalities (low circulating 3rd and 4th complement components). As well as the symptoms of HUV, patients will suffer from systemic problems such as: episcleritis or uveitis (bloodshot or inflamed eyes) (found in 30 per cent of patients); mi...
Who Are Affected?
- NUV is most common between the ages of 30-40 and is found in women more than men. HUV and HUVS are almost exclusively found in women.
What Is The Aetiology (Cause)?
- The cause of Urticarial Vasculitis is not known in 50 per cent of cases. However it can be associated with or triggered by autoimmune/connective tissue diseases like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE or simply Lupus) Rheumatoid Arthritis, or occur in the context of a systemic vasculitis syndrome, such as Churg Strauss syndrome (Eosinophillic Granulomatosis with Polya…
What Are The Symptoms?
- The main symptom is a recurring urticarial (“stinging nettle”) rash that lasts for longer than 24 hours and “burns” rather than “itches”, leaving marks behind on the skin when it clears.
Diagnosis
- As in other types of vasculitis, diagnosis will depend on the doctor recognising the pattern of symptoms and examination findings. Blood is commonly taken to test for raised levels of “C-reactive protein” (CRP) and “Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate” (ESR) which indicate inflammation in the body. Skin and kidney biopsies may also be taken to confirm the diagnosis. Testing for C1q, …
Treatment
- Milder cases of Urticarial Vasculitis may simply be treated with antihistamines and NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen. Corticosteroids such as Prednisolone might be used for more persistent cases. However for the more severe forms of Urticarial Vasculitis, steroids such as Prednisolone are usually prescribed to reduce inflammation as well as immunosuppressants such as Azathioprin…
Drugs and Side Effects
- For information on the main drugs prescribed for Urticarial Vasculitis see: 1. Azathioprine 2. Cyclophosphamide 3. Methotrexate 4. Mycophenolate Mofetil (Cellcept) 5. Rituximab 6. Steroids For information on other drugs used in the treatment of vasculitis see Glossary of drugs and side effects.
Treatments – Procedures
- Plasma exchange or plasmapheresis This treatment is sometimes used in patients with severe vasculitis where antibodies in the blood are thought to be important in causing the disease. The treatment involves removing antibodies from the blood using a machine and returning the “cleaned” blood back to the patient. The treatment may necessitate giving blood products to the …