How do hydrophilic emulsifiers work?
Hydrophilic emulsifiers work by detergent action. After the penetrant dwell time, parts are pre-rinsed with water before application of the hydrophilic emulsifier. Parts are immersed in a mildly agitated tank of hydrophilic emulsifier.
What are the different types of emulsifiers?
There are two major types of emulsifiers as lipophilic emulsifiers and hydrophilic emulsifiers. The key difference between lipophilic and hydrophilic emulsifier is that lipophilic emulsifiers work with oil-based emulsions whereas hydrophilic emulsifiers work with water-based emulsions.
What are lipophilic emulsifiers?
Lipophilic emulsifiers are emulsifying agents that work with oil-based emulsions. These chemical reagents are important in removing a penetrant when a defect due to over-washing of the emulsion is a concern. Here, lipophilic emulsifiers can make the excess penetrant more removable with washing using water.
Why is hydrophilic emulsifier used in the penetrant removal process?
Hydrophilic emulsifier is necessary to remove excess penetrant from the test surface. The Method D penetrant process allows for tighter control of the penetrant removal step and improved sensitivity of the fluorescent penetrant process. Method D fluorescent penetrant inspection utilizes Hydrophilic Emulsifier to remove the surface penetrant.
How to make 5% emulsifier?
What supplies are needed for hydrophilic emulsifier concentrate?
Why is the method D hydrophilic?
How does method D penetrant inspection work?
Why is it important to control the penetrant rinse time?
What is the refractometer reading of 14?
What is the concentration of hydrophilic emulsifier?
See 2 more

What is a lipophilic emulsifier?
Lipophilic emulsifiers are emulsifying agents that work with oil-based emulsions. These chemical reagents are important in removing a penetrant when a defect due to over-washing of the emulsion is a concern. Here, lipophilic emulsifiers can make the excess penetrant more removable with washing using water.
Are emulsifiers hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
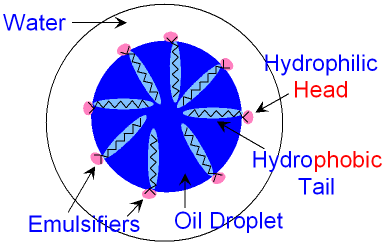
A type of surfactant (see Sidebar), emulsifiers contain both a hydrophilic (water-loving, or polar) head group and a hydrophobic (oil-loving, or nonpolar) tail. Therefore, emulsifiers are attracted to both polar and nonpolar compounds.
What are the 4 types of emulsifying agents?
Commonly used emulsifying agents include polymers (Spans and Tweens), sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate, and tragacanthins (Haba et al., 2014).
What is emulsifier in dye penetrant?
What is an Emulsifier. An emulsifier is an agent that enables removal of excess post emulsifiable penetrant on part surfaces with water. Proper emulsification and rinse times allow removal of excess surface penetrant while any penetrant in discontinuities is not removed.
What are 3 emulsifiers examples?
Some examples of emulsifiers are lecithin, soy lecithin, diacetyl tartaric acid ester of monoglyceride, Mustard, sodium stearoyl lactylate, and sodium phosphates.
What is the role of emulsifier?
Emulsifiers thus form and stabilize oil-in-water emulsions (e.g., mayonnaise), uniformly disperse oil-soluble flavour compounds throughout a product, prevent large ice-crystal formation in frozen products (e.g., ice cream), and improve the volume, uniformity, and fineness of baked products.
What is a natural emulsifying agent?
Natural Emulsifying Agents are substances derived from either vegetable sources such as acacia, tragacanth, alginates, Chondrus, xanthan, and pectin or animal sources such as gelatin, egg yolk, casein, wool fat, cholesterol, wax, and lecithin.
What are the 3 types of emulsions?
There are three kinds of emulsions: temporary, semi-permanent, and permanent. An example of a temporary emulsion is a simple vinaigrette while mayonnaise is a permanent emulsion. An emulsion can be hot or cold and take on any flavor from sweet to savory; it can be smooth or have a bit of texture.
What are the 2 types of emulsions?
Emulsions easily fall into two categories: an oil-in-water (O/W) or water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion, depending on the continuous phase. The type of emulsion that forms depends largely on the volume ratio of the two materials, with the more abundant phase forming the continuous phase.
What is the primary advantage of hydrophilic emulsifier?
Since it is more sensitive than the lipophilic post emulsifiable method it has made the later method virtually obsolete. The major advantage of hydrophilic emulsifiers is that they are less sensitive to variation in the contact and removal time.
Which emulsifier is water based?
Reactsurf® 0092 is an alkylphenol ethoxylate (APE)-free and non-ionic reactive water-based emulsifier for solid epoxy resins mainly for use in industrial coatings or binders.
What is HLB value?
Hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) is the balance of the size and strength of the hydrophilic and lipophilic moieties of a surfactant molecule. The HLB scale ranges from 0 to 20. In the range of 3.5 to 6.0, surfactants are more suitable for use in W/O emulsions.
How do you know if something is hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Something defined as hydrophilic is actually attracted to water, while something that is hydrophobic resists water. This means when hydrophobic items come in contact with liquids, water is encouraged to bead up and roll off the surface- almost pushing it away like a magnet pushes away metal objects.
What is hydrophobic and hydrophilic examples?
Many metal surfaces are hydrophilic, for example aluminium foil. Hydrophobic surfaces tend to repel water, causing it to form droplets; lotus leaves are incredibly hydrophobic and cause water to bead, due to their surface structure.
What makes something hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Materials with a special affinity for water — those it spreads across, maximizing contact — are known as hydrophilic. Those that naturally repel water, causing droplets to form, are known as hydrophobic.
What types of substances are hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic substances are composed of non-polar molecules that repel bodies of water and attract other neutral molecules and non-polar solvents. Examples of these molecules are alkanes, oils and fats in general.
How does lipophilic emulsifier work?
The lipophilic emulsifier works primarily by diffusion into the post emulsifiable penetrant. Lipophilic emulsifiers are supplied in a ready to use form by the manufacturer. No pre-rinse step takes place. After the penetrant dwell time is completed, lipophilic emulsifier is usually applied by dip, and then the lipophilic emulsifier drains from the parts. The emulsification and drain step is timed to prevent over emulsification and possible removal of penetrant from discontinuities. Parts go through a water rinse immediately after the emulsification time.
What is an emulsifier?
An emulsifier is an agent that enables removal of excess post emulsifiable penetrant on part surfaces with water. Proper emulsification and rinse times allow removal of excess surface penetrant while any penetrant in discontinuities is not removed.
Why do post emulsifiable penetrants resist removal from discontinuities during the water rinse step?
Post emulsifiable penetrants resist removal from discontinuities during the water rinse step because of the lack of surfactants in their formulas . However, an emulsifier is required to remove excess post emulsifiable penetrant from the part surface during the penetrant removal step.
Do post emulsifiable penetrants rinse?
Unlike water washable penetrants (Method A), post emulsifiable penetrants will not rinse from part surfaces with water alone. An emulsifier is required for Methods B and D penetrant processes.
Can hydrophilic emulsifier be applied by spray?
Hydrophilic emulsifier may also be applied to parts by spray. With spray application of hydrophilic emulsifier, the pre-rinse step is usually omitted. The hydrophilic emulsification step is followed by a final water rinse.
How to make 5% emulsifier?
Using a 100 ml graduated cylinder, prepare the 5% emulsifier solution by adding 5 ml of hydrophilic emulsifier to 95 ml of water for a total of 100 ml of 5% emulsifier solution. Adding the hydrophilic emulsifier to the water will facilitate the mixing of the solution. Pour the 5% emulsifier solution into a labeled beaker. Follow this procedure to prepare the remaining known emulsifier concentrations.
What supplies are needed for hydrophilic emulsifier concentrate?
Supplies needed are unused hydrophilic emulsifier concentrate as supplied by manufacturer, graduated cylinder, and several beakers. Alternate method: volumetric pipets and volumetric flasks may be used in place of graduated cylinders and beakers.
Why is the method D hydrophilic?
The Method D hydrophilic post emulsifiable penetrant process offers tighter control of surface penetrant removal because the post emulsifiable penetrant is not removable with water alone. Hydrophilic emulsifier is necessary to remove excess penetrant from the test surface. The Method D penetrant process allows for tighter control of the penetrant removal step and improved sensitivity of the fluorescent penetrant process.
How does method D penetrant inspection work?
Method D fluorescent penetrant inspection utilizes Hydrophilic Emulsifier to remove the surface penetrant. Hydrophilic Emulsifier is supplied as a concentrate by the manufacturer, and the hydrophilic emulsifier is diluted with water prior to use. The steps in the Method D penetrant process are penetrant application, penetrant dwell, water spray pre-rinse, immersion in the diluted hydrophilic emulsifier solution and then a water spray post rinse, followed by hot air drying, developer application, and inspection under UV light. The hydrophilic emulsifier is used at the concentration recommended by the manufacturer, typically 20% by volume for immersion applications.
Why is it important to control the penetrant rinse time?
In the water washable penetrant process, Method A, it is critical to control the penetrant rinse time since water washable penetrant has the potential to be over washed. Decreased sensitivity and decreased brightness of penetrant indications may result from over removal of water washable penetrant.
What is the refractometer reading of 14?
Refractometer reading of 14 corresponds to 17% hydrophilic emulsifier concentration.
What is the concentration of hydrophilic emulsifier?
The hydrophilic emulsifier is used at the concentration recommended by the manufacturer, typically 20% by volume for immersion applications.
