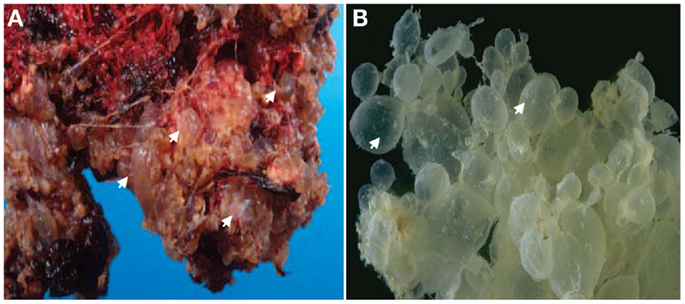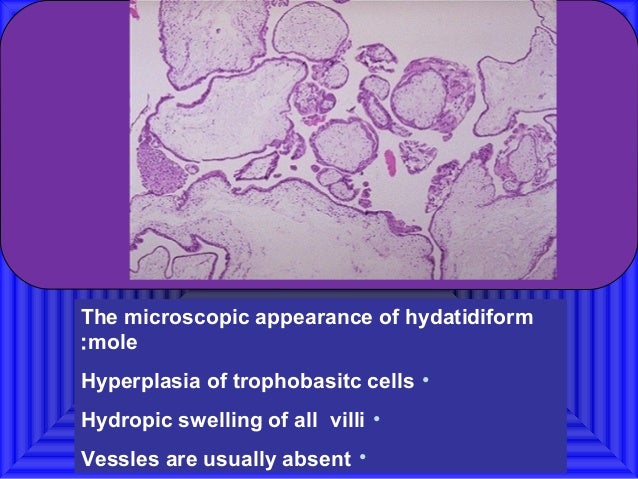
What are hydropic villi and hydatidiform villi?
Hydropic villi are an abnormality of chorionic villi. Hydropic villi in the placenta are fluid-filled swollen chorionic villi that lack blood vessels. They are seen in an abnormal pregnancy called a molar pregnancy. A hydatidiform mole consists of edematous hydropic villi with abnormal genetic content.
What are chorionic villi in placenta?
Chorionic villi are the small outgrowths which looks like finger present inside the placenta. Chorionic villi also contains genetic material which is same as present inside the cells of fetus. The term chorion means a membrane present during pregnancy between mother and fetus. And this membrane contains villi on it.
What is the function of chorionic villi?
The term chorion means a membrane present during pregnancy between mother and fetus. And this membrane contains villi on it. This membrane is responsible for the covering of embryo in many mammals, birds and reptiles. Chorion also helps in the development of fetus. Chorionic villi are considered as the main functional unit of placenta.
What is hydropic degeneration of the placenta?
Hydropic degeneration of the placenta is a phenomenon where numerous cystic spaces are formed within the placenta which is often accompanied by placental enlargement. It can occur in a number of situations which include.

What is Hydropic degeneration of villi?
These findings indicate that so-called "hydropic degeneration of villi" represents an intravillous accumulation of strongly sulfated mucosubstances rather than the result of the accumulation of water.
What is Hydropic degeneration?
Hydropic degeneration is a result of ion and fluid homestasis that lead to an increase of intracellular water. The vacuolated swelling of the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes of the GNPs treated rats might indicate acute and subacute liver injury induced by the GNPs.
What does Hydropic change mean?
Hydropic change or cellular swelling or vacuolar degeneration is one of the factors of reversible cell injury, which can be appreciated under light microscope.
What is Hydropic abortion?
The hydropic abortus (HA) yields substantially less tissue on curettage and presents as a missed or spontaneous abortion, typically at 6-14 weeks gestation. Beta HCG is not elevated, and the uterine size is either normal or low for dates.
Is Hydropic degeneration reversible or not?
Cellular swelling (synonyms: hydropic change, vacuolar degeneration, cellular edema) is an acute reversible change resulting as a response to nonlethal injuries.
What does Hydropic mean?
Medical Definition of hydropic 1 : exhibiting hydrops especially : edematous. 2 : characterized by swelling and taking up of fluid —used of a type of cellular degeneration.
What is cell degeneration?
Nonlethal injury to a cell may produce cell degeneration, which is manifested as some abnormality of biochemical function, a recognizable structural change, or a combined biochemical and structural abnormality. Degeneration is reversible but may progress to necrosis if injury persists.
What happens when your cells swell?
Cell swelling activates compensatory processes that lead to an efflux of osmolytes and a reduction of cell volume. This is called a regulatory volume decrease (RVD).
What are the two causes of cellular injury?
Physical agents capable of causing cell injury include mechanical trauma, extremes of temperature (burns and deep cold), sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, radiation, and electric shock. Chemical Agents and Drugs. The list of chemicals that may produce cell injury defies compilation.
What does p57 positive mean?
The p57 expression pattern was interpreted as 'discordant' when there was any combination/admixture of negative and positive results for villous stromal cells and cytotrophoblast within individual villi, including positive staining in cytotrophoblast and negative staining in villous stromal cells, or vice versa.
How is hydatidiform mole diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects a molar pregnancy, he or she will order blood tests, including one to measure the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) — a pregnancy hormone — in your blood. He or she will also recommend an ultrasound.
What is a trophoblastic tumor?
A placental-site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT) is a rare type of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia that forms where the placenta attaches to the uterus. The tumor forms from trophoblast cells and spreads into the muscle of the uterus and into blood vessels. It may also spread to the lungs, pelvis, or lymph nodes.
What is degeneration in pathology?
Degeneration refers to the process by which tissue deteriorates and loses its functional ability due to traumatic injury, aging and wear and tear.
What is cell degeneration?
Nonlethal injury to a cell may produce cell degeneration, which is manifested as some abnormality of biochemical function, a recognizable structural change, or a combined biochemical and structural abnormality. Degeneration is reversible but may progress to necrosis if injury persists.
What is hyaline degeneration?
Medical Definition of hyaline degeneration : tissue degeneration chiefly of connective tissues in which structural elements of affected cells are replaced by homogeneous translucent material that stains intensely with acid stains.
What are signs of irreversible cell injury?
Irreversiblecellular swelling.nuclear chromatin clumping.ribosomal detachment. secondary to decreased protein synthesis.membrane blebbing.fatty change.
What is a chorionic villi?
Chorionic Villi Definition, Development, Miscarriage, Histology. Chorionic villi are the small outgrowths which looks like finger present inside the placenta. Chorionic villi also contains genetic material which is same as present inside the cells of fetus. The term chorion means a membrane present during pregnancy between mother and fetus.
What happens to villi in the first stage of development?
At the initial stage of development of villi, each villi follow the same procedure. Later, the structural morphology and the functions associated are changed. In week two (primary villi), trophoblastic cells form villi. In week three (secondary villi), the mesoderm from extra embryonic turns into villi and covers the whole sac also forms chorionic plate. In week four (tertiary villi), capillary network forms in villi which connects with the vessels of placenta and forms a stalk which connects both. The stalk contains:
What is hydropic degeneration?
hydropic degeneration a form in which the epithelial cells absorb much water. lattice degeneration of retina a frequently bilateral, usually benign asymptomatic condition, characterized by patches of fine gray or white lines that intersect at irregular intervals in the peripheral retina, usually associated with numerous, round, ...
Which type of degeneration forms when the epithelial cells absorb much water?
hydropic degenerationa form in which the epithelial cells absorb much water.
What are the only significant lesions in the kidneys?
Histologically, the only significant lesions are vacuolar hydropic degeneration and pyknosis of the epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubes of the kidneys (PASSOS, 1983).
What is the term for a regressive change in cells in which the cytoplasm takes on a?
hepatolenticular degeneration Wilson's disease. hyaline degeneration a regressive change in cells in which the cytoplasm takes on a homogeneous, glassy appearance; also used loosely to describe the histologic appearance of tissues. hydropic degeneration a form in which the epithelial cells absorb much water.
What are the hallmarks of hyperkeratosis?
Histological hallmarks include hyperkeratosis with follicular plugging of stratum corneum but thinning and flattening of stratum malpighii with hydropic degenerationof basal cells and lymphocytic infiltrate arranged along the dermal-epidermal junction, perivascular and periappendageal structure.1
What is the definition of caseous degeneration?
2). cerebromacular degeneration ( cerebroretinal degeneration) 1. degeneration of brain cells and of the macula retinae, as occurs in tay-sachs disease. 2. any lipidosis with cerebral lesions and degeneration of the retinal macula. 3. any form of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis.
What causes intracellular water to accumulate?
Swelling of cells due to injury to the membranes affecting ionic transfer; causes an accumulation of intracellular water.
What is Chorionic Villi?
Fetal development occurs within an amniotic sac inside the maternal uterus to cushion, nourish, and protect the developing fetus. The amniotic sac is composed of an inner layer (the amnion) and an outer layer called the chorionic membrane.
Chorionic Villi Function
The chorionic villi function to support and nourish the developing fetus. The chorionic villi in the placenta are microscopic finger-like projections that reach into the inner lining of the maternal uterus (endometrium).
Chorionic Villi Sampling
The definition of chorionic villus sampling is a procedure performed in early pregnancy to determine fetal genetic makeup. This is because chorionic villi contain the chromosomes and DNA of the developing fetus. Chorionic villus sampling is also a procedure used to evaluate for fetal genetic abnormalities.
Role Play Activity
The chorionic villi are made of a series of blood vessels that help to transfer nutrients and oxygen from the mother's bloodstream to the future baby throughout pregnancy. Imagine you are a doctor, and you have a pregnant woman in your office that needs a chorionic villi sampling.
What is the role of chorionic villi in the diagnosis of a baby?
Chorionic villi exchange nutrients and oxygen between a mother and fetus and are crucial in the diagnosis of many illnesses that could affect a baby. Explore the definition of chorionic villi and learn about sampling. Updated: 09/13/2021
Why does a chorionic villi test need to be done?
She needs the chorionic villi sampling done because of her age and the fact that she has a history of chromosomal abnormalities running in her family. The test is optional, but in her case, is recommended by the doctors.
When can you do chorionic villi sampling?
The advantage of the chorionic villi sampling is that it can be done any time after 10 weeks of pregnancy. She would have to wait until around week 20 for an amniocentesis.
Why is the presence of neutrophils insufficient?
Must demonstrate infectious organisms in placental parenchyma or membranes; the presence of neutrophils is insufficient because they may be a reaction to necrotic decidua
Why do we remove residual trophoblastic tissue?
D&C to remove residual trophoblastic tissue to confirm intrauterine pregnancy and rule out gestational trophoblastic disease
What percentage of a woman's hCG is induced intrauterine loss?
Naturally occurring intrauterine loss is observed in 10 - 15% of clinically recognized pregnancies and 22% of pregnancies detected via hCG levels. May be due to fetal factors (e.g. genetic abnormalities) or maternal factors (e.g. anatomic, infectious or autoimmune)
Is gestational hyperplasia intrauterine?
Decidual reaction, gestational hyperplasia (glandular secretion, stromal edema) and Arias-Stella reaction are suggestive of pregnancy ( not necessarily intrauterine) but are nonspecific (also occur with hormones)