
What is 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
From Genetics Home Reference. Learn more 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an inherited disorder that affects the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys and produce a variety of hormones that regulate many essential functions in the body.
What is phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that results in intolerance to the dietary intake of the essential amino acid phenylalanine. It occurs in approximately 1:15,000 individuals. Deficiency of this enzyme produces a spectrum of disorders including classic phenylket …
What is disease 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency?
Disease definition. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency is a very rare form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH; see this term) characterized by glucocorticoid deficiency, hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism and severe hypokalemic hypertension.
What are the signs and symptoms of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency?
In some cases, the severe form of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency is characterized by abnormal brain function that develops during infancy and slowly gets worse (progressive infantile encephalopathy). Affected children may also experience episodes of profuse sweating, malaise, lethargy, irritability and excessive drooling.
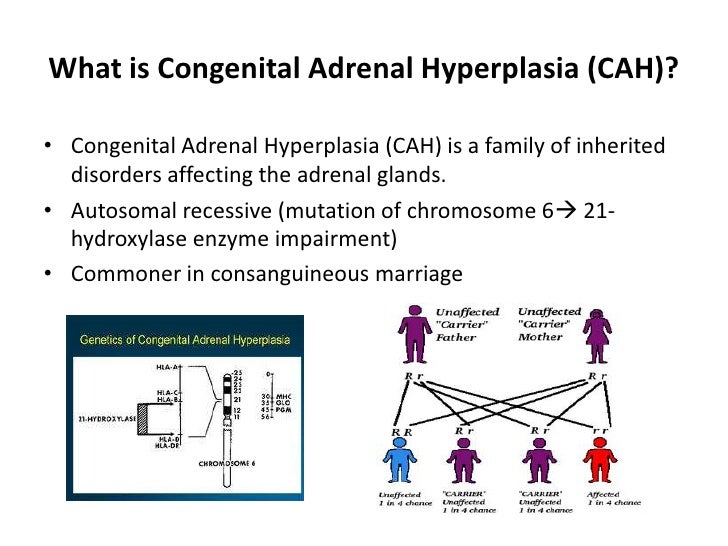
Is 21-hydroxylase deficiency fatal?
Adrenal crises in children with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency (CAH) are life-threatening and have the potential to death.
How is 21-hydroxylase deficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosis. Routine newborn screening typically includes measuring serum levels of 17-hydroxyprogesterone. If levels are elevated, the diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency is confirmed by identifying low blood levels of cortisol and by identifying high blood levels of DHEA, androstenedione, and testosterone.
Where is 21-hydroxylase deficiency most common?
The most common form of CAH, 21 hydroxylase deficiency, affects approximately 1:10,000 to 1:15,000 people in the United States and Europe. Among the Yupik Eskimos, the occurrence of the salt-wasting form of this disorder may be as high as 1 in 282 individuals. Other forms of CAH are much rarer.
What are the symptoms of salt-wasting?
Salt-wasting CAH is the severe form of classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency....Symptoms may include:Dehydration.Poor feeding.Diarrhea.Vomiting.Heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias)Low blood pressure.Very low blood sodium levels.Low blood glucose.More items...•
What is the symptoms with 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
Females with the non-classic type of 21-hydroxylase deficiency have normal female genitalia . As affected females get older, they may experience hirsutism, male pattern baldness, irregular menstruation, and decreased fertility. Males with the non-classic type may have early beard growth and small testes.
Does CAH shorten life expectancy?
Patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) with 21-hydroxylase deficiency have increased mortality rates, according to a study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. More than 95% of all CAH patients have 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
What causes female adrenal hyperplasia?
The most common cause of CAH is the lack of the enzyme known as 21-hydroxylase. CAH may sometimes be called 21-hydroxylase deficiency. This enzyme is required by the body to make proper amounts of hormones. There are other much rarer enzyme deficiencies that also cause CAH .
How do you test for adrenal hyperplasia?
An ACTH stimulation test is used to diagnose congenital adrenal hyperplasia and determine the type your child has. Blood samples are taken before and after giving your child an injection of synthetic ACTH, or adrenocorticotropic hormone, which signals the adrenal glands to release the hormone cortisol.
How do you fix adrenal hyperplasia?
Classic CAH is treated with steroids that replace the low hormones. Infants and children usually take a form of cortisol called hydrocortisone. Adults take hydrocortisone, prednisone, or dexamethasone, which also replace cortisol.
What is adrenal crisis?
Acute adrenal crisis is a medical emergency caused by a lack of cortisol. Patients may experience lightheadedness or dizziness, weakness, sweating, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, or even loss of consciousness.
How do you test for congenital adrenal hyperplasia in adults?
Blood and urine tests. These tests look for hormones produced by the adrenal glands at levels outside the standard ranges. The tests also check the levels of electrolytes. These are minerals such as sodium that balance the amount of water in the body.
What are adrenal disorders?
Adrenal disorders are the result of your glands making too much or not enough of certain hormones. Hormones produced by the adrenals include hydrocortisone (also called cortisol), adrenaline and aldosterone.
What is 21 hydroxylase deficiency?
21-hydroxylase deficiency is caused by genetic changes in the CYP21A2 gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Newborn screening is available in all 50 states of the US to test for this disorder at birth. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical symptoms, biochemical and genetic testing. [4] Treatment is available and involves managing the symptoms through steroids and other medications. [3] [4] The long-term outlook for people with 21-hydroxylase deficiency depends on the severity of symptoms and the ability to manage the condition with medications.
How many copies of each gene are there in 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
21-hydroxylase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. [2] All individuals inherit two copies of each gene. To have 21-hydroxylase deficiency, a person must have a mutation in both copies of the responsible gene in each cell. There is nothing either parent can do, before or during a pregnancy, to cause a child to have this.
What is the most common cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
21-hydroxylase deficiency is the most common cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH). CAH is a group of disorders that affect how the adrenal glands work. In 21-hydroxylase deficiency, a missing enzyme leads to overproduction of specific hormones made by the adrenal glands. There are three types of 21-hydroxylase deficiency ...
What is 21 hydroxylase?
There are three forms of 21-hydroxylase deficiency: the classic salt wasting form, the simple virilizing form, and the non-classic form. Most patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency will have the classic salt-wasting form or the simple virilizing form. [3]
How is 21 hydroxylase diagnosed?
[5] The less severe, non-classical form of 21-hydroxylase def is diagnosed based on the clinical symptoms, biochemical testing to look for excess hormone production. Genetic testing may also be helpful to determine the type and severity of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. [6]
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
Is 21 hydroxylase rare?
The non-classical form is not considered a rare disease and some people with this form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency may not experience any signs or symptoms. Last updated: 4/11/2019. This table lists symptoms that people with this disease may have. For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person.
What is a tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency?
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) deficiency is a rare inherited condition that affects the nervous system. There are three different forms of the condition that vary in severity. The mild form is called TH-deficient dopa-responsive dystonia and typically develops between age twelve months and six years. The two severe forms, which are called infantile parkinsonism and progressive infantile encephalopathy , often begin shortly after birth or during early infancy. Although there is some overlap of features among the three forms, each is associated with unique signs and symptoms. TH deficiency is caused by changes ( mutations) in the TH gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Affected people are usually treated with levodopa therapy. [1] [2] [3]
How old is a child with tyrosine hydroxylase?
Children affected by this form typically develop features of the condition between age twelve months and six years. Symptoms may include an abnormal gait (manner ...
What is the severe form of TH deficiency?
The severe form of TH deficiency is called infantile parkinsonism. Children affected by this form generally begin developing features of the condition between age three to twelve months. Signs and symptoms of infantile parkinsonism may include: [1] [3]
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
How early can you tell if you have a TH deficiency?
The very severe form of TH deficiency which is called progressive infantile encephalopathy, generally develops before age three to six months. Early symptoms may include fetal distress; feeding difficulties; low muscle tone; and small head circumference, height and/or weight from birth. Babies affected by this form generally have severe physical and intellectual disability due to underlying brain dysfunction and structural abnormalities. Other signs and symptoms include severe delay in motor milestones; rigidity and/or spasticity of arms and legs; ptosis of both eye lids; and episodes of profuse sweating, lethargy, irritability and/or excessive drooling. [2] [3]
Is tyrosine hydroxylase inherited?
Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [3] . This means that to be affected, a person must have a mutation in both copies of the responsible gene in each cell. The parents of an affected person usually each carry one mutated copy of the gene and are referred to as carriers.
Is tyrosine hydroxylase a good prognosis?
The long-term outlook ( prognosis) for people with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) deficiency varies based on the severity of the condition. The mild form of TH deficiency (TH-deficient dopa-responsive dystonia) is generally associated with a good prognosis. People affected by this form usually respond quickly and completely to treatment with levodopa, often seeing a full reversal of symptoms. [1] [2] [3]
What is the name of the database that lists articles that discuss 11 beta hydroxylase deficiency?
PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Click on the link to view a sample search on this topic.
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
What is the name of the condition where the adrenal glands produce excess androgens?
Listen. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency is one of a group of disorders (collectively called congenital adrenal hyperplasia) that affect the adrenal glands. In this condition, the adrenal glands produce excess androgens (male sex hormones ). This condition is caused by mutations in ...
What is MedlinePlus Genetics?
MedlinePlus Genetics contains information on 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. This website is maintained by the National Library of Medicine.
What is autosomal recessive gene?
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
Does 11-beta-hydroxylase cause high blood pressure?
About two-thirds of individuals with the classic form have high blood pressure which develops in the first year of life. [1] Females with the non-classic form of 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency have normal female genitalia. As affected females get older, they may develop excessive body hair growth and irregular menstruation.
What are the symptoms of 17-hydroxylase deficiency?from medlineplus.gov
Hormone imbalances lead to the characteristic signs and symptoms of 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which include high blood pressure ( hypertension ), low levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia), and abnormal sexual development . The severity of the features varies. Two forms of the condition are recognized: complete 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which is more severe, and partial 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which is typically less so.
What is the 17 alpha hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency?from medlineplus.gov
17 alpha (α)-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency is a condition that affects the function of certain hormone-producing glands called the gonads ( ovaries in females and testes in males) and the adrenal glands. The gonads direct sexual development before birth and during puberty and are important for reproduction.
What is 17 hydroxylase?from medlineplus.gov
17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency is one of a group of disorders , known as congenital adrenal hyperplasias, that impair hormone production and disrupt sexual development and maturation.
How many people have 17-hydroxylase?from medlineplus.gov
17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency accounts for about 1 percent of congenital adrenal hyperplasia cases. It is estimated to occur in 1 in 1 million people worldwide.
What happens if you have too much 17-20 lyase?from medlineplus.gov
An excess of these salt-regulating hormones leads to hypertension and hypokalemia . Loss of 17,20-lyase activity impairs sex hormone production. Shortage of these hormones disrupts development of the reproductive system and impairs the onset of puberty in males and females with 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency.
Can 17-hydroxylase cause infertility?from medlineplus.gov
Women with partial 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency may develop some secondary sex characteristics; menstruation is typically irregular or absent. Either form of the disorder results in an inability to conceive a baby (infertility).
What happens if you don't have a DBH gene?
DBH gene mutations result in the production of a nonfunctional dopamine β-hydroxylase enzyme. People who lack functional dopamine β-hydroxylase cannot convert dopamine to norepinephrine, which leads to a shortage of norepinephrine in the body. The lack of norepinephrine causes difficulty with regulating blood pressure and other autonomic nervous ...
What is the DBH gene?
The DBH gene provides instructions for producing the enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase. This enzyme converts dopamine to norepinephrine, both of which are chemical messengers ( neurotransmitters) that transmit signals between nerve cells. DBH gene mutations result in the production of a nonfunctional dopamine β-hydroxylase enzyme.
What causes difficulty with regulating blood pressure and other autonomic nervous system problems?
The lack of norepinephrine causes difficulty with regulating blood pressure and other autonomic nervous system problems seen in dopamine β-hydroxylase deficiency. Learn more about the gene associated with Dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Expand Section. DBH.
What are the symptoms of dopamine deficiency?
Early signs and symptoms may include episodes of vomiting, dehydration, decreased blood pressure (hypotension), difficulty maintaining body temperature, and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Individuals with dopamine β-hydroxylase deficiency typically experience a sharp drop in blood ...
What is an autosomal recessive gene?
Expand Section. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
Is dopamine hydroxylase rare?
Dopamine β-hydroxylase deficiency is a very rare disorder. Fewer than 20 affected individuals, all of Western European descent, have been described in the scientific literature.
What are the symptoms of 17-hydroxylase deficiency?from medlineplus.gov
Hormone imbalances lead to the characteristic signs and symptoms of 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which include high blood pressure ( hypertension ), low levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia), and abnormal sexual development . The severity of the features varies. Two forms of the condition are recognized: complete 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which is more severe, and partial 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency, which is typically less so.
What is the 17 alpha hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency?from medlineplus.gov
17 alpha (α)-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency is a condition that affects the function of certain hormone-producing glands called the gonads ( ovaries in females and testes in males) and the adrenal glands. The gonads direct sexual development before birth and during puberty and are important for reproduction.
What is 17 hydroxylase?from medlineplus.gov
17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency is one of a group of disorders , known as congenital adrenal hyperplasias, that impair hormone production and disrupt sexual development and maturation.
What is the chromosome of a female with 17 hydroxylase?from medlineplus.gov
Females (who have two X chromosomes) with 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency are born with normal external female genitalia; however, the internal reproductive organs, including the uterus and ovaries, may be underdeveloped. Women with complete 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency do not develop secondary sex characteristics, ...
How many people have 17-hydroxylase?from medlineplus.gov
17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency accounts for about 1 percent of congenital adrenal hyperplasia cases. It is estimated to occur in 1 in 1 million people worldwide.
What happens if you have too much 17-20 lyase?from medlineplus.gov
An excess of these salt-regulating hormones leads to hypertension and hypokalemia . Loss of 17,20-lyase activity impairs sex hormone production. Shortage of these hormones disrupts development of the reproductive system and impairs the onset of puberty in males and females with 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency.
What is autosomal recessive gene?from medlineplus.gov
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
What are the symptoms of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency?
Common symptoms include an uncoordinated or clumsy manner of walking (abnormal gait) and dystonia . Dystonia is a general term for a group of muscle disorders generally characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that force the body into abnormal, sometimes painful, movements and positions (postures). Dystonia in tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency usually affects the legs. Additional symptoms that may occur include tremors, eye abnormalities, and a tendency of affected children to walk on their tiptoes. The severe form of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency causes symptoms at a very young age (first months of life). The symptoms generally do not resemble those of a movement disorder, but rather give the impression of a severe, diffuse brain disorder. Mild and moderate forms of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency show dramatic improvement when treated with levodopa. Levodopa is an amino acid that is converted to dopamine. Dopamine is a brain chemical that serves as a neurotransmitter and is deficient in children with tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency. Treatment options for severe tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency have been less effective. Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency occurs due to disruptions or changes (mutations) of the TH gene. The TH gene mutation is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait.
How many cases of tyrosine hydroxylase are there?
The exact incidence of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency in the general population is unknown. Fewer than 50 cases have been reported in the medical literature. Researchers believe that the disorder is often misdiagnosed or goes undiagnosed, making it difficult to determine its true frequency in the general population.
When do tyrosine hydroxylase symptoms appear?
In more moderate or mild cases, symptoms may become apparent later during infancy or even during early childhood. The case reports of individuals with tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency in the medical literature are limited, making it difficult to determine an accurate picture of the disorder.
Is tyrosine hydroxylase a disease?
Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency represents a spectrum of disease ranging from a mild form to a severe form. The symptoms of tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency can vary greatly from one person to another. In the severe form, symptoms may be obvious early in infancy. In more moderate or mild cases, symptoms may become apparent later during infancy or even during early childhood. The case reports of individuals with tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency in the medical literature are limited, making it difficult to determine an accurate picture of the disorder.
How does recessive genetic disorder occur?
Recessive genetic disorders occur when an individual inherits the same abnormal gene for the same trait from each parent. If an individual receives one normal gene and one gene for the disease, the person will be a carrier for the disease, but usually will not show symptoms. The risk for two carrier parents to both pass the defective gene and, therefore, have an affected child is 25 percent with each pregnancy. The risk to have a child who is a carrier like the parents is 50 percent with each pregnancy. The chance for a child to receive normal genes from both parents and be genetically normal for that particular trait is 25 percent. The risk is the same for males and females.
Is tyrosine hydroxylase a metabolic disorder?
Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency may be classified as a form of dystonia, an inherited neurotransmitter disorder, and a metabolic disorder. Dystonia is a group neuromuscular disorders in which involuntary muscle contractions force the body into abnormal, sometimes painful, movements and positions (postures).
What is phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that results in intolerance to the dietary intake of the essential amino acid phenylalanine. It occurs in approximately 1:15,000 individuals.
What is phenylketonuria caused by?
Classic phenylketonuria is caused by a complete or near-complete deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity and without dietary restriction of phenylalanine most children will develop profound and irreversible intellectual disability. Mild phenylketonuria and mild hyperphenylalaninemia are associated with lower risk ...
Is phenylalanine a target for adolescence?
Phenyla lanine targets in adolescence and adulthood are less clear. A significant proportion of patients with phenylketonuria may benefit from adjuvant therapy with 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin stereoisomer. Special consideration must be given to adult women with hyperphenylalaninemia because of the teratogenic effects of phenylalanine.
