
Two-factor theory distinguishes between:
- Motivators (e.g., challenging work, recognition, responsibility) that give positive satisfaction, arising from intrinsic conditions of the job itself, such as recognition, achievement, or personal growth, and
- Hygiene factors (e.g. status, job security, salary, fringe benefits, work conditions) that do not give positive satisfaction, though dissatisfaction results from their absence. ...
Full Answer
What are hygienic factors of motivation?
Hygiene factors are 'good to have' factors of motivation in an organization, which further motivate the employee if they are given to the employee. Lack of presence of hygiene factors, will leave the employee dissatisfied, and will reduce his/her morale to perform well.
Does motivation hygiene theory hold for employee satisfaction?
If the motivation-hygiene theory holds, management not only must provide hygiene factors to avoid employee dissatisfaction, but also must provide factors intrinsic to the work itself for employees to be satisfied with their jobs.
What is hygiene factor in management?
Definition: Hygiene Factor. Hygiene factors refer to those motivation factors for an employee which if not present in an organization, can demotivate the individual & reduce their performance. Hygiene factors include a good salary, job profile, benefits, company sponsored vacations etc.
What is Herzberg's two-factor motivation hygiene?
Herzberg's 1959 two-factor motivation-hygiene research identified several factors that motivate and demotivate employees.
What are motivational hygiene factors?
Hygiene factors (e.g. status, job security, salary, fringe benefits, work conditions, good pay, paid insurance, vacations) that do not give positive satisfaction or lead to higher motivation, though dissatisfaction results from their absence. The term "hygiene" is used in the sense that these are maintenance factors.
How do hygiene factors affect motivation?
Hygiene issues, according to Herzberg, cannot motivate employees but can minimize dissatisfaction, if handled properly. In other words, they can only dissatisfy if they are absent or mishandled. Hygiene topics include company policies, supervision, salary, interpersonal relations and working conditions.
What are hygiene factors according to Herzberg's theory?
What Herzberg termed hygiene factors (also called dissatisfiers) are extrinsic elements of the work environment such as company policy, relationships with supervisors, working conditions, relationships with peers and subordinates, salary and benefits, and job security.
What is the meaning of hygiene theory?
The Herzburg two-factor theory, also known as the Herzburg's Hygiene Theory, posits that job satisfaction and dissatisfaction are not opposites. The research underpinning this theory identifies characteristics of jobs that related to job satisfaction - while a different set of job factors lead to dissatisfaction.
Are hygiene factors more important than motivation factors?
Empirical studies of job satisfaction in nurses, such as those of Kacel et al. (2005) and Jones (2011) support Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory by asserting that hygiene factors are less important to job satisfaction, while motivational factors lead to job satisfaction (Alshmemri et. al., 2017).
What is an example of Herzberg's two-factor theory?
» Two Factor Theory is subject to bias. For example, when an employee is satisfied they will give themselves credit for that satisfaction. Conversely, when they are dissatisfied they will blame external factors.
Why is Herzberg two-factor theory important?
Herzberg's two-factor theory holds that employers cannot choose between motivation or hygiene but instead must strive to improve both. Employers can tailor company policy to improve employee welfare and thus avoid low motivation and low hygiene simultaneously.
How do you use Herzberg two-factor theory?
Here are some useful steps for implementing the Herzberg two factor theory as a way to increase employee motivation:Remove the 'hygiene' factors first.Focus on motivation and job enrichment.Talk to employees and team members.Be an example.Give a voice to employees.
What are the hygiene factors and motivational factors affecting the performance of employees?
The characteristics associated with job dissatisfaction are called hygiene factors. When these have been adequately addressed, people will not be dissatisfied nor will they be satisfied. If you want to motivate your team, you then have to focus on satisfaction factors like achievement, recognition and responsibility.
What four ways can the hygiene factors be used to motivate employees in your organization?
4 hygiene factors that affect employee motivation1) Flexibility = to enable staff to choose where they work. ... 2) Freedom = to allow staff to perform personal tasks while at work. ... 3) High quality tools = to provide staff with the right tools to do their job. ... 4) Recognise = to show appreciation for a job well done.
Why are hygiene factors important?
Hygiene factors- Hygiene factors are those job factors which are essential for existence of motivation at workplace. These do not lead to positive satisfaction for long-term. But if these factors are absent / if these factors are non-existant at workplace, then they lead to dissatisfaction.
What are Herzberg's hygiene and motivational factors how can managers use them to motivate workers?
How can managers use them to motivate workers? Hygiene factors include adequate wages, comfortable and safe working conditions, fair company policies, and job security. These factors do not necessarily motivate people, but if they did not exist, it would prevent employees from working.
What Is a Hygiene Factor?
Herzberg's 1959 two-factor motivation-hygiene research identified several factors that motivate and demotivate employees. He called the demotivators hygiene factors because these are common factors in any work environment, but if they are not present, or if the hygiene factors are in any way managed or implemented improperly, they cause employees to be demotivated and disillusioned with their jobs.
How does hygiene affect a business?
Other hygiene factors, such as workplace policies and working conditions, can also adversely affect a business if they work against employees.
What motivates people in the workplace?
His research, coined the two-factor motivation-hygiene theory, focused on what motivates employees. Its basis is human behavior and fulfillment of basic human needs. Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory sheds light on how intrinsic satisfaction – not just money – is what compels employees to perform at optimal levels in the workplace.
How does self esteem improve?
But here is where recognition comes into play – employee self-esteem improves when they receive recognition for their work. Recognition isn't a reward; it's not a monetary gift based on employee performance. Recognition is a pat on the back for a job well done or a public "thank you" in the presence of their peers. In addition to the employee's self-esteem, other employees respect the recognized employee and value the employee's contributions to the team and the organization.
Why is poor leadership important?
They, too, are essential for business because, according to Branham's research, poor leadership is one of the primary reasons why employees look for opportunities elsewhere. Ineffective relationships in the workplace can cause employees to become disengaged and demotivated.
How to motivate employees?
Recognition, however, can include anything from a casual "thank you for a job well done," to commending the employee for her work during an all-staff meeting. Recognizing employee achievements, particularly when co-workers are present, is an ideal way to motivate employees. This can motivate all employees, not just the employee you recognize. Employees who witness their employer publicly (or privately) praising a co-worker's accomplishments not only are proud of the co-worker, but they typically will think highly of the company for recognizing employees.
Why do companies value their employees?
Companies that value their employees won't have these problems since they focus on team-building and team development to nurture cohesive and collaborative working relationships. Placing a high value on employees is how companies turn around the Herzberg hygiene factors and make them work for the company instead of allowing these factors to cause workplace malaise.
What are the factors of hygiene?
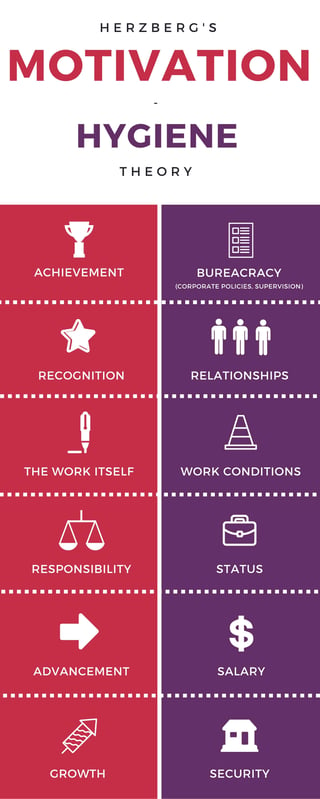
Hygiene factors consists of a set of 10 factors: company policies and administration, quality of technical supervision, quality of interpersonal relations among peers, subordinates, and superiors, salary, job security, personal life, working conditions, and status.
What are motivation factors?
They cover intrinsic needs such as achievement, recognition, and advancement. Motivation factors allow employees to be content in their jobs and promote growth. Hygiene factors: factors that are not related to workplace satisfaction but must be present in the workplace in order to prevent dissatisfaction.
What did Herzberg study?
Herzberg focused on the attitudes of workers and job satisfaction (Figure 2). He made some interesting discoveries, including the lack of linear relationship between intrinsic and extrinsic needs.
How to apply Herzberg's theory to the workplace?
In order to apply Herzberg’s theory in the workplace, one must examine the hygiene factors. As stated above, hygiene factors do not contribute to workplace satisfaction but must be present in order to prevent workplace dissatisfaction. Hygiene factors are closely related to extrinsic needs:
What is the key idea of Herzberg's theory?
There is one key idea that one must keep in mind when using Herzberg’s theory: intrinsic needs and extrinsic needs are distinct things. An individual will not suddenly become satisfied with their job if you suddenly change the environment or remove what is bothering them.
What is the two factor theory of motivation?
Herzberg’s two-factor theory outlines that humans are motivated by two things: motivators ...
How can a supervisor increase employee satisfaction?
Managers can often increase workplace satisfaction by simply having a conversation with their colleagues to find out what they are unhappy with. Some problems have easy solutions, such as keeping supplies organized or having more materials in stock. An employee’s pay is often a more challenging issue to rectify, but supervisors should still evaluate their business plan and compensation strategy. Supervisors should also reach out to employees to discover if there are any factors in their personal lives that may affect their job satisfaction. Overwhelmed and stressed employees are rarely productive or happy. It is vital that workplaces offer emotional support and maintain positive relationships with their employees.
What are motivation factors?
Motivation factors are intrinsic conditions that influence the level of employee engagement. They have the ability to satisfy one’s own psychological needs including sense of achievement, personal and professional growth, proficiency and status in the organization.
What are the factors that motivate employees to perform their best?
The factors such as working conditions, organizational culture, remuneration, perks and benefits, job security and relationship with colleagues and subordinates and immediate supervisors play an important role and make them stay within the organization and grow with it.
What are the factors that influence employee engagement?
In fact, they have proven to be dependable and unswerving predictors of the level of involvement and engagement of employees towards their jobs. Motivation factors are intrinsic conditions that influence the level of employee engagement.
What is interesting and challenging work?
Interesting and Challenging Work: Different tasks must be assigned to employees at different times. Managers should try to assign them interesting and challenging tasks that motivates them to do something different from their routine job and feel a sense of achievement.
What is the first requirement to attract a pool of talent and actively engage them in their jobs?
Remuneration and Benefits: The wages and additional benefits are the first requirement to attract a pool of talent and actively engage them in their jobs.
What is personal and professional growth?
Personal and Professional Growth: This is something that motivates employees to work harder and perform their best. If they see their personal and professional growth with the organization, they will stay and develop a feeling of belongingness towards the organization.
How to apply the theory of motivation?
To apply the theory, you need to adopt a two-stage process to motivate people. Firstly, you need to eliminate the dissatisfaction they're experiencing and, secondly, you need to help them find satisfaction.
How to motivate people?
When you're seeking to motivate people, firstly get rid of the things that are annoying them about the company and the workplace. Make sure they're treated fairly, and with respect.
How to create satisfaction in a job?
To create satisfaction, Herzberg says you need to address the motivating factors associated with work. He called this "job enrichment." His premise was that every job should be examined to determine how it could be made better and more satisfying to the person doing the work. Things to consider include: 1 Providing opportunities for achievement. 2 Recognizing people's contributions. 3 Creating work that is rewarding and that matches people's skills and abilities. 4 Giving as much responsibility to each team member as possible. 5 Providing opportunities to advance in the company through internal promotions. 6 Offering training and development opportunities, so that people can pursue the positions they want within the company.
What is the cause of dissatisfaction called?
Herzberg called the causes of dissatisfaction "hygiene factors." To get rid of them, you need to:
What are the characteristics of a job that are consistently related to job satisfaction?
These are: Factors for Satisfaction. Factors for Dissatisfaction. Achievement.
Why do managers like to use this approach?
Perhaps managers like to use this approach because they think people are more financially motivated than, perhaps, they are, or perhaps it just takes less management effort to raise wages than it does to reevaluate company policy, and redesign jobs for maximum satisfaction.
Who asked the question "What is the effect of attitude on motivation"?
The psychologist Fredrick Herzberg asked the same question in the 1950s and 60s as a means of understanding employee satisfaction. He set out to determine the effect of attitude on motivation, by asking people to describe situations where they felt really good, and really bad, about their jobs. What he found was that people who felt good about ...
What is Hygiene Factors?
Hygiene factors refer to those motivation factors for an employee which if not present in an organization, can demotivate the individual & reduce their performance. Hygiene factors may include a salary, job profile, benefits, company sponsored vacations etc. Hygiene factors are included in the Fredrick Herzberg's two factor theory of motivation. In the current business content, the organizations need to keep focus on the hygiene factors and make sure that the employees are not demotivated or leaving the organization due to lack of these factors. The two factor theory talks about hygiene factors and motivators as the two factors of motivation.
Why is hygiene important?
Importance of Hygiene Factors. Hygiene factors are 'good to have' factors of motivation in an organization, which further motivate the employee if they are given to the employee. Lack of presence of hygiene factors, will leave the employee dissatisfied, and will reduce his/her morale to perform well. Employees or individuals seek a good place ...
What are the factors that contribute to job satisfaction?
For any employee, his job role is the primary factor, whereas the workplace culture, the environment, privacy etc. are the hygiene factors . The employee will witness high levels of job satisfaction only if the hygiene factors are taken into consideration along with the primary factors.
What is the two factor model of motivation?
However, Herzberg added a new dimension to this theory by proposing a two-factor model of motivation, based on the notion that the presence of one set of job characteristics or incentives lead to worker satisfaction at work, while another and separate set of job characteristics lead to dissatisfaction at work.
What are the advantages of motivation theory?
This approach to the study and understanding of motivation would appear to have certain conceptual advantages over other theories: First, unlike Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories, it is capable of handling individual differences. Second, its focus is toward the present and the future, in contrast to drive theory, which emphasizes past learning. Third, it specifically correlates behavior to a goal and thus eliminates the problem of assumed relationships, such as between motivation and performance. Fourth, it relates motivation to ability: Performance = Motivation*Ability.
How are attitudes related to motivation?
Attitudes and their connection with industrial mental health are related to Maslow’s theory of motivation. His findings have had a considerable theoretical, as well as a practical, influence on attitudes toward administration. According to Herzberg, individuals are not content with the satisfaction of lower-order needs at work, for example, those associated with minimum salary levels or safe and pleasant working conditions. Rather, individuals look for the gratification of higher-level psychological needs having to do with achievement, recognition, responsibility, advancement, and the nature of the work itself. So far, this appears to parallel Maslow’s theory of a need hierarchy. However, Herzberg added a new dimension to this theory by proposing a two-factor model of motivation, based on the notion that the presence of one set of job characteristics or incentives lead to worker satisfaction at work, while another and separate set of job characteristics lead to dissatisfaction at work. Thus, satisfaction and dissatisfaction are not on a continuum with one increasing as the other diminishes, but are independent phenomena. This theory suggests that to improve job attitudes and productivity, administrators must recognize and attend to both sets of characteristics and not assume that an increase in satisfaction leads to decrease in unpleasurable dissatisfaction.
Why is the two factor result observed?
Critics of Herzberg’s theory argue that the two-factor result is observed because it is natural for people to take credit for satisfaction and to blame dissatisfaction on external factors. Furthermore, job satisfaction does not necessarily imply a high level of motivation or productivity. Herzberg’s theory has been broadly read ...
What does "kita" mean in hygiene?
Herzberg often referred to these hygiene factors as “KITA” factors, where KITA is an acronym for Kick In The Ass, the process of providing incentives or a threat of punishment to cause someone to do something.
What is Maslow's theory of motivation?
Attitudes and their connection with industrial mental health are related to Maslow’s theory of motivation. His findings have had a considerable theoretical, as well as a practical, influence on attitudes toward administration. According to Herzberg, individuals are not content with the satisfaction of lower-order needs at work, for example, ...
What is the two factor theory?
The two-factor theory (also known as Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory) states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction, while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction. It was developed by Frederick Herzberg, a psychologist, ...
What are the motivating factors of a job?
Their absence, on the other hand, does not cause any disappointment. Recognition for accomplishments, progress in the work itself, the potential of growth and development, and responsibility are all motivating factors.
What is Herzberg's motivation?
Only a difficult job can bring work satisfaction. Herzberg’s motivation factors are inextricably linked to the nature of the work. The central theme of his theory is that a worker derives genuine pleasure from his work. When we consider the situation in India, workers place a higher value on job security because employment opportunities are limited due to a large number of applicants.
What is the motivational factor of Frederick Herzberg?
Herzberg’s Motivation Theory model, also known as the Two Factor Theory, identifies two factors that influence workplace motivation. Hygiene and motivational factors are two of these factors. If hygiene factors are not present, an employee will work less. If motivating factors are present, an employee would be encouraged to work harder. Hence, health and safety comes under Frederick Herzberg’s Hygiene factor.
Why is it important to have a clean work environment?
According to Herzberg, having a clean work environment is essential for preventing employee dissatisfaction. Because the two-factor theory states that motivational and hygiene factors must be discussed separately, employers must understand what hygiene factors are and how to improve them. According to Herzberg, the following are some of the most important hygiene factors (also known as maintenance factors):
What is the two factor theory?
Herzberg’s two-factor theory is a psychological theory on organizational motivation formulated in the 1960s by psychologist Frederick Herzberg. Herzberg’s theory divided workplace requirements into two categories: motivation factors that provide workers with a sense of fulfilment , and hygiene factors that decide the basic level of job stability and security .
What is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
There is another theory proposed by Maslow. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a psychological motivational theory that consists of a five-tier characteristic of social needs, which is often represented as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. Physiological (food and clothing), safety (job security), love and belonging needs (friendship), esteem, and self-actualization are the needs from the bottom of the hierarchy up. Entities must attend to lower-level needs before they can attend to higher-level needs.
What are the concerns of Herzberg?
Other criticisms centre on Herzberg’s methodology’s inconsistency, the theory’s failure to account for the effect of individual characteristics, and the presumed correlation between performance and retention . Nonetheless, Herzberg’s queries about the related to job fulfilment and the impacts of internal and external factors on employee behaviour have proven to be an important addition to the development of performance and employee fulfilment concepts.
What are factors of motivation?
Factors of motivation are strategies, incentives, recognitions and any other elements that increase an employee's overall motivation to perform their duties at work . You can implement several different factors of motivation within your team or for yourself to increase productivity and satisfaction.
What is motivation in work?
Motivation refers to the process that guides and maintains behaviors that help employees work towards a particular goal or effectively perform tasks.
How to increase motivation in a team?
Creating open spaces that entice the senses, implementing specific areas of the workplace that are committed to the wellbeing of employees and allowing employees to communicate with each other throughout the day can all work to increase motivation in a team.
How to motivate employees to work flexible hours?
Offering employees the opportunity to create their own schedules or work flexible hours is another great way to instill motivation in your team. Flexible schedules allow employees to better accommodate family needs, holidays and other personal daily responsibilities that more rigid schedules often don't.
What are the different types of motivation?
Motivation refers to the process that guides and maintains behaviors that help employees work towards a particular goal or effectively perform tasks. The most common types of motivation include: 1 Extrinsic motivation: This type of motivation refers to factors that are outside of the person, such as bonuses, social recognition and praise. 2 Intrinsic motivation: Intrinsic motivation is a type of motivation that occurs within the individual. For example, personal gratification and a feeling of accomplishment are two types of intrinsic motivations.
What are the three theories of motivation?
The following are a few of the most well-known theories of motivation that can be implemented in the workplace: 1. Hertzberg's two-factor theory. Frederick Hertzberg designed a theory regarding employee satisfaction that focuses on two primary factors: motivation and hygiene.
What is extrinsic motivation?
Extrinsic motivation: This type of motivation refers to factors that are outside of the person, such as bonuses, social recognition and praise.
