
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS) is a potentially life threatening condition involving extremely high blood sugar (glucose) levels. When your blood sugar gets too high, the kidneys try to compensate by removing some of the excess glucose through urination.
What does hypoglycemic shock mean?
If you are diabetic, it is important to check your blood sugar on a regular basis. If the levels get too low, it can cause severe hypoglycemia —also referred to as hypoglycemic shock and diabetic shock, which are not medical terms. What Is Severe Hypoglycemia?
What is hyperglycemic shock?
Severe hypoglycemia, or insulin shock, is a serious health risk for anyone with diabetes. Also called insulin reaction, as a consequence of too much insulin, it can occur anytime there is an imbalance between the insulin in your system, the amount of food you eat, or your level of physical activity.
What does hyperglycemia feel like?
Your mouth is dry, your skin is dry, and your body feels bloated and full. There you go with the fatigue, and the foggy-brained feeling. You want to drag back to bed, but life won’t let you. You get a hot feeling, and sometimes a headache. You get nausea, sometimes vomiting, and weight loss.
What are the first signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Early signs and symptoms of diabetic hypoglycemia include: Shakiness: you may notice yourself lightly shaking or trembling. Sweating: you may start to produce sweat on the face and body, similar to if you were very hot, nervous, or have just exercised. Dizziness: you may feel lightheaded, woozy, or unbalanced.
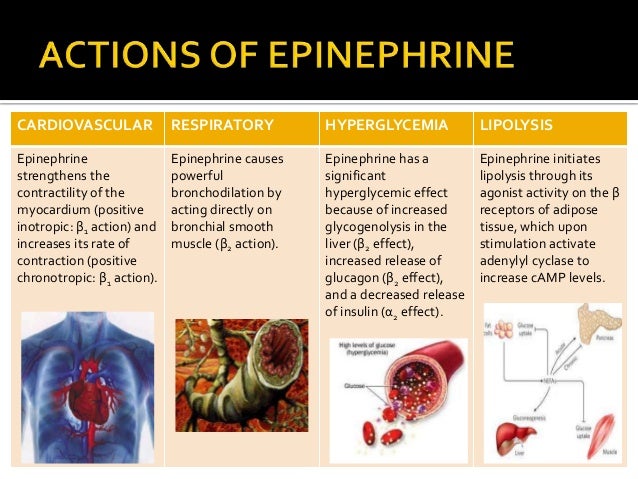
What causes hypoglycemia shock?
Severe hypoglycemia, or insulin shock, is a serious health risk for anyone with diabetes. Also called insulin reaction, bcause of too much insulin, it can occur anytime there is an imbalance between the insulin in your system, the amount of food you eat, or your level of physical activity.
What causes hyperglycemia in shock?
In stress situations the body is thought to activate the central nervous system and neuroendocrine axes which release hormones such as catecholamines, glucagon and cortisol which are known to stimulate hepatic glucose production and lead to hyperglycemia (5).
What does hyperglycemic shock feel like?
People often experience headaches, dizziness, sweating, shaking, and a feeling of anxiety. However, when a person experiences diabetic shock or severe hypoglycemia, they may lose consciousness, have trouble speaking, and experience double vision.
How do you treat hyperglycemic shock?
If your blood sugar level is too high, you may need: Intravenous fluids to restore water to your body. Potassium, sodium or phosphate supplements to help your cells work correctly. Insulin to help your body absorb the glucose in your blood.
What are 5 signs of a diabetic emergency?
What are the signs and symptoms of a diabetic emergency?hunger.clammy skin.profuse sweating.drowsiness or confusion.weakness or feeling faint.sudden loss of responsiveness.
How long does stress hyperglycemia last?
The good news about stress hyperglycemia is that it often subsides as soon as the stress recedes. But the bad news is that between 30% and 60% of nondiabetic patients who develop transient stress hyperglycemia while hospitalized will have confirmed diabetes within a year.
At what level can you go into diabetic shock?
“Insulin shock” is a common term for low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia. It may also be called an insulin reaction. The exact blood sugar level that leads to symptoms varies, but is generally less than 70 mg/dL. A low blood sugar level triggers your body to release the hormone epinephrine, also called adrenaline.
Is diabetic shock life-threatening?
When blood sugar is very high, the extra sugar passes from the blood into the urine. That triggers a process that draws a large amount of fluid from the body. If it isn't treated, this can lead to life-threatening dehydration and a diabetic coma.
When is hyperglycemia an emergency?
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS) occurs when blood sugar levels become dangerously high, usually above 600 mg/dl. This may happen with or without DKA, and it can be life-threatening.
What are the three classic signs of hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia usually doesn't cause symptoms until blood sugar (glucose) levels are high — above 180 to 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 10 to 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L)....Watch for:Frequent urination.Increased thirst.Blurred vision.Feeling weak or unusually tired.
What is the fastest way to cure hyperglycemia?
When your blood sugar level gets too high — known as hyperglycemia or high blood glucose — the quickest way to reduce it is to take fast-acting insulin. Exercising is another fast, effective way to lower blood sugar. In some cases, you should go to the hospital instead of handling it at home.
How do hospitals treat hyperglycemia?
Insulin is the best way to control hyperglycemia in the inpatient setting especially in the critically ill patient. A variable rate, intravenous insulin infusion is the preferred method to achieve the recommended glycemic target.
What is the pathophysiology of hyperglycemia?
Pathophysiology. Hyperglycemia in a patient with type 1 diabetes is a result of genetic, environmental, and immunologic factors. These lead to the destruction of pancreatic beta cells and insulin deficiency. In a patient with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and abnormal insulin secretion lead to hyperglycemia.
Can stress cause high glucose?
If stress doesn't go away, it can keep your blood sugar levels high and put you at higher risk of diabetes complications. It can also affect your mood and how you look after yourself, which can start to affect your emotional health.
Why does hyperglycemia cause ketoacidosis?
Without enough insulin, the body begins to break down fat as fuel. This causes a buildup of acids in the bloodstream called ketones. If it's left untreated, the buildup can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
Why would a hyperglycemic patient possibly present with a decreased level of consciousness?
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can make you dehydrated which can cause you to lose consciousness. Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can cause you to lose consciousness if the brain isn't receiving enough glucose to function.
What are the symptoms of hyperglycemia?
Signs and symptoms include: Fruity-smelling breath. Nausea and vomiting. Shortness of breath.
What happens when blood glucose levels rise?
When the glucose level in your blood rises, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. The insulin unlocks your cells so that glucose can enter and provide the fuel your cells need to function properly. Any extra glucose is stored in your liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Why does diabetes lower insulin levels?
As your blood sugar level returns to normal, so does the secretion of insulin from your pancreas. Diabetes drastically lowers insulin's effects on your body. This may be because your pancreas is unable to produce insulin (type 1 ...
How long does it take for hyperglycemia to show?
Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks. The longer blood sugar levels stay high, the more serious the symptoms become. However, some people who've had type 2 diabetes for a long time may not show any symptoms despite elevated blood sugar levels.
Why is it important to treat hyperglycemia?
It's important to treat hyperglycemia, because if left untreated, hyperglycemia can become severe and lead to serious complications requiring emergency care, such as a diabetic coma. In the long term, persistent hyperglycemia, even if not severe, can lead to complications affecting your eyes, kidneys, nerves and heart.
How to keep blood sugar in target range?
Prevention. The following suggestions can help keep your blood sugar within your target range: Follow your diabetes meal plan. If you take insulin or oral diabetes medication, it's important that you be consistent about the amount and timing of your meals and snacks.
Why does blood sugar rise when you have surgery?
Being injured or having surgery. Experiencing emotional stress, such as family conflict or workplace challenges. Illness or stress can trigger hyperglycemia because hormones produced to combat illness or stress can also cause your blood sugar to rise.
What Causes Hypoglycemia?
For people who have type 1 diabetes, on average they could experience up to two mild to low blood sugar episodes a week. If there are lows without known symptoms, there is a chance that the incidence of low blood sugar episodes could be higher.
Why is it important to know the symptoms of hypoglycemia?
This information can be useful because it can be an indication that blood sugar is low and necessary steps are needed to normalize the levels.
What happens if your blood sugar is too low?
If you are diabetic, it is important to check your blood sugar on a regular basis. If the levels get too low, it can cause severe hypoglycemia —also referred to as hypoglycemic shock and diabetic shock, which are not medical terms. Fertnig / Getty Images.
What are the symptoms of a low blood sugar?
Severe symptoms typically occur when the blood sugar is less than 40 mg/dL. Severe symptoms include: 1. Confusion. Seizure. Shock. Glucagon —a hormone that stimulates the liver to release glucose that is stored in the bloodstream—can be given to help with severe symptoms.
What hormone is released when blood sugar levels are low?
This will trigger and release a hormone called epinephrine, also known as the fight-or-flight hormone. Epinephrine can cause some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia such as: Sweating.
What is it called when blood sugar levels fall below a safe level?
When blood sugar levels fall below a safe level and a person feels no symptoms, this is called hypoglycemia unawareness. This is dangerous because the person doesn’t know that they need to treat their blood sugar. The levels can fall so low that it can create a dangerous situation for the person with hypoglycemia. 1.
What happens if you don't treat hypoglycemia?
If hypoglycemia is not treated, the plummeting blood sugar levels may lead to severe symptoms requiring immediate medical attention. 1
What is Diabetic Shock?
A diabetic shock refers to the emergency that occurs when blood sugar either raises or lowers to dangerous levels for a diabetic. Diabetic shock caused by hypoglycemia can include seizures or unconsciousness. The diabetic emergencies that can occur because of hyperglycemia include:
What are the emergencies that can occur because of hyperglycemia?
The diabetic emergencies that can occur because of hyperglycemia include: Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) (For information on how to avoid diabetic shock, please see our posts Dealing with Blood Sugar Levels and Normal Glucose Levels: Check Your Numbers .)
What Is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia in diabetics can occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from eating too much to the stress of an illness to insufficient glucose-lowering medications. The symptoms of mild hyperglycemia typically are increased thirst and frequent urination.
What does it mean when your blood glucose is elevated?
Persistent mildly elevated blood glucose levels often mean that you need to reevaluate your diet, exercise, and sometimes medication regimen with your healthcare provider. There are two true diabetic emergencies characterized by hyperglycemia: diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). ...
What is the confusion of diabetes?
Confusion is a symptom of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, which can lead to diabetic shock. Diabetic emergencies and diabetic shock can occur either when your blood glucose level becomes dangerously low (hypoglycemia) or when it becomes dangerously high (hyperglycemia). If you’re managing diabetes, it’s important to understand ...
What is the best treatment for hypoglycemia?
In more severe cases of hypoglycemia—true hypoglycemic emergencies such as when diabetic shock (including seizures or unconsciousness) occurs—injectable glucagon, a hormone that causes your liver to release glucose into the blood stream, is needed. Glucagon injection kits are available by prescription and can be injected into the arm, buttocks, or thigh.
Why do diabetics have hypoglycemia?
It can be the result of simply having skipped a meal or having exercised too much for the amount of food you have consumed or medication you have taken. It can also be the consequence of insulin or insulin promoting medications.
What are the risk factors for hyperglycemia?
Major risk factors for hyperglycemia are: You have a family history of type 2 diabetes. You are African American, Native American, Hispanic or Asian American. You are overweight. You have high blood pressure or cholesterol. You have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). You have a history of gestational diabetes.
What is the term for a person who has too much sugar in their blood?
Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose, occurs when there is too much sugar in the blood. This happens when your body has too little insulin (the hormone that transports glucose into the blood), or if your body can't use insulin properly. The condition is most often linked with diabetes.
How to manage hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes?
People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
How long does it take for blood glucose to go up after eating?
A person has hyperglycemia if their blood glucose is greater than 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating. If you have hyperglycemia and it’s untreated for long periods of time, you can damage your nerves, blood vessels, tissues and organs.
What is the blood glucose level of a diabetic?
The condition is most often linked with diabetes. Hyperglycemia is blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) while fasting (not eating for at least eight hours; a person with a fasting blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL has diabetes). A person has impaired glucose tolerance, or pre-diabetes, ...
What causes insulin resistance?
Endocrine conditions, such as Cushing syndrome, that cause insulin resistance. Pancreatic diseases such as pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and cystic fibrosis. Certain medications (such as diuretics and steroids). Gestational diabetes, which happens in 4% of pregnancies, and is due to decreased insulin sensitivity.
What does it mean when you have high blood sugar?
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar) Hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) means there is too much sugar in the blood because the body lacks enough insulin. Associated with diabetes, hyperglycemia can cause vomiting, excessive hunger and thirst, rapid heartbeat, vision problems and other symptoms. Untreated hyperglycemia can lead to serious health ...
Why is HHS a result of diabetes?
Blood that’s too concentrated begins to draw water out of other organs, including the brain. Any illness that makes you dehydrated or reduces your insulin activity can lead to HHS. It’s commonly a result of unmanaged or undiagnosed diabetes. An illness or infection can trigger HHS.
Which type of diabetes is more likely to develop HHS?
Older people with type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop HHS.
What is HHS in medical terms?
Outlook. Prevention. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS) is a potentially life threatening condition involving extremely high blood sugar (glucose) levels. When your blood sugar gets too high, the kidneys try to compensate by removing some of the excess glucose through urination. If you don’t drink enough fluids to replace ...
What is HHS treatment?
Untreated HHS can lead to life threatening complications, including: dehydration. shock. coma. HHS is a medical emergency.
How to prevent HHS?
The best way to prevent HHS is to monitor your diabetes carefully and manage it.
What are the complications of hyperglycemia?
Frequent and long-standing hyperglycemia can lead to a host of complications known as micro (small) and macro (large) vascular issues. They include damage to the: 1 Eye (retinopathy) 2 Kidney (nephropathy) 3 Peripheral and autonomic neuropathy (nerve loss in the feet and other areas of the body such as the intestine)
What is the term for the body's ability to get rid of excess sugar?
Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia) In an effort to restore blood sugar balance, your body tries to get rid of excess sugar through urine. As a result, the kidneys are forced to work overtime absorbing excess sugar.
How does ketoacidosis feel?
As it progresses, you may have extreme hunger with unexpected weight loss, feel fatigued and confused, experience trouble breathing, and have dry skin. 6.
What are the signs of diabetes?
Mouth and Breathing Changes. Nausea, vomiting, fruity breath, deep and rapid breathing, and loss of consciousness are indications that you need to seek emergency help. These symptoms can be warning signs of other diabetes-related conditions that can result in death if not treated immediately.
Why does blood sugar rise?
Excess sugar in your bloodstream means that your body is unable to utilize it for fuel. Hence, your cells become starved for energy and you feel extra hungry and, in extreme cases, unsatiable. But the more carbohydrates you consume, the higher the blood sugars rise.
Is hyperglycemia a sign of diabetes?
Experiencing common hyperglycemia symptoms may be a diabetes warning sign for those who have not yet been diagnosed. 2 If you know you have diabetes, noting these symptoms may be an indication that a tweak in your treatment plan is needed.
Can diabetes cause hunger?
People with diabetes may also feel excessive hunger, and, untreated, diabetic hyperglycemia may cause more severe symptoms.
How to treat hyperglycemia?
If you have frequent episodes of hyperglycemia, your doctor may adjust the dosage or timing of your medication. Follow your diabetes eating plan. It helps to eat smaller portions and avoid sugary beverages and frequent snacking. If you're having trouble sticking to your meal plan, ask your doctor or dietitian for help. Check your blood sugar.
Why does blood sugar rise?
Illness or infections can cause your blood sugar to rise, so it's important to plan for these situations. Talk to your doctor about creating a sick-day plan. Questions to ask include:
What is the A1C level for diabetes?
However, for some people, especially older adults and those with certain medical conditions or limited life expectancy, a higher A1C level of up to 8% may be appropriate.
What is the recommended blood sugar level for diabetics?
For many people who have diabetes, the American Diabetes Association generally recommends the following target blood sugar levels: Between 80 and 130 mg/dL (4.4 and 7.2 mmol/L) before meals. Your target blood sugar range may differ, especially if you're pregnant or you have developed diabetes complications.
What is the blood sugar level for ketoacidosis?
If your blood sugar level is 240 mg/dL (13.3 mmol/L) or above, use an over-the-counter urine ketones test kit. If the urine test is positive, your body may have started making the changes that can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. You'll need your doctor's help to lower your blood sugar level safely.
How to control blood sugar?
Your doctor may suggest the following treatments: Get physical. Regular exercise is often an effective way to control your blood sugar.
What happens when your body chemistry returns to normal?
As your body chemistry returns to normal, your doctor will consider what may have triggered the severe hyperglycemia. Depending on the circumstances, you may need additional evaluation and treatment.
What is diabetic shock?
Summary. Diabetic shock occurs when blood sugar levels drop dangerously low. Diabetic shock is not a medical term, but people often use it to describe a state of severe hypoglycemia that requires another person’s help. People with mild low blood sugar, which doctors call insulin reaction or hypoglycemia, are usually conscious ...
How to prevent diabetic shock?
There are some general lifestyle changes a person can make to help avoid diabetic shock and hypoglycemia, including: monitoring their blood sugar levels closely. avoiding skipping meals or snacks. taking medication as prescribed, on time, and in precise amounts.
Why is it important to treat hypoglycemia?
Early treatment is essential because blood sugar levels that stay low for too long can lead to seizures or diabetic coma. Hypoglycemia can sometimes happen rapidly and may even occur when a person follows their diabetes treatment plan.
What to do if your glucose level is low?
If the levels are still low, repeat the process and consume another sugary food or drink. Once the levels have returned to normal, a person can return to their regular meal and snack schedule. Doctors may prescribe a hormone called glucagon to people who are at risk of diabetic shock.
How long does it take to check blood sugar?
If the levels are low, consume a sugary snack or drink containing 15 grams (g) of carbohydrate, then recheck blood sugar levels after about 15 minutes.
What are the symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia can include drowsiness and double vision. If a person with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes starts to notice symptoms of low blood sugar, they can take some steps to help raise their blood glucose levels to a normal range.
What happens when blood glucose levels are too low?
When blood glucose levels are too low, it can affect brain functioning and lead to complications, such as: loss of consciousness. seizures. death. When treating hypoglycemia, it is vital that a person does not take more glucose than they need, as this can cause blood sugar levels to rebound too high.
What is the name of the condition where blood sugar levels are high for a long period of time?
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome. A serious complication of diabetes mellitus, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome (HHS) happens when blood sugar levels are very high for a long period of time. Symptoms of HHS can include extreme thirst, frequent urination, changes in your vision and confusion.
What happens when blood sugar is too high?
HHS occurs when the blood sugar of a person with diabetes becomes too high (hyperglycemia) for a long time. The extra sugar is passed into the urine, which causes the person to urinate frequently. As a result, he or she loses a lot of fluid, which can lead to severe dehydration (extreme thirst).
What is the term for a person who has high blood sugar?
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome ( HHS) is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus. HHS occurs when a person’s blood glucose (sugar) levels are too high for a long period, leading to severe dehydration (extreme thirst) and confusion.
How to reduce risk of HHS?
You can reduce your risk of developing HHS again by controlling your diabetes and managing your diet and lifestyle.
Why does glucose build up in the body?
The glucose builds up because their bodies either don’t make enough insulin, or have trouble using the insulin that they do make. (Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, which helps the body use sugar for energy.)
How many people die from HHS?
The outlook for patients who have HHS largely depends on the person’s age, general health and how severe the disease is. Up to 20% of people who have HHS die from the condition. If you’ve had HHS, you will need to work closely with your doctor once you are home from the hospital.
How to prevent HHS?
The best way to prevent HHS is by following a healthy lifestyle and managing your diabetes. You should:

Overview
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) affects people who have diabetes. Several factors can contribute to hyperglycemia in people with diabetes, including food and physical activity choices, illness, nondiabetes medications, or skipping or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication. It's important to treat hyperglycemia, because if left untreated, hyperglycemia can become sever…
Symptoms
- Hyperglycemia doesn't cause symptoms until glucose values are significantly elevated — usually above 180 to 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 10 to 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks. The longer blood sugar levels stay high, the more serious the symptoms become. However, some people who've had typ…
Causes
- During digestion, your body breaks down carbohydrates from foods — such as bread, rice and pasta — into various sugar molecules. One of these sugar molecules is glucose, a main energy source for your body. Glucose is absorbed directly into your bloodstream after you eat, but it can't enter the cells of most of your tissues without the help of insulin — a hormone secreted by your …
Risk Factors
- Many factors can contribute to hyperglycemia, including: 1. Not using enough insulin or oral diabetes medication 2. Not injecting insulin properly or using expired insulin 3. Not following your diabetes eating plan 4. Being inactive 5. Having an illness or infection 6. Using certain medications, such as steroids 7. Being injured or having surgery 8. Experiencing emotional stres…
Complications
- Long-term complications
Keeping your blood sugar in a healthy range can help prevent many diabetes-related complications. Long-term complications of untreated hyperglycemia can include: 1. Cardiovascular disease 2. Nerve damage (neuropathy) 3. Kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy… - Emergency complications
If blood sugar rises high enough or for a prolonged period of time, it can lead to two serious conditions. 1. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis develops when you don't have enough insulin in your body. When this happens, sugar (glucose) can't enter your cells for energy. Your bl…
Prevention
- The following suggestions can help keep your blood sugar within your target range: 1. Follow your diabetes meal plan.If you take insulin or oral diabetes medication, it's important that you be consistent about the amount and timing of your meals and snacks. The food you eat must be in balance with the insulin working in your body. 2. Monitor your blood sugar.Depending on your tre…