
What is hyposalivation and how is it treated?
What is hyposalivation? Hyposalivation means that there is insufficient saliva or low saliva production. There are many reasons why hyposalivation may occur and it may be short lived (acute) or persist for long periods of time (chronic). The problem arises when the salivary glands do not produce or secrete sufficient saliva.
What is xerostomia and hyposalivation?
Hyposalivation, which is characterised by decreased salivary flow, and xerostomia, the subjective feeling of a dry mouth, may or may not be associated. There are also oral manifestations that may precede the diagnosis of xerostomia or hyposalivation.
Does the salivary gland cause hyposalivation?
However, the root cause may not always be with the salivary gland itself as its activity is influenced by a host of factors. The main symptom of hyposalivation is a dry mouth although it can have a host of other effects due to the function of saliva.
What are the symptoms of hyposalivation?
A dry mouth (xerostomia) is the most obvious symptom of hyposalivation. It is important to note that dry mouth is not always due to hyposalivation. Mouth breathing for example can lead to dryness of the mouth due to the airflow although the daily saliva production is within the normal range.

What can cause hyposalivation?
The three most common causes of hyposalivation are medications, chronic anxiety or depression, and dehydration. Some medications that cause dry mouth are treatments for sinusitis, high blood pressure (such as “water pills”), anxiety and depression, psychiatric disorders, or a hyperactive bladder.
How do you manage hyposalivation?
Traditional treatment options include daily oral medications to diminish saliva production, periodic injections of a medication called Botox for temporary reduction in saliva production, or a variety of open surgical procedures to remove some salivary glands or disconnect others from the mouth.
What is the difference between xerostomia and hyposalivation?
Most authors agree that xerostomia and hyposalivation are two separate entities: xerostomia denotes the subjective feeling, the symptom, of dry mouth, whereas hyposalivation denotes the sign, a decreased saliva flow rate3,8. The term “dry mouth” has been used to describe both conditions9.
What are examples of Sialogogues?
Salivation may be promoted by using a stimulant: (sialogogue) such as; chewing gums (containing sorbitol or xylitol, not sucrose) diabetic sweets. cholinergic drugs such as pilocarpine, bethanecol, cevimeline or anetholetrithione.
What doctor treats parotid glands?
Head and neck surgeons treat salivary gland conditions. If cancer is detected, our team of radiation oncologists work closely with your head and neck surgeon to provide a comprehensive treatment plan.
What is the best medicine for drooling?
Take medication Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, intercepts nerve impulses before they reach the salivary glands. This medication is often delivered in the form of a patch placed behind the ear. The patch releases the medication continuously, and one patch typically lasts for about 72 hours.
How is hyposalivation diagnosed?
As a consequence, clinical diagnosis of hyposalivation can be obtained only with the patient's history and oral examination12. In addition, other complementary methods like sialometry, sialochemistry and sialography are accurate for the diagnosis of hyposalivation3,18.
What is the most common cause of dry mouth or xerostomia?
Dry mouth, or xerostomia (zeer-o-STOE-me-uh), refers to a condition in which the salivary glands in your mouth don't make enough saliva to keep your mouth wet. Dry mouth is often due to the side effect of certain medications or aging issues or as a result of radiation therapy for cancer.
What are the major causes of dry mouth?
Possible causes of dry mouth include:Dehydration. Dehydration happens when your body loses too much fluid without getting replenished. ... Medications. Dry mouth can be a side effect of many types of medication. ... Radiation therapy. ... Stress and anxiety. ... Aging. ... Mouth breathing and snoring. ... Smoking and recreational drug use.
What are Sialogogues drugs?
A sialogogue (also spelled sialagogue, ptysmagogue or ptyalagogue) is a drug or substance that increases the flow rate of saliva.
What helps a dry mouth at night?
Nighttime Dry Mouth RemediesUse a humidifier at night to add moisture to the air.Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.Use a fluoride toothpaste and/or use a fluoride rinse.Use a moisturizing dry mouth mouthwash and avoid those with alcohol.Avoid spicy, acidic, and sugary foods before bed.More items...
What is a natural remedy for dry mouth at night?
using a humidifier in your bedroom when you sleep. taking over-the-counter saliva substitutes. chewing sugarless gum or sucking on sugarless hard candy. using over-the-counter toothpastes, rinses, and mints.
What is the prevention of dry or sticky mouth?
Chewing sugar-free gum Similar to sugarless candies, chewing sugar-free gum may help keep saliva flowing and stimulate saliva production, which could prevent the mouth from drying out.
What is prevention of dry mouth?
Avoid decongestants and antihistamines when possible. Sip water before swallowing capsules or tablets. The water moistens your mouth. Take medication in the morning, not at night. Dry mouth at night is more likely to cause mouth problems such as cavities.
What is the prevention of dry mouth and tongue?
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day (but preferably more often), after every meal and before bedtime. Flossing your teeth every day. Using a toothpaste that contains fluoride.
What organisms are affected by hyposalivation?
Prolonged hyposalivationincreases the number of cariogenic, organisms (such as Streptococcus and Lactobacillus), and caries progression [6].
How many patients with xerostomia have hyposalivation?
Hyposalivationwas found in 10 of the 35 patients with xer ostomia (28.6%) and in 2 patients without it (p < 0.011).
Which process leads to submandibular gland and periodontal alterations?
The Process of Acclimation to Chronic Hypoxia Leads to Submandibular Gland and Periodontal Alterations: An Insight on the Role of Inflammatory Mediators
What are the symptoms of hyposalivation?
The following symptoms may be present with hyposalivation as a direct result of the low saliva volume: Diminished taste. Difficulty chewing and swallowing. Speech disturbance, sometimes slurring or sensation of a thick tongue. Tooth decay.
What causes a decrease in saliva production?
Sjogren syndrome is one of the most common rheumatologic conditions that affects glands such as the salivary and tear glands. It arises when the immune system attacks these glands. As a result saliva production is reduced. Sjogren syndrome is a chronic disorder and the exact cause is unknown. However, as with many autoimmune disorders the cause is believed to be due to a prior viral or bacterial infection. Women, particularly those with a history of rheumatoid arthritis or SLE, are more likely to develop Sjogren syndrome.
How much saliva is produced daily?
Collectively about 800mL to 2L of saliva is produced daily. A slight decrease in saliva volume is not usually a problem. However, once symptoms and complications ...
What does it mean when your saliva is low?
Hyposalivation means that there is insufficient saliva or low saliva production. There are many reasons why hyposalivation may occur and it may be short lived (acute) or persist for long periods of time (chronic). The problem arises when the salivary glands do not produce or secrete sufficient saliva. However, the root cause may not always be with the salivary gland itself as its activity is influenced by a host of factors. The main symptom of hyposalivation is a dry mouth although it can have a host of other effects due to the function of saliva.
Why is saliva reduced?
Dehydration. Dehydration is one of the more common causes of reduced saliva production. Since there fluid volume in the body is low, the body reduces the production of secretions like saliva. Dehydration can occur for various reasons.
Why is saliva important?
It moisturizes the mouth cavity, lubricates the movement of food around the mouth and down the throat, and also contains enzymes that aid with digestion. We do not give saliva much thought unless there are problems like too much or too little of it. The latter can cause a host of symptoms beyond just a dry mouth.
How to treat low saliva?
It is therefore important that the exact cause of the salivary gland malfunction is diagnosed. Treatment options may vary and can include dietary or lifestyle changes, medication and/or surgery.
Abstract
Saliva has many essential functions. As the first digestive fluid in the alimentary canal, saliva is secreted in response to food, assisting intake and initiating the digestion of starch and lipids. During this process, saliva acts as a solvent of taste substances and affects taste sensitivity.
Similar articles
The rôle of saliva in maintaining oral health and as an aid to diagnosis.
What happens when you have hypersalivation?
In hypersalivation, your salivary glands produce more saliva than usual. If the extra saliva begins to accumulate, it may begin to drip out of your mouth unintentionally .
What is the best treatment for hypersalivation?
Injections. Your doctor may recommend botulinum toxin (Botox) injections if your hypersalivation is constant. Your doctor will inject the drug into one or more of the major salivary glands. The toxin paralyzes the nerves and muscles in the area, preventing the glands from producing saliva.
Why does saliva build up?
Constant hypersalivation is usually caused by chronic health conditions that affect muscle control. When you have impaired muscle control, it can affect your ability to swallow, leading to saliva buildup. This can result from: When the cause is chronic, symptom management is key.
Why does my mouth produce more saliva?
For example, if you’re dealing with an infection, your mouth may produce more saliva to help flush out the bacteria. Hypersalivation usually stops once the infection has been successfully treated. Constant hypersalivation (sialorrhea) often relates back to an underlying condition that affects muscle control.
Can hypersalivation be treated at home?
Your treatment plan will vary depending on the underlying cause. Although home remedies may be beneficial for temporary cases, chronic hypersalivation usually requires something more advanced.
Can hypersalivation cause choking?
When the cause is chronic, symptom management is key. If left untreated, hypersalivation can affect your ability to speak clearly or swallow food and drink without choking.
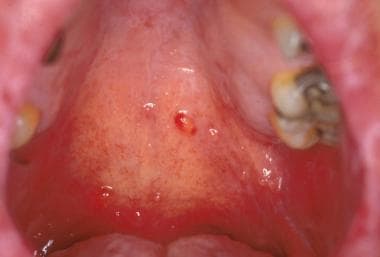
What Is Hyposalivation?
- When there is hyposalivation, the saliva loses its buffering function. This means that the oral mucosa is reddened and vulnerable to inflammation. Sometimes gums bleed. The lack of secretion of saliva is known as hyposalivation. The opposite is the above-average secretion of saliva, which is also known as hypersalivation. When the flow of saliva is...
Causes
- The most common cause of hyposalivation or dry mouth are physiological signs of aging. Salivary secretion naturally decreases with age because the salivary glands are less active. In addition, many people of a certain age take medication that can reduce the flow of saliva. These drugs include, for example, antihypertensives, anticholinergics, tricyclic antidepressants, antihistamine…
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
- When there is hyposalivation, the saliva loses its buffering function. This means that the oral mucosa is reddened and vulnerable to inflammation. Sometimes gums bleed. Pain in the mouth is therefore a frequent side effect of hyposalivation. Above all, a burning sensation on the tongue characterizes the clinical picture. The risk of tooth decay also increases with reduced saliva secr…
Diagnosis & Course of Disease
- Hyposalivation is usually diagnosed by palpation. The doctor uses a glove that sticks to the oral mucosa if there is insufficient saliva secretion in the oral vestibule. When he tries to smear the salivary glands, the glands do not produce any salivary secretion. In visual diagnosis, reddened areas and possible inflammation and caries lesions indicate hyposalivation. The anamnesis can …
Complications
- Hyposalivation mainly causes discomfort in the oral cavity. The mucous membrane becomes reddened and pain and inflammation occur. In most cases, hyposalivation also means that the patient is no longer able to eat or drink normally, so that the patient usually suffers from being underweight or suffering from various deficiency symptoms. It is not uncommon for the tongue t…
When Should You Go to The Doctor?
- Symptoms such as repeated bleeding from the gums and a burning sensation on the tongue indicate hyposalivation. A doctor’s visit is indicated if the symptoms persist over a longer period of time and no clear cause can be determined. If other symptoms such as bad breath or difficulty swallowing appear, medical advice is required. Caries or a generally unpleasant feeling in the m…
Treatment & Therapy
- The treatment of hyposalivation is based on the cause. If too little liquid has simply been taken in, then the deficiency can be easily regulated. If the lack of saliva is due to the patient sleeping with his mouth open at night, the nose must be opened so that nasal breathing can replace mouth breathing. If reduced salivary secretion is a symptom of another condition that may not be curabl…
Prevention
- Most causes of hypersalivation or dry mouth cannot be counteracted. Hyposalivation as a result of dehydration can be avoided by drinking at least 1.5 liters of fluids per day. Dry mouth caused by mouth breathing while sleeping can be prevented by removing the polyps.
Aftercare
- For follow-up care for hyposalivation, doctors often recommend sugar-free chewing gum. These increase the flow of saliva, which reduces the risk of inflammation and tooth decay. Depending on how severely the saliva stimulation is impaired, medication can also be used. In patients who suffer from the disease due to other medications, however, doctors usually advise against furthe…
You Can Do That Yourself
- In the case of hyposalivation, the person concerned has a number of options for self-help, so that a doctor does not always have to be consulted. In most cases, hyposalivation occurs due to insufficient fluid intake. If the person concerned does not drink enough fluids, this habit must be changed. As a rule, the patient should then drink about two liters of liquid a day. Sleeping with y…