
What stimulates the hypoxic drive?
- Abdo WF, Heunks LM. Oxygen-induced hypercapnia in COPD: myths and facts. Critical Care. 2012;16 (5):323. doi:10.1186/cc11475.
- Aubier M, Murciano D, Milic-Emili J, Touaty E, Daghfous J, Pariente R, Derenne JP. ...
- organ, G.E., Mikhail, M.S., Murray, M.J. Clinical Anesthesiology: Fourth Edition. Chapter 22 Respiratory Physiology: The Effects of Anesthesia. Pg. ...
What does hypoxic drive stand for?
What does HYPOXIC DRIVE mean? The hypoxic drive is a form of respiratory drive in which the body uses oxygen chemoreceptors instead of carbon dioxide receptors to regulate the respiratory cycle.
Why is too much oxygen bad for COPD?
Why is too much oxygen bad for COPD? In individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and similar lung problems, the clinical features of oxygen toxicity are due to high carbon dioxide content in the blood (hypercapnia). This leads to drowsiness (narcosis), deranged acid-base balance due to respiratory acidosis, and death.
What is the normal oxygen level for someone with COPD?
A normal oxygen level for a patient suffering from COPD is between 95 and 100 percent, according to About.com. Although some people are able to function normally with an oxygen level as low as 90 percent, a doctor should always be consulted with regard to optimal saturation level.
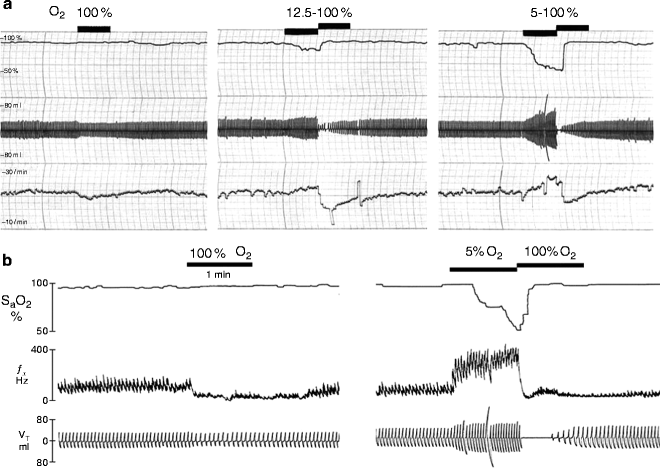
Why is hypoxic drive necessary?
The theory goes then that because of this chronically elevated level of carbon dioxide in the chemo receptors become tolerant of these high levels and therefore the carbon dioxide ceases to be that person's drive to breathe. What therefore drives them to breathe is the hypoxic drive, or the lower levels of oxygen.
What is hypoxic drive quizlet?
hypoxic drive. A condition in which chronically low levels of oxygen in the blood stimulate the respiratory drive; seen in patients with chronic lung diseases. Pulmonary diseases include. Emphysema, chronic bronchitis.
What influences hypoxic drive?
Nut Shell from medical book: The hypoxic drive theory is a result of chronic CO2 retention not the other way around. The body has a high CO2, low oxygen, and low pH( whether it's due to respiratory or metabolic) drive to breath.
What is hypoxic ventilatory drive?
Hypoxic ventilatory response (HVR) is the increase in ventilation induced by hypoxia that allows the body to intake and process oxygen at higher rates. It is initially elevated in lowlanders who travel to high altitude, but reduces significantly over time as people acclimatize.
What is the abnormal stimulus to breathe in patients with a hypoxic drive?
Respiratory Monitoring in Critical Care Hypoxemia is a weaker ventilatory stimulus that is potentiated by hypercapnia and blunted by hypocapnia. Thus, respiratory drive can be assessed as the response to carbon dioxide in the blood in the hypercapnic ventilatory response.
When is arterial carbon dioxide level?
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) is the measure of carbon dioxide within arterial or venous blood. It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg, or 4.7 to 6.0 kPa.
Why are COPD patients given low oxygen?
One is high levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) and the other is low levels of oxygen. Because COPD patients spend their lives with chronically high CO2 levels, they no longer respond to that stimulus, and their only trigger for respiratory drive is the level of oxygen (or lack of) in their blood.
What happens if you give a COPD patient too much oxygen?
In some individuals, the effect of oxygen on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is to cause increased carbon dioxide retention, which may cause drowsiness, headaches, and in severe cases lack of respiration, which may lead to death.
Why do COPD patients retain CO2?
Patients with late-stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are prone to CO2 retention, a condition which has been often attributed to increased ventilation-perfusion mismatch particularly during oxygen therapy.
What is the Hypercapnic drive?
Hypercapnia, on the other hand, triggers a breathing pattern of deep and slow breaths with a relatively more significant increase in tidal volume than respiratory rate. This pattern aims to limit dead space ventilation and optimize carbon dioxide elimination.
How does hypoxia affect ventilation?
Initially, ventilation increases during hypoxia, but after several minutes, ventilation decreases and apnea may ensue. The ventilatory response to carbon dioxide is decreased in the micropremie, and hypoxia further blunts this response. Anesthetic drugs depress the ventilatory responses to both hypoxia and hypercapnia.
How does hypoxia affect breathing?
Hypoxic exposure resulted in significant increases in diaphragmatic amplitude, respiratory rate, and minute diaphragmatic activity as well as heart rate. The biphasic response of diaphragm amplitude peaked at 1 min, whereas the responses of respiratory frequency and heart rate were sustained.
Are we missing a good definition for Hypoxic drive? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
Is hypoxemia real?
This is known as the hypox ic drive, and it is real.
Is hypoxic drive a scientific theory?
Furthermore, the hypoxic drive theory is one in which there really is no scientific evidence to support and yet continues to prosper in every aspect of care in regard to the chronic lung patient, from prehospital all the way to intensive care unit and home care therapy. This subject review will hopefully enhance some understanding of what exactly goes on with these patients and the importance of providing oxygen when it is desperately needed.
