What is IGMP (Internet Group management protocol)?
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a Host-Router Multicast Signalling Protocol that provides dynamically registration of the hosts to the desired Multicast Groups. With IGMP, Host requests to join to the Multicast Groups. This join request comes to the DR (Designated Router). DR translates this to the Multicast Routing Protocol (PIM).
What is the IGMP join process for hosts?
When a host wants to join a multicast group, the host sends one or more unsolicited membership reports for the multicast group it wants to join. The IGMP join process is the same for IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 hosts. In IGMPv3, the join process for hosts proceeds as follows:
What is a multicast group in IGMP?
A set of hosts, routers, and/or switches that send or receive multicast data streams to or from the same sources is called a multicast group, and all devices in the group use the same multicast group address. The multicast group running version 2 of IGMP uses three fundamental types of messages to communicate:
What is the leave group message in IGMP (IGMPv1)?
Previous version of IGMP ( IGMPv1) does not have any Leave Group message to inform the local router about a multicast client’s intention to leave a multicast group.
What is the purpose of IGMP?
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) manages the membership of hosts and routing devices in multicast groups. IP hosts use IGMP to report their multicast group memberships to any immediately neighboring multicast routing devices.
What is IGMP and should I use it?
IGMP, an important feature of network multicast, is used to establish and manage memberships of hosts and routing devices in a multicast group.
Should I turn IGMP on?
I suggest you keep the IGMP Proxy enabled to not generate additional network traffic, which in turn leads to better productivity and efficiency of your wireless devices. What is this? Enabling IGMP Proxying also resolves mirroring issues that are commonly observed in networks.
Is IGMP good for gaming?
IGMP can be used for online streaming video and gaming, and can allow more efficient use of resources when supporting these types of applications. IGMP Proxy enables hosts that are not directly connected to a downstream router to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network.
Is IGMP a ping?
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol and IGMP stands for Internet Group Message Protocol....Difference between ICMP and IGMP.S.NOICMPIGMP2.ICMP has PING features.While it has the Multicast feature.7 more rows•Jul 29, 2020
Is IGMP snooping good?
Makes networks faster: The more traffic that travels across a network, the less bandwidth the network has. IGMP snooping conserves bandwidth by cutting down on the amount of traffic that switches forward. This leaves more bandwidth available, making the network faster.
Should I turn off IGMP?
IGMP proxying should be left enabled unless it causes problems. This allows the router to convert Multicast traffic into Unicast traffic, allowing for the network especially wireless devices, to work more efficiently.
Does IGMP snooping slow down traffic?
IGMP Snooping optimizes that performance overhead. The Router decides which devices will receive the applicable multicast traffic to improve the overall network speed. But if you have little multicast traffic to begin with, say your home based wireless network where you just use it for basic internet and gaming use.
Why would you want to disable IGMP snooping?
By default, traffic from unknown addresses is allowed. In rare circumstances, such as when you are having trouble with a streaming application, you might want to turn off IGMP snooping temporarily or allow traffic from unknown multicast addresses.
What multicast rate should I use?
First off, the best setting for multicast rate for your router is usually the lowest amount. Lower mbps value will typically benefit your normal web uses like browsing or file loading. In this case, You should turn off or disable IGMP Snooping and set the multicast rate to be fixed at the lowest value possible.
Should I use IGMP v2 or v3?
IGMPv2 improves over IGMPv1 by adding the ability for a host to signal desire to leave a multicast group and IGMPv3 improves over IGMPv2 mainly by adding the ability to listen to multicast originating from a set of source IP addresses only.
What is IGMP role?
To sum up, IGMP provides three basic jobs between Hosts and Routers. These roles are: • Join to the Multicast Group, • Remain in the Multicast Group, • Leave the Multicast Group. Now, let’s talk about some of the important operations of Internet Group Management Protocol.
What is IGMP protocol?
What is IGMP? IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a Host-Router Multicast Signalling Protocol that provides dynamically registration of the hosts to the desired Multicast Groups. With IGMP, Host requests to join to the Multicast Groups. This join request comes to the DR (Designated Router).
What is IGMPv1?
IGMPv1 is the first and the basic version of Internet Group Management Protocol. Basically IGMPv1 has two mechanims. These are “ membership query ” and “ membership report ”. In the Multicast network that uses IGMPv1, routers send Membership Queries to 224.0.0.1 Multicast address every 60 seconds.
What is the difference between IGMPv3 and IGMPv3?
In IGMPv3 there is also another difference. All the hosts response to the Queries. In the other IGMP versions, only one host was responding, the others was suspended to reply. IGMPv3 Message consist of more areas that the other IGMP versions.
Is Igmv1 compatible with other versions?
If after three IGMP Query attempt, there is no Membership Report, then that multicast member deleted form the IGMP table of router. IGMP1 is not compatible with other versions. If one version 1 routers exist in the network, all of them must work like it.
Can you test your IP multicast knowledge?
You can test your IP Multicast knowledge with Multicast Quizes. The hosts also stays connected to the Multicast Group with Internet Group Management Protocol. After a while, leaving from the Multicast Group is also a responsibility of Internet Group Management Protocol. To sum up, IGMP provides three basic jobs between Hosts and Routers.
What is IGMP in network?
IGMP provides a means to automatically control and limit the flow of multicast traffic throughout your network with the use of special multicast queriers and hosts. A querier is a network device, such as a router, that sends query messages to discover which network devices are members of a given multicast group.
What is IGMP in LAN?
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used to dynamically register individual hosts in a multicast group on a particular LAN segment. Enabling Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) on an interface also enables IGMP operation on that interface.
What is IGMP proxy?
An IGMP proxy enables hosts in a unidirectional link routing (UDLR) environment that are not directly connected to a downstream router to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network.
What is IGMP extended access list?
IGMP extended access lists also can be used to permit or filter (deny) traffic based on (0.0.0.0, G), that is, (*, G) in IGMP reports that are non-SSM, such as Any Source Multicast (ASM).
How many versions of IGMP are there?
There are three versions of IGMP, as defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). IGMPv2 improves over IGMPv1 by adding the ability for a host to signal desire to leave a multicast group and IGMPv3 improves over IGMPv2 mainly by adding the ability to listen to multicast originating from a set of source IP addresses only.
What is IGMPv3 membership report?
IGMPv3 membership reports are not utilized by the software to filter or restrict traffic for multicast groups that are not configured in Source Specific Multicast (SSM) mode. Effectively, Cisco IOS software interprets all IGMPv3 membership reports for groups configured in dense, sparse, or bidirectional mode to be group membership reports and forwards traffic from all active sources onto the network.
What happens when all hosts leave a multicast group?
In other words, the port continues to receive traffic from that multicast group.
What is a IGMP?
IGMP has a Query-Response type of operation. A term you have to remember related with IGMP is Querier. A Querier device is normally a local multicast enabled router. A Querier sends IGMP Membership Query (MR) messages periodically to find out which devices are members of a particular multicast group.
What is IGMP protocol?
IGMP is an integral protocol of TCP/IP protocol suite. IGMP messages are encapsulated in IPv4 datagram. IGMP messages allows multicast clients to; Join to any available multicast group if interested. Remain in the multicast group and receive multicast traffic addressed to that multicast group. Leave the multicast group when no longer interested.
Why do routers use IGMP?
Local multicast routers use IGMP to keep track of different multicast groups its computers are interested, so that the router can deliver the multicast traffic belongs to that specific multicast groups to computers those are interested.
What is IGMP in IP?
IGMP is an internal protocol of the IP suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using switches, multicast routers, and hosts that support IGMP. A multicastrouter is not necessary as long as a switch is configured to support IGMP with the querierfeature enabled. A set of hosts, routers, and/or switches that send or receive multicast data streams to ...
What is a multicast group?
A set of hosts, routers, and/or switches that send or receive multicast data streams to or from the same sources is called a multicast group, and all devices in the group use the same multicast group address. The multicast group running version 2 of IGMP uses three fundamental types of messages to communicate: Query.
Can IGMP be fast leave?
In this scenario, fast-leave IGMP can actually increase the problem of multicast flooding by removing the IGMP group filter before the Querier has recognized the IGMP leave.
Can Igmp be used without IP address?
The limitation on IGMP without IP addressing is that the switch cannot become Querier on any VLANs for which it has no IP address—so the network administrator must ensure that another IGMP device will act as Querier.
Does PIM-DM forward multicast?
At first, both border routers will flood the traffic into the PIM-DM domain. However, PIM-DM only forwards multicasts based on the shortest reverse path back to the source of the traffic as determined by the unicast routing tables (routing FIB.) Only one multicast stream is sent to the joining host.
Does IGMPv3 include source?
The switch does not support the IGMPv3 "Exclude Source" or "Include Source" options in the Join Reports. Rather, the group is simply joined from all sources. The switch does not support becoming a version 3 Querier. It becomes a version 2 Querier in the absence of any other Querier on the network.
Can I configure IGMP?
You can configure an IGMP proxy on a selected VLAN that will forward IP joins (reports) and IGMP leaves to the upstream border router between the two multicast domains. You must specify the VLANs on which the proxy is enabled as well as the address of the border router to which the joins are forwarded.
Introduction
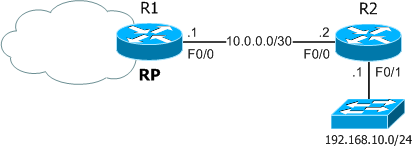
This document describes how the ip igmp join-group and ip igmp static-group commands function within the Cisco IOS ®.
Statically Join the IGMP Group
If the router has the ip igmp join-group command on any of the interfaces, the router itself becomes a receiver for the multicast stream.
IGMP Join Command
If the router R1 does not receive a PIM Join request for the multicast stream from the router R4 (for any reason), then the multicast stream does not flow. One possible reason is that the PIM is not allowed to form a neighborship between the routers R1 and R4 because the routers belong to a different administrative domain.
IGMP Static Command
The ip igmp static-group command is used as a solution in order to forward the traffic from the router R1 towards the router R4 in a static fashion. In this scenario, the router R1 sends a PIM Join request upstream (to the source or RP) and attracts the multicast stream (10.1.3.3, 232.1.1.1).
PIM DR Role
Neither the ip igmp static-group command nor the ip igmp join-group command takes effect if the router R1 is not the PIM DR for the interface Etherent0/0.
Safe Use of the ip igmp join-group Command
In order to troubleshoot issues, you might desire to perform a test with multicast, even outside of the lab. In such a case, ensure that you use the ip igmp join-group command in a safe manner. The reason that you should use the ip igmp join-group command over the ip igmp static-group command is because the multicast packets are punted.
Important Notes About Command Use
The best practice is not to use the ip igmp join-group command unless it is for test purposes in the lab or a temporary test on a live network. Remove the command after all tests are complete. If the multicast traffic must be forwarded only statically, use the ip igmp static-group command instead.
What is IGMP in routers?
Routers also use IGMP to advertise multicast group memberships to neighboring switches and routers. To function, Layer 3 aware devices listen to join and leave messages from clients wanting to join and leave multicast groups through use of an IGMP Querier, common setups rely on a Designated Querier (DQ) per VLAN.
What is IGMP layer 3?
By default, a switch will treat a multicast packet like a broadcast packet, and send it to all ports, unless that switch supports IGMP snooping .
What is Internet Group Management Protocol?
Internet Group Management Protocol introduces the concept of IP multicast groups, raising the question of "How does a router or switch know which ports to send each multicast packet to?"
What is PIM in routing?
Multicast routing protocols evolved over time to the most common one applied today: Protocol Independent Multicast, or PIM. The protocol gains its independence through leveraging other unicast routing protocols on the network i.e. RIP, EIGRP, OSPF, BGP, or static routes via Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) to define its traffic patterns.
What is IP multicast?
Where traditional IP communication over hubs and switches allowed a device to send packets directly to another single device (unicast transmission) or to all devices (broadcast transmission) on the network, the need for IP multicast created a third possibility for allowing hosts the ability to send packets to a subset of all hosts as a group transmission.
Is IGMP v3 backwards compatible?
The IGMP version used by the switch must match the sending host in order to be functional, IGMP v3 is backwards compatible to 2, and 2 to 1. It is best to match the versions so similar versions but should defer to manufacturer for appropriate version.
Type field of IGMPv2 message
Type field is used to identify different types of IGMPv2 messages. Please refer following table to know different Type values.
The Maximum Response Time of IGMPv2 message
The Maximum Response Time field of IGMPv2 message is used in Membership Query (MQ) messages. Maximum Response Time field specifies the maximum time a host can wait before sending a Membership Report message for a corresponding Membership Query message. The Maximum Response Time field is for Membership Query type of messages.
Checksum field of IGMPv2 message
The Checksum field is 16-bit in length and it contains a 16-bit checksum for the message.
Group Address field of IGMPv2 message
Group Address field in IGMPv2 message contains the Class D multicast address of the multicast group.
IGMPv2 Join Messages
In IGMPv2, multicast clients interested in joining a multicast group generate and send unsolicited Membership Report (MR) messages. IGMPv2 Membership Report (MR) messages are sent to the multicast group address they wanted to join.
IGMPv2 Membership Query (MQ) messages
Similar to IGMPv1, in IGMPv2 local multicast router periodically sends out General Membership Query (MQ) messages to verify that at least one multicast client is available in the subnet which is interested to receive traffic from that particular multicast group.
IGMPv2 Leave Group (LG) messages
Previous version of IGMP ( IGMPv1) does not have any Leave Group message to inform the local router about a multicast client’s intention to leave a multicast group.