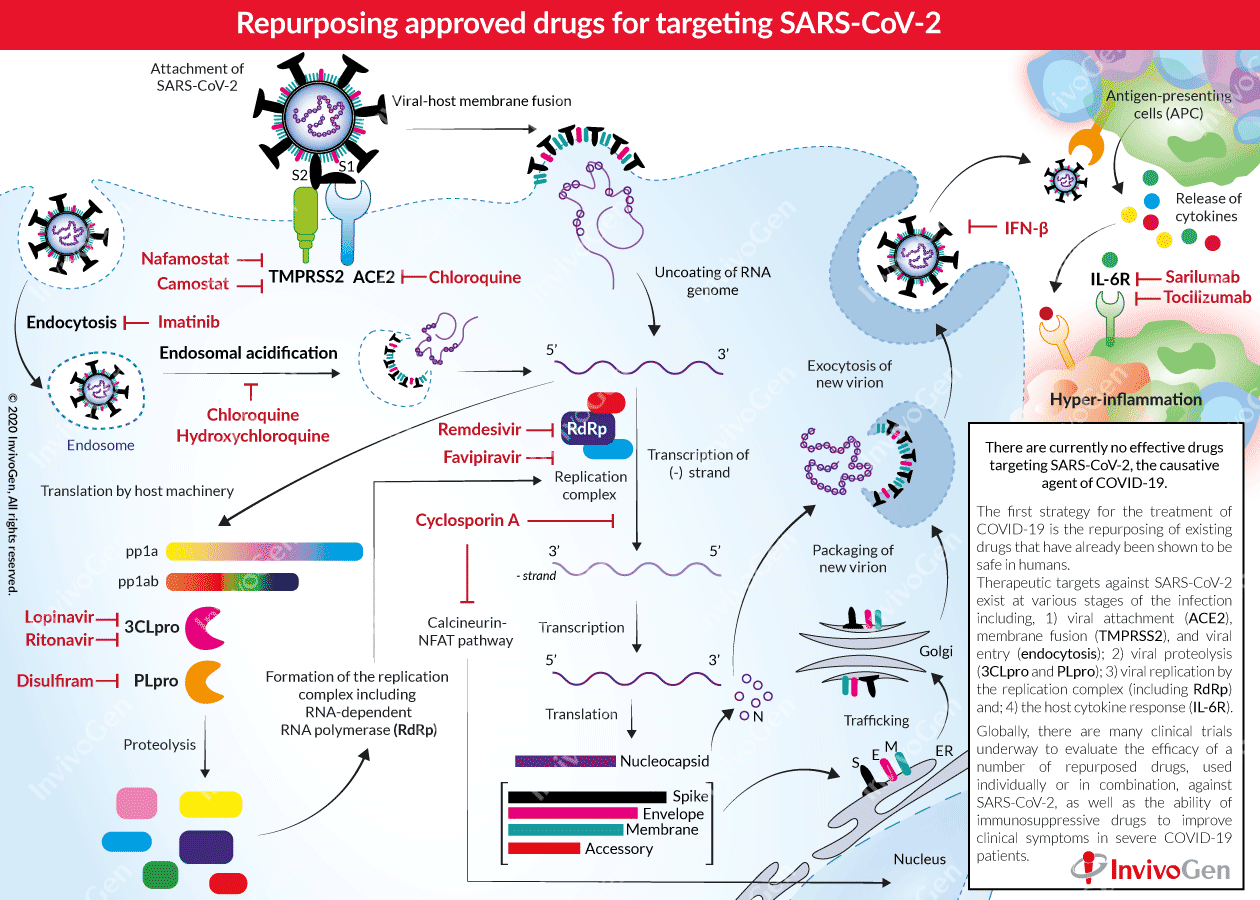
Precautions
Imatinib interferes with the growth of some cancer cells. Imatinib is used to treat certain types of leukemia (blood cancer), bone marrow disorders, and skin cancer. Imatinib is also used to treat certain tumors of the stomach and digestive system. Imatinib can lower blood cells that help your body fight infections and help your blood to clot.
How does imatinib work to treat cancer?
Imatinib targets other than bcr/abl and their clinical relevance in myeloid disorders Imatinib mesylate is a small molecule drug that in vitro inhibits the Abelson (Abl), Arg (abl-related gene), stem cell factor receptor (Kit), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor A and B (PDGFRA and PDGFRB) tyrosine kinases.
What is imatinib mesylate?
The tyrosine kinase (TK) inhibitor, Imatinib, has revolutionized the therapy of malignancies that are addicted to one of its target kinases, c-ABL, c-KIT, and PDGFR. Currently, Imatinib is the standard of care in CML and GIST as it has dramatically changed the outlook of these diseases.
What is imatinib (TK inhibitor)?
It is also used to treat specific digestive tract tumors called GISTs. The lowest GoodRx price for the most common version of imatinib is around $699.13, 82% off the average retail price of $3,939.40.
How much does imatinib cost?
See more
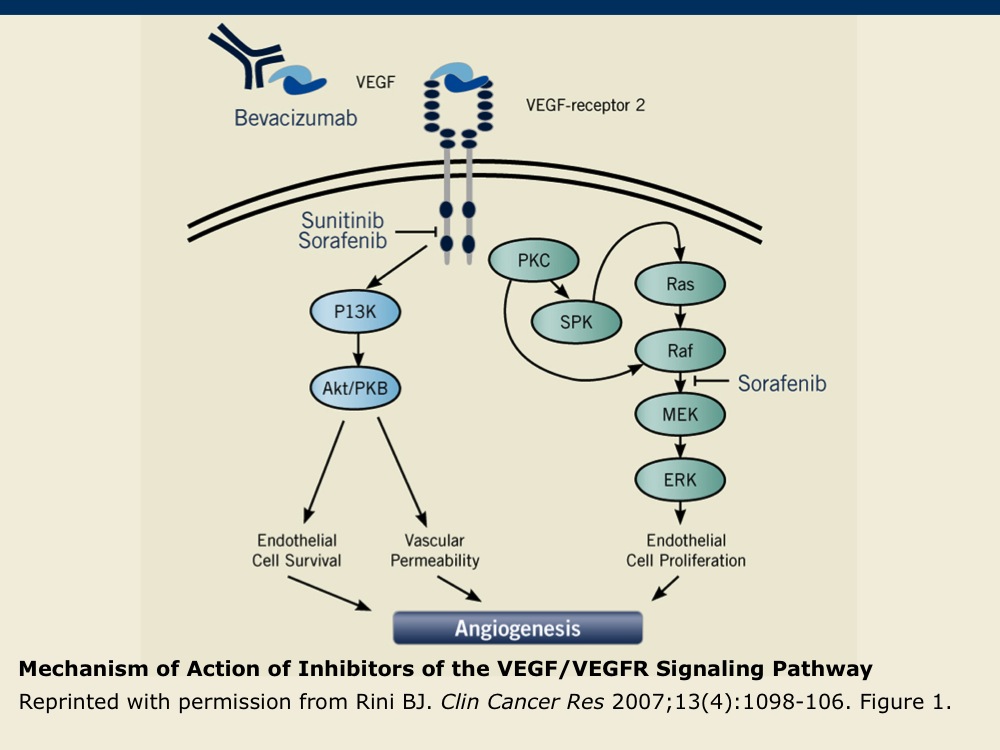
What is imatinib How does it work?
Imatinib is in a class of medications called kinase inhibitors. It works by blocking the action of the abnormal protein that signals cancer cells to multiply. This helps stop the spread of cancer cells.
What is the molecular target of the anti cancer drug Gleevec?
It inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in bcr-abl positive cell lines as well as fresh leukemic cells from Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia.
What does Gleevec target in cancer cells?
Gleevec blocks the overactive KIT enzyme in the tumor cells. This disables the GIST cells so that many of them are destroyed. Although the drug also inhibits the KIT enzyme in normal cells, it does not seem to damage them.
How does imatinib target BCR-ABL?
Imatinib binds to Abl domain via six hydrogen bond interactions. This stabilizes the imatinib Bcr-Abl complex and prevents ATP from reaching its binding site.
How successful is imatinib?
Approximately 39 to 45% of patients who attempt treatment-free remission after having a durable deep molecular response with imatinib therapy can remain in remission for 3 years or longer.
Does imatinib suppress immune system?
This impaired T-cell function was confirmed in a murine model of delayed-type hypersensitivity, indicating that imatinib might have immunosuppressive effects by inhibiting antigen presentation and T-cell effector functions [53].
Does imatinib destroy GIST cancer cells?
In our studies we have found that when GIST patients are treated with imatinib for as few as 3 days, tumor cells in the surgically resected specimen are undergoing apoptosis (reference 4). Although the mechanism is not clear, treatment with imatinib can induce cell death.
Does Gleevec shrink tumors?
For most recurrences, treatment with the targeted drug imatinib (Gleevec) is often the first option to try to shrink any tumors, as long as it is still effective and the patient can tolerate taking it.
How do the cancers develop resistance to Gleevec?
Acquired point mutations within the target genes (Bcr-Abl, KIT and PDGFRα) are a major mechanism of resistance to Gleevec in some patients with hematologic malignance. The mutations are believed to block the binding of Gleevec to ATP binding pockets of these tyrosine kinases.
How does imatinib work in CML?
Imatinib binds to BCR-ABL kinase domain by preventing the transfer of a phosphate group to tyrosine on the protein substrate and the subsequent activation of phosphorylated protein. As the result, the transmission of proliferative signals to the nucleus is blocked and leukemic cell apoptosis is induced.
Does imatinib inhibit ABL?
Imatinib mesylate is a small molecule drug that in vitro inhibits the Abelson (Abl), Arg (abl-related gene), stem cell factor receptor (Kit), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor A and B (PDGFRA and PDGFRB) tyrosine kinases.
How does BCR-ABL cause CML?
The swapping of DNA between the chromosomes leads to the formation of a new gene (an oncogene) called BCR-ABL. This gene then produces the BCR-ABL protein, which is the type of protein called a tyrosine kinase. This protein causes CML cells to grow and divide out of control.
How does Gleevec work at the molecular level?
Gleevec, the thin molecule shown here in blue, has a specific shape which blocks the active site of the abnormal protein. By binding to the active site, Gleevec prevents the trigger protein from causing the release the white blood cells and alleviates the symptoms of the disease.
What kind of inhibitor is Gleevec?
Imatinib (Gleevec) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) used in the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) [298]. In normal cells, tyrosine kinase enzymes are turned on and off as required.
What is the drug Gleevec used for?
This medication is used to treat certain types of cancer (such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases). It works by slowing or stopping the growth of cancer cells.
What type of drug is Gleevec?
Drug type: Gleevec is a targeted therapy. Gleevec is classified as a signal transduction inhibitor - protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
When was imatinib approved?
Imatinib featured on the front cover of Time magazine and was hailed as a “magic bullet”. It was indeed a revolution of its time – after it was approved in 2001, bed-ridden patients who’d been given just months to live were up on their feet and re-energised, thanks to their cancer being eradicated by imatinib.
What was the first cancer drug?
Thirty years ago, we published research that was a key early step in the journey towards the first genetically tailored cancer drug, imatinib (also known as Glivec, or Gleevec in the United States).
Does imatinib kill cancer cells?
Imatinib is unlike the conventional chemotherapy drugs that came before it. Such ‘cytotoxic’ chemo indiscriminately kills rapidly dividing cells. These include the intended target – cancer cells – but also some healthy cells like those lining the gut and mouth and hair follicle cells. Imatinib on the other hand, is specific to a molecule produced by certain cancer cells.
Is imatinib a targeted cancer treatment?
Imatinib set the stage for tailored cancer treatments. Today, there are many more targeted cancer therapies in use or in trials, several of which are underpinned by our work – erlotinib (Tarceva), gefitinib (Iressa), cetuximab (Erbitux), trastuzumab (Herceptin) and vismodegib (Erivedge), to name but a few.
Did imatinib work in mice?
The drug worked in cells and mice, but would it work in patients? In the mid-1990s, Brian Druker led the team which carried out the clinical trials. The results were nothing short of astonishing. The drug worked quickly and effectively in patients for whom there had previously been no hope, and imatinib became the fastest drug to be approved in history.
What is imatinib specific for?
Imatinib is specific for the TK domain in abl (the Abelson proto-oncogene), c-kit and PDGF-R ( platelet-derived growth factor receptor). In chronic myelogenous leukemia, the Philadelphia chromosome leads to a fusion protein of abl with bcr ( breakpoint cluster region ), termed bcr-abl.
What is imatinib used for?
Imatinib is used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and a number of other malign ancies. In 2006 the FDA expended approved use to include Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP), Myelodysplastic /myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD), Aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM).
What is the FDA approved drug for?
The FDA has approved imatinib for use in adults with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL), myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor gene rearrangements, aggressive systemic mastocytosis without or an unknown D816V c-KIT mutation, hypereosinophilic syndrome and/or chronic eosinophilic leukemia who have the FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase (CHIC2 allele deletion) or FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase negative or unknown, unresectable, recurrent and/or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. On 25 January 2013, Gleevec was approved for use in children with Ph+ ALL.
How was imatinib developed?
Imatinib was developed by rational drug design . After the Philadelphia chromosome mutation and hyperactive bcr-abl protein were discovered, the investigators screened chemical libraries to find a drug that would inhibit that protein. With high-throughput screening, they identified 2-phenylaminopyrimidine. This lead compound was then tested and modified by the introduction of methyl and benzamide groups to give it enhanced binding properties, resulting in imatinib.
How is imatinib eliminated?
The major route of elimination is in the bile and feces; only a small portion of the drug is excreted in the urine. Most of imatinib is eliminated as metabolites ; only 25% is eliminated unchanged. The half-lives of imatinib and its main metabolite are 18 h and 40 h, respectively.
How does imatinib work?
Imatinib works by stopping the Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase. This can slow growth or result in programmed cell death of certain types of cancer cells. Imatinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
What are the risks of imatinib?
The only known contraindication to imatinib is hypersensitivity to imatinib. Cautions include: 1 Hepatic impairment 2 Risk of severe CHF or left ventricular dysfunction, especially in patients with comorbidities 3 Pregnancy, risk of embryo-fetal toxicity 4 Risk of fluid retention 5 Risk of growth stunting in children or adolescents
What is imatinib mesylate?
Imatinib mesylate is a small molecule drug that in vitro inhibits the Abelson (Abl), Arg ( abl -related gene), stem cell factor receptor (Kit), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor A and B (PDGFRA and PDGFRB) tyrosine kinases. The drug has acquired therapeutic relevance because of similar inhibitory activity against certain activating mutations of these molecular targets. The archetypical disease in this regard is chronic myeloid leukemia, where abl is constitutively activated by fusion with the bcr gene ( bcr/abl ). Similarly, the drug has now been shown to display equally impressive therapeutic activity in eosinophilia-associated chronic myeloproliferative disorders that are characterized by activating mutations of either the PDGFRB or the PDGFRA gene. The former usually results from translocations involving chromosome 5q31-33, and the latter usually results from an interstitial deletion involving chromosome 4q12 ( FIP1L1-PDGFRA ). In contrast, imatinib is ineffective, in vitro and in vivo, against the mastocytosis-associated c- kit D816V mutation. However, wild-type and other c- kit mutations might be vulnerable to the drug, as has been the case in gastrointestinal stomal cell tumors. Imatinib is considered investigational for the treatment of hematologic malignancies without a defined molecular drug target, such as polycythemia vera, myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia, and acute myeloid leukemia.
Does imatinib inhibit mast cell growth?
The demonstration of imatinib- induced inhibition of Kit-associated signal transduction formed the rationale to use the drug in SM. In vitro, imatinib effectively inhibits normal mast cell growth and development. 83 Additionally, in vitro, imatinib inhibits the growth of human mast cell lines that carry the V560G but not the D816V c- kit mutation. 84 Similarly, the drug was lethal to clonal mast cells from patients who carry wild-type c- kit but not D816V c- kit mutations. 84, 85 The first study that evaluated imatinib therapy in SM was performed before the discovery of FIP1L1-PDGFRA and included 12 patients treated at a lower dose of the drug (100 mg/d). 86 Overall, 5 patients (42%) experienced measurable responses. The most impressive response was seen in 3 patients with associated eosinophilia (SM-eos) later shown to carry the FIP1L1-PDGFRA mutation. 14 In contrast, none of the 2 patients with SM-eos and the c- kit D816V mutation responded. In addition, 2 of the 7 patients with SM not associated with blood eosinophilia experienced partial remission. 86
Does imatinib help with PV?
Imatinib has recently been reported to have clinical activity in the treatment of PV. 97, 101-103 Given that the precise molecular basis for sustenance of the autonomous erythropoiesis that characterizes PV is unknown, there is uncertainty regarding the molecular mechanism by which clinical benefit is derived for PV patients who respond to imatinib therapy. In preclinical studies, imatinib was shown to dramatically decrease erythroid burst-forming units (BFU-Es) from peripheral blood and bone marrow mononuclear cells from PV patients in the absence, but not in the presence, of exogenous growth-promoting cytokines. 104 Whether this is linked to the presence of an imatinib-sensitive phosphoprotein in PV primary cells 105 or represents a general effect on myeloid progenitor cells 106 remains to be clarified.
Is bcr/abl negative CMPD?
The diversity in the clinical phenotype and the underlying molecular lesion (s) in bcr/abl -negative CMPD continue to pose a significant challenge to the identification of patients who have imatinib-responsive disease. To date, most, if not all, bcr/abl - negative myeloid disorders that have displayed a marked response to imatinib therapy have been associated with prominent blood eosinophilia. Therefore, it is reasonable to routinely screen patients with eosinophilia-associated myeloid disorder for imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant mutations. At present, this entails looking for the FIP1L1-PDFRA fusion by RT-PCR 11, 17, 46 or FISH, 14 c- kit mutations by RT-PCR, 54 and chromosomal translocations that involve 5q31-33 by cytogenetic analysis. 47 Figure 3 provides an algorithm in this regard.
What is imatinib used for?
Imatinib is also used to treat certain tumors of the stomach and digestive system.
What other drugs will affect imatinib?
Sometimes it is not safe to use certain medications at the same time. Some drugs can affect your blood levels of other drugs you take, which may increase side effects or make the medications less effective.
How does gleevec work?
Gleevec, known generically as imatinib, works by slowing or stopping the growth of certain cancer cells. Gleevec inhibits (or blocks) specific enzymes in the body called tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are involved in many cell functions, including cell signaling (communication), growth, and division. Blocking these enzymes may help to slow cancer growth. Continue reading
Can you share imatinib with children?
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use imatinib only for the indication prescribed.
Can you take imatinib on an empty stomach?
Take imatinib with a meal and a large glass of water. Do not take imatinib on an empty stomach.
Can you use imatinib while pregnant?
Do not use imatinib if you are pregnant. It could harm the unborn baby or cause birth defects. Use effective birth control to prevent pregnancy while you are using imatinib and for at least 14 days after your last dose.
Can you take imatinib if you are allergic to it?
You should not use imatinib if you are allergic to it.
What is imatinib used for?
Imatinib is used alone or together with other medicines to treat different types of cancer or bone marrow conditions. It prevents or stops the growth of cancer cells and is called an antineoplastic (cancer) agent. Imatinib is used for these conditions:
How much does Imatinib cost?
It is also used to treat specific digestive tract tumors called GISTs. The lowest GoodRx price for the most common version of imatinib is around $136.05, 98% off the average retail price of $9,666.64. Specialty Drug: Specialty drugs are often expensive and may need to be filled through specialty pharmacies.
What is generic gleevec?
Generic Gleevec. IMATINIB is a medicine that targets proteins in cancer cells and stops the cancer cells from growing. It is used to treat certain leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, and other cancers. It is also used to treat specific digestive tract tumors called GISTs.
Does imatinib help with Philadelphia chromosome positive?
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of imatinib to treat Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) in children younger than 1 year of age. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Can imatinib cause weight gain?
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated geriatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of imatinib in the elderly. However, serious side effects (eg, swelling of the face, hands, fingers, feet, and/or lower legs, and unusual weight gain) may be more likely to occur in elderly patients, who may be more sensitive than younger adults to the effects of imatinib.
What is a Glivec?
It is a treatment for many different types of cancer.
Does imatinib block tyrosine kinases?
There are a number of different tyrosine kinases and blocking them stops the cancer cells growing. Imatinib targets different tyrosine kinases, depending on the type of cancer.
Why does imatinib stop working?
This is known as imatinib resistance. Resistance to imatinib seems to be caused by changes in the genes of the CML cells. Sometimes this resistance can be overcome by increasing the dose of imatinib, but some patients need to change to a different drug, such as one of the other TKIs.
What is Ponatinib used for?
Because this drug can cause some serious side effects, it's only used to treat patients with CML if all of the other TKIs don’t work or if their leukemia cells have a gene change called the T315I mutation. Ponatinib is the first TKI to work against CML cells that have this mutation.
What TKI is used for CML?
Bosutinib (Bosulif) is another TKI that targets the BCR-ABL protein. It can be used as the first treatment for CML, but most often it’s used if another TKI is no longer working.
What is the first drug to target the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase protein?
Imatinib. Imatinib (Gleevec) was the first drug to specifically target the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase protein, because of this it's known as a first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Almost all CML patients respond to treatment with imatinib, and most of these responses seem to last for many years.
How long can you eat before taking Nilotinib?
It's taken as a pill. The patient cannot eat 2 hours before taking nilotinib and for 1 hour after taking it.
Can you stop taking myeloid leukemia pills?
But for some people who have very good, long-lasting responses to treatment, it might be possible to stop taking these drugs, or at least lower the dose. (See Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Phase to learn more.) These drugs are pills you take at home. To get the best outcomes, it's important to take them exactly the way your doctor tells you ...
Does Ponatinib help with CML?
Ponatinib (Iclusig) These drugs seem to work best when CML is in the chronic phase, but they also can help patients with more advanced disease (accelerated or blast phases). In most people, the TKIs don't seem to make the leukemia go away forever, so these drugs need to be taken indefinitely.

Overview
This medication is used to treat certain types of cancer (such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases).
May Treat: Aggressive systemic mastocytosis · Philadelphia chromosome positive ALL · Accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome (+) CML · Adjuvant therapy of CD117+ gastrointest stromal tumor · Chronic eosinophilic leukemia and more
Brand Names: Gleevec
Drug Class: Antineoplastic - Protein-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult your doctor. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
May Treat: Aggressive systemic mastocytosis · Philadelphia chromosome positive ALL · Accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome (+) CML · Adjuvant therapy of CD117+ gastrointest stromal tumor · Chronic eosinophilic leukemia and more
Brand Names: Gleevec
Drug Class: Antineoplastic - Protein-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult your doctor. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
Lactation: This drug should not be given to breastfeeding mothers
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Research
Medical uses
Contraindications and cautions
Side effects
Overdose
One study demonstrated that imatinib mesylate was effective in patients with systemic mastocytosis, including those who had the D816V mutation in c-KIT. However, since imatinib binds to tyrosine kinases when they are in the inactive configuration and the D816V mutant of c-KIT is constitutively active, imatinib does not inhibit the kinase activity of the D816V mutant of c-KIT. Experience has shown, however, that imatinib is much less effective in patients with this mu…
Interactions
Imatinib is used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and a number of other malignancies. In 2006 the FDA expended approved use to include dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP), myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD), and aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM).
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved imatinib as first-line treatment for Phi…
Pharmacology
The only known contraindication to imatinib is hypersensitivity to imatinib. Cautions include:
• Hepatic impairment
• Risk of severe CHF or left ventricular dysfunction, especially in patients with comorbidities
• Pregnancy, risk of embryo-fetal toxicity