What are the steps of a nerve impulse?
Which is the first step in the path of a nerve impulse?
- TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE SYNAPSE.
- THE IMPULSE TRAVELS.
- Re- Polarization. - When the cell membrane becomes depolarized, Potassium automatically leaves the cell until the cell is back into complete resting stage.
- DEPOLARIZATION. - A nerve cell is stimulated.
- REFRACTORY PERIOD.
What are the 4 main functions of the nervous system?
What Are the Four Functions of the Nervous System?
- Parts of the Nervous System. The nervous system consists of the brain, organs used to provide sensory information, spinal cord and all the nerves that connect them.
- S
- ensory Function. The sensory function of the nervous system is the part that gathers information about both the world around you and the inside of the body.
- C
- ommunicative Function. ...
- I. ...
What are the steps of nerve impulse transmission?
- Calcium gates open. At the end of the axon from which the impulse is coming, the membrane depolarizes, gated ion channels open, and calcium ions (Ca2+) are allowed to enter ...
- Releasing a neurotransmitter. ...
- The neurotransmitter binds with receptors on the neuron. ...
- Excitation or inhibition of the membrane occurs. ...
How to repair nervous system?
- Use Somadevic to monitor your blood pressure and to improve your psychological well-being; (read Somavedic reviews here)
- Keep off tobacco products;
- Drink plenty of fresh structured water and other fluids that are not overly sweetened;
- Avoid head injuries/accidents by all means;
- Finish your shower with cold water to relax your nervous system. ...
What is a nerve impulse example?
For example, if your finger touches a hot stove, nerve impulses support quick communication between nerve cells in the hand and the brain so you avoid a serious burn.
What means nerve impulse?
A nerve impulse is a gradual physicochemical change in a nerve fiber's membrane that occurs after stimulation. It helps to send a record of sensation or a signal from a receptor. It also carries information along the neuron and throughout the nervous system.
What are called impulses?
: a sudden spontaneous inclination or incitement to some usually unpremeditated action.
What is an impulse in biology?
AKA: nerve impulse. The signal that travels along the length of a nerve fiber and ends in the release of neurotransmitters. Nerve impulses are the means by which information is transmitted along the neuron and throughout the nervous system.
How are impulses formed?
A nerve impulse is generated when the stimulus is strong. This stimulus triggers the electrical and chemical changes in the neuron. As mentioned already there are different ions on either side of the cell membrane. The exterior side has sodium ions that are positively charged and are more in number.
What are the two types of impulses?
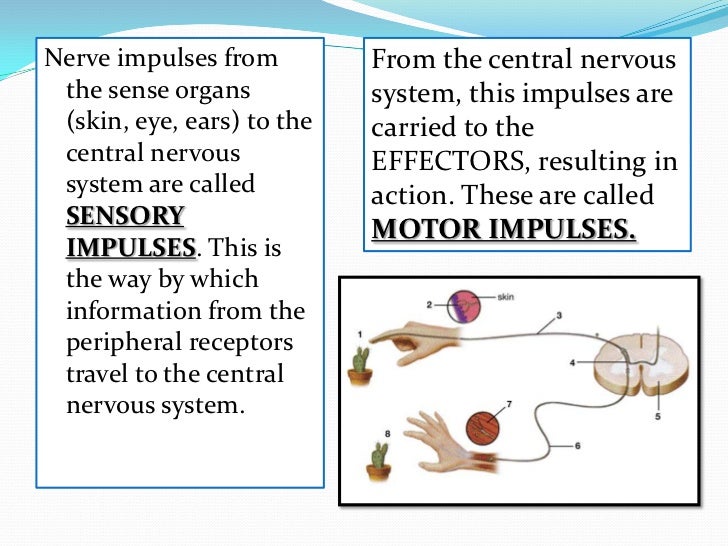
Sensory impulses are neural messages that travel from the internal and external environment to the spinal cord and brain. Motor impulses are neural messages that travel from the spinal cord and brain to the body.
Why are nervous impulses important?
Nerve impulses are signals carried along nerve fibers. These signals convey, to the spinal cord and brain, information about the body and about the outside world. They communicate among centers in the central nervous system and they command your muscles to move.
What is impulse known for?
impulseSV, also known simply as impulse, is a YouTuber and Hermitcraft member. He joined in Season 3. He has 1,160,000 subscribers on his YouTube channel. He is well-known for his farm designing skills and the tutorials he creates for his designs.
What is impulse Class 9 biology?
Hint: The overall effect of force on the motion of a body is known as the impulse. Its value is the product of the applied force and the time interval during which the force is applied. When a force is applied for a short time period ′dt, the result is a force impulse.
What are the three impulses?
Therefore, we conclude that nerve impulses appear to be an ensemble of three inseparable, interdependent, concurrent states: the physiological action potential, the APPulse and the CAP.
What are electric impulses?
The electrical signal that travels down an axon is called a nerve impulse. The electricity produced by our bodies is what allows synapses, signals and even heartbeats to occur.
What are impulses made of?
In neurons, the most important ions we will need to know are sodium ions (Na+), potassium ions (K+), and calcium ions (Ca2+). These ions are literally the carriers of electric charge across the membrane which ultimately make up all those electrical impulses.
What is the presynaptic area of the cell?
At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of the molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 11.4. 5, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called synaptic vesicles that are packed with chemicals called neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell, it opens channels that allow calcium to enter the terminal. Calcium causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane, releasing their contents into the narrow space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. This area is called the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter molecules travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors, which are proteins that are embedded in the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
What is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump?
The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of active transport that moves sodium ions out of cells and potassium ions into cells.
Why is ATP used in the cell?
ATP is used to pump sodium out and potassium into the cell. There is more concentration of sodium outside the membrane and more concentration of potassium inside the cell due to the unequal movement of these ions by the pump.
How does neurotransmitter affect post-synaptic cells?
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells.
What happens when a neuron reaches a certain threshold?
The change in membrane potential results in the cell becoming depolarized.
What is the difference between sodium and potassium?
Sodium is the principal ion in the fluid outside of cells, and potassium is the principal ion in the fluid inside of cells. These differences in concentration create an electrical gradient across the cell membrane, called resting potential. Tightly controlling membrane resting potential is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Why do nerve impulses occur?
A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
Why does action potential arise?
Action potential arise due to differential concentrations of Na+ and K+ on opposite sides of the membrane, and the subsequent flow of these ions.
Which vesicles bind to the plasma membrane and release their contents into the synaptic gap?
3. Neurotransmitter vesicles bind to the plasma membrane and release their contents into the synaptic gap.
Which neurons connect to other neurons or to muscles to signal contraction?
4) Dendrites may connect to other neurons or to muscles to signal contraction.
Which system is responsible for connecting nerves to tissue?
Peripheral nervous system - the nerves (sensory and motor) which radiate from spinal cord to connect to tissue.
Where does the reversal of charges take place?
The reversal of charges takes place through ions.
What is the contribution of the resting membrane potential?
The main contribution to the resting membrane potential (a polarized nerve) is the difference in permeability of the resting membrane to potassium ions versus sodium ions. The resting membrane is much more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium ions resulting in slightly more net potassium ion diffusion ...
How does polarization occur?
Polarization is established by maintaining an excess of sodium ions (Na +) on the outside and an excess of potassium ions (K +) on the inside. A certain amount of Na + and K + is always leaking across the membrane through leakage channels, but Na +/K + pumps in the membrane actively restore the ions to the appropriate side.
What is resting potential?
Resting potential. The resting potential describes the unstimulated, polarized state of a neuron (at about –70 millivolts).
What happens when the K+ channels close?
Hyperpolarization. By the time the K + channels close, more K + have moved out of the cell than is actually necessary to establish the original polarized potential. Thus, the membrane becomes hyperpolarized (about –80 millivolts).
What is the transmission of nerve impulses?
The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron. The membrane of an unstimulated neuron is polarized—that is, there is a difference in electrical charge between the outside and inside of the membrane.
What happens to the Na+ membrane in response to a stimulus?
In response, Na + on the outside of the membrane becomes depolarized (as in a graded potential). If the stimulus is strong enough—that is, if it is above a certain threshold level—additional Na + gates open, increasing the flow of Na + even more, causing an action potential, or complete depolarization (from –70 to about +30 millivolts).
What happens when a stimulus opens a K+ channel?
A graded potential occurs when the stimulus causes Na + or K + gated channels to open. If Na + channels open, positive sodium ions enter, and the membrane depolarizes (becomes more positive). If the stimulus opens K + channels, then positive potassium ions exit across the membrane and the membranehyperpolarizes (becomes more negative).
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
The basic unit of the nervous system is a nerve cell, or neuron. The human brain contains about 100 billion neurons. A neuron has a cell body, which includes the cell nucleus, and special extensions called axons (pronounced AK-sonz) and dendrites (pronounced DEN-drahytz ). Bundles of axons, called nerves, are found throughout the body.
What is the name of the cell that sends electrical signals to neighboring neurons?
The nervous system also includes non-neuron cells, called glia (pronounced GLEE-uh ). Glia perform many important functions that keep the nervous system working properly.
What is the name of the chemical messengers released by the axon?
The axon then releases the chemical signal with chemical messengers called neurotransmitters (pronounced noor-oh-TRANS-mit-erz) into the synapse (pronounced SIN-aps )—the space between the end of an axon and the tip of a dendrite from another neuron.
What are the functions of the glia?
These networks allow different parts of the brain to “talk” to each other and work together to control body functions, emotions, thinking, behavior, and other activities.
What are the parts of the brain that communicate?
The brain is made up of many networks of communicating neurons and glia. These networks allow different parts of the brain to “talk” to each other and work together to control body functions, emotions, thinking, behavior, and other activities. 1, 2, 3.
What are the functions of neurons?
Sensory neurons detect light, sound, odor, taste, pressure, and heat and send messages about those things to the brain. Other parts of the nervous system control involuntary processes. These include keeping a regular heartbeat, releasing hormones like adrenaline, opening the pupil in response to light, and regulating the digestive system.
What is the central nervous system made of?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
Why do nerves get trapped?
Nerves can be pinched or trapped for many reasons, such as overuse (as in carpal tunnel syndrome ), a tumor, or structural problems like sciatica. Toxic substances: Chemotherapy medicines, illegal drugs, excessive alcohol and poisonous substances can cause peripheral neuropathy or nerve damage.
How many people have diabetes?
Around 30 million Americans have diabetes and nearly 50% of them have some nerve damage. Diabetic neuropathy usually affects the arms, legs, hands, feet, fingers and toes. Lupus: About 1.5 million Americans live with lupus, and 15% of them have experienced nerve damage.
How do nerves regulate your body?
It regulates your body’s systems and allows you to experience your environment. A vast network of nerves sends electrical signals to and from other cells, glands, and muscles all over your body. These nerves receive information from the world around you.
What part of the body sends electrical signals?
Each part contains billions of cells called neurons, or nerve cells. These special cells send and receive electrical signals through your body to tell it what to do. Central nervous system (CNS): Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS. Your brain uses your nerves to send messages to the rest of your body.
How to prevent nerve damage?
It needs care to keep working correctly. See your doctor regularly, eat a healthy diet, avoid drugs, and only drink alcohol in moderation . The best way to avoid nerve damage from disease is to manage conditions that can injure your nerves, such as diabetes.
What is the function of the nervous system?
Your nervous system uses specialized cells called neurons to send signals, or messages, all over your body. These electrical signals travel between your brain, skin, organs, glands and muscles. The messages help you move your limbs and feel sensations, such as pain.
What do motor neurons tell you?
Motor neurons tell your muscles to move. Sensory neurons take information from your senses and send signals to your brain. Other types of neurons control the things your body does automatically, like breathing, shivering, having a regular heartbeat and digesting food.
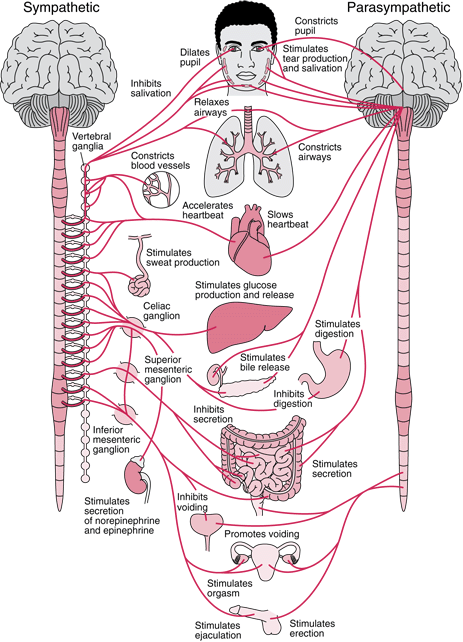
What is the acronym for parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses. An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest.
How does the PSNS work?
An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: 1 Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest. 2 Lacrimation: Lacrimation is a fancy word for making tears. Tears keep your eyes lubricated, preserving their delicate tissues. 3 Urination: The PSNS contracts the bladder, which squeezes it so urine can come out. 4 Digestion: The PSNS stimulates the release of saliva to promote digestion. It also enacts peristalsis, or the movement of the stomach and intestines, to digest food as well as release bile for the body to digest fats. 5 Defecation: The PSNS constricts the sphincters in the intestine and moves digested food material down the digestive tract so a person can have a bowel movement.
What happens if your parasympathetic nervous system doesn't work?
Your PSNS is a vital part of your body’s key functions. When it doesn’t work properly, you can face a number of bodily dysfunctions that affect your health. If you think you may be having trouble with one of your body’s parasympathetic nervous system functions, talk to your doctor to find out how you can get help.
What is the nervous system?
Your nervous system is a wild and wonderful network of nerves that act in different key functions to keep your body moving, responding, sensing, and more. This article is going to examine the parasympathetic nervous system, one of two majors divisions of the larger autonomic system. In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic ...
What are the receptors in the heart?
Parasympathetic nervous system and your heart. There are a number of special receptors for the PSNS in your heart called muscarinic receptors. These receptors inhibit sympathetic nervous system action. This means they’re responsible for helping you maintain your resting heart rate.
Where do parasympathetic nerves come from?
Trusted Source. of all parasympathetic nerve fibers in the body come from this nerve. This nerve has branches in many key organs, including the stomach, kidneys, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, bladder, anal sphincter, vagina, and penis.
How many halves are there in the autonomic system?
In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic and sympathetic portions of the autonomic system are two halves of the same whole.