
What is the retropharyngeal space in the head and neck?
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Retropharyngeal Space The retropharyngeal space (RPS) is an anatomical region that spans from the base of the skull to the mediastinum. Its location is anterior to the prevertebral muscles and posterior to the pharynx and esophagus.
What is the retropharyngeal space made of?
The retropharyngeal space is a midline deep compartment of the head and neck that consists largely of fatty areolar tissue and lymph nodes that drain the pharynx, nose, and middle ear. The inferior extent of the retropharyngeal space can be confusing.
What causes air in the retropharyngeal space?
Air within the retropharyngeal space and tracking anteriorly along other neck fascial planes. The cause of the air leak may be a local perforation of the upper aerodigestive tract or the air may have tracked from the chest such as may be seen in pneumomediastinum related to asthma or with esophageal perforation.
What is thin air in the retropharynx?
Thin air is seen within the retropharyngeal space and also tracks anteriorly along other neck fascial planes. No radiopaque foreign body such as a bone is identified within the soft tissues of the neck. Case Discussion Air within the retropharyngeal spaceand tracking anteriorly along other neck fascial planes.
What is the retropharyngeal space continuous with?
The retropharyngeal space It is continuous with the parapharyngeal space anteriorly and the sublingual space. The retropharyngeal space runs between the base of the skull to the level of the seconds thoracic vertebra where the fascial layers fuse.
What forms the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space is a midline deep compartment of the head and neck that consists largely of fatty areolar tissue and lymph nodes that drain the pharynx, nose, and middle ear.
What is the difference between the retropharyngeal space and the danger space?
True retropharyngeal space is between visceral fascia and alar fascia of deep layer of deep cervical fascia. Danger space is between alar and prevertebral layers of deep cervical fascia. These two components cannot be distinguished on MRI and CT in healthy patient.
Is the retropharyngeal space a potential space?
Anatomical Parts The retropharyngeal space is a potential space of the head and neck, bounded by the buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and the prevertebral fascia posteriorly. Because serious infections of teeth can spread down this space into the posterior mediastinum, it is often confused with the danger space.
What is retropharyngeal?
A retropharyngeal (reh-tro-fah-RIN-jee-ul) abscess is an infection that forms behind the back wall of the throat. Retropharyngeal abscesses are uncommon in children.
What is the danger space in the neck?
The danger space is immediately posterior to the retropharyngeal space and immediately anterior to the prevertebral space, between the alar and prevertebral divisions of the deep layer of the deep cervical fascia. It extends from the skull base to the posterior mediastinum and diaphragm.
What fascia separates the esophagus from the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space comprises the posterior part of the visceral compartment, in which the esophagus, trachea, and thyroid glands are enclosed by the middle layer of deep cervical fascia (see Fig. 65-5).
What is the danger space?
The danger space is a deep compartment of the head and neck located behind the true retropharyngeal space, extending from the skull base to the mediastinum.
Why is retropharyngeal space important?
The retropharyngeal space is a significant region to consider when evaluating a patient with neck pain as a multitude of pathologies can manifest and affect this area. The connection of the danger space to the mediastinum allows for the spread of infections from the oral cavity to the thoracic cavity.
Where does the danger space end?
the diaphragmIt is bounded at the top by the skull base, at the front by the alar fascia and behind by the prevertebral fascia. It comes to an end at the level of the diaphragm.
Where are the retropharyngeal lymph nodes located?
The lateral retropharyngeal lymph node (LRPLN) is located between the internal carotid artery and the prevertebral muscles. The LRPLN is most often seen anterior to the arch of C1, but is sometimes found at the level of the soft palate.
What are the deep neck spaces?
Deep neck spaces are regions of loose connective tissue filling areas between the 3 layers of deep cervical fascia, namely, superficial, middle, and deep layers. The superficial layer is the investing layer, The pretracheal layer is the intermediate layer and the prevertebral layer is the deepest layer.
What is Gillette space?
Retropharyngeal space: A potential space between buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and prevertebral fascia posteriorly. It is divided into 2 halves by a midline band. These 2 halves are called “Space of Gillette”
What is the parapharyngeal space?
The parapharyngeal space (PPS) is a potential space lateral to the upper pharynx. The PPS is shaped like an inverted pyramid, extending from the skull base superiorly to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone inferiorly.
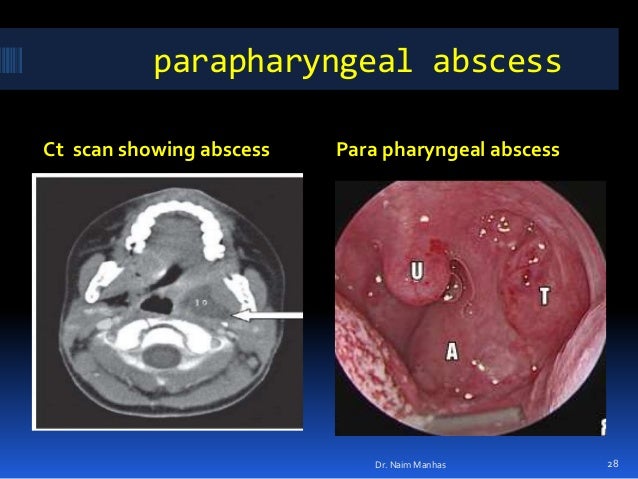
What is the difference between retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess?
Two main types of deep abscesses within the neck are parapharygeal abscess which is infection and accumulation of purulent discharge within the parapharyngeal space and retropharyngeal abscess which is infection and accumulation of purulent discharge within the retropharyngeal space.
Are tonsils retropharyngeal?
Abscesses can develop in lymph nodes behind the throat (“retropharyngeal”) or in the area of the tonsils (“peritonsillar”). The tonsils are lymph tissue located at the back of the mouth; they can easily be seen when enlarged.
What is a retropharyngeal cyst?
Lesions of the retropharyngeal space (RPS) are uncommon, and they generally present as solitary, painless masses, which are often cystic. They usually originate from branchial arches anomalies, and only in a few cases do they turn out to be bronchogenic cysts.
What are deep neck space infections?
Deep neck space infections (DNSI) are serious diseases that involve several spaces in the neck. The common primary sources of DNSI are dental infections, tonsillar and salivary gland infections, malignancies, and foreign bodies. With widespread use of antibiotics, the prevalence of DNSI has been reduced.
What is danger space 4?
Danger Space 4 An area of delicate loose connective tissue that lies between the alar and prevertebral fascia. Extends from the base of the skull to the mediastinum.
What are the most common complications in case of deep neck infections?
Life-threatening complications include: descending mediastinitis, septic shock, upper airway obstruction, jugular vein thrombosis, venous septic embolus, carotid artery pseudoaneurysm or rupture, pleural empyema, pericarditis, pericardial effusion, aortopulmonary fistula, adult respiratory distress syndrome, acute ...
What are retropharyngeal lymph nodes?
The retropharyngeal lymph nodes (RLNs) are known as Rouviere nodes, which are located medially to the internal carotid artery. Enlarged retropharyngeal nodes can be the result of inflammatory diseases or malignancy. Pathologic types of metastatic carcinoma in retropharyngeal nodes can be various.
What are the deep neck spaces?
Deep neck spaces are regions of loose connective tissue filling areas between the 3 layers of deep cervical fascia, namely, superficial, middle, and deep layers. The superficial layer is the investing layer, The pretracheal layer is the intermediate layer and the prevertebral layer is the deepest layer.
What is Gillette space?
Retropharyngeal space: A potential space between buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and prevertebral fascia posteriorly. It is divided into 2 halves by a midline band. These 2 halves are called “Space of Gillette”
What causes retropharyngeal edema?
Sometimes, retropharyngeal edema can simulate a collection; it can be caused by radiation therapy, or retropharyngeal calcium tendonitis. 4 The differential diagnosis of retropharyngeal edema is mainly the infectious diseases (abscesses and phlegmons); retropharyngeal tumors are very rare.
What is the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space (RPS) lies between the visceral division of the middle layer of the deep cervical fascia behind the pharyngeal constrictors and the alar division of the deep layer of the deep cervical fascia posteriorly. Retropharyngeal space infection (RPSI) may follow infection in the nasopharynx, oropharynx, sinonasal region and rarely mastoiditis. RPSI may also occur directly after a traumatic perforation of the posterior pharyngeal wall or oesophagus, or indirectly, from the parapharyngeal space. Most RPSIs in children are secondary to URI, whereas trauma or foreign bodies cause most RPSIs in adults. Retropharyngeal lymph nodes tend to regress by the age of 5, causing infection in this area to be much more common in children than in adults. RPSI may drain into the prevertebral space and through this space into the chest, thus causing mediastinitis. Symptoms of RPSI include sore throat, dysphagia, stiff neck, fever and rarely posterior neck and shoulder pain aggravated by swallowing. Examination reveals anterior displacement or bulging of one or both sides of the posterior pharyngeal wall due to involvement of lymph nodes, which are distributed lateral to the midline fascial raphe. Lateral neck radiograph (demonstrating widening of the retropharyngeal space) and CT scan with contrast of the neck facilitate diagnosis and assessment of the extent of RPSI. Early diagnosis is important and treatment with aggressive intravenous antibiotics is mandatory. Transoral incision and drainage is recommended in cases with abscess formation.
Where is the retropharyngeal space located?
The retropharyngeal space (RPS) spans the length of the neck from the skull base to the mediastinum. As its name indicates, it lies posterior to the pharynx. More inferiorly in the neck it lies posterior to the esophagus. It is located anterior to the cervical and upper thoracic spine and the prevertebral muscles.
What age do retropharyngeal lymph nodes regress?
Retropharyngeal lymph nodes tend to regress by the age of 5 , causing infection in this area to be much more common in children than in adults. RPSI may drain into the prevertebral space and through this space into the chest, thus causing mediastinitis.
Where does retropharyngeal space infection occur?
Retropharyngeal space infection (RPSI) may follow infection in the nasopharynx, oropharynx, sinonasal region and rarely mastoiditis. RPSI may also occur directly after a traumatic perforation of the posterior pharyngeal wall or oesophagus, or indirectly, from the parapharyngeal space.
Which layer of the cervical fascia is the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space is bound anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal membrane and part of the middle layer of the deep cervical fascia, laterally by the alar fascia, and posteriorly by the prevertebral fascia.
What is the RPS in a patient?
The RPS contains only medial and lateral RPS lymph nodes and fat. This results in a very short differential diagnosis for pathology in this space, primarily a tumor or infection affecting the nodes. While this makes diagnosing easier, the RPS is actually an imaging and clinical "blind spot," with RPS nodes being inaccessible to direct observation or physical examination. Additionally, nonnecrotic nodes often appear isodense to prevertebral muscles on CECT and frequently lie far lateral in the RPS and medial to the internal carotid arteries. Therefore, it is critical that the clinician methodically searches the RPS for adenopathy on imaging, particularly in patients with head and neck (H&N) malignancies.
What is the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space is a potential space of the head and neck, bounded by the buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and the alar fascia posteriorly. It contains the retropharyngeal lymph nodes.
Where is the danger space?
The danger space is actually between the alar fascia and the prevertebral fascia and extends from the cranial base above to the level of the diaphragm.
Where is the alar fascia located?
It is limited above by the base of the skull, and below where the alar fascia fuses with the buccopharyngeal fascia at about the level of T4 and the carina.
Can midline raphe spread?
A midline raphe is present in this space making some infections appear unilateral. However without treatment infections can easily spread from one space to the adjacent space.
What is the lateral pharyngeal space?
This fascial space is also known as the lateral pharyngeal space. It is classed as one of the suprahyoid fascial spaces because it is situated on the lateral aspect of the pharynx and is continuous with the retropharyngeal space posteriorly and the submandibular space anteriorly. It runs from the base of the skull caudally towards ...
Which layer of the cervical fascia covers the esophagus and the pharynx?
The retropharyngeal space is a fascial space that transverses the length of the neck in its entirety. It sits posterior to the buccopharyngeal layer of middle cervical fascia which covers the esophagus and the pharynx and is anterior to the alar fascia.
What is suprahyoid in anatomy?
suprahyoid. infrahyoid. fascial spaces that span the entire length of the neck. This article will highlight the main anatomical information that is known about the parapharyngeal space and the retropharyngeal space. It will also give an extremely brief example of the pathology associated with the fascial spaces.
Which layer of the cervical fascia covers the medial pterygoid muscle?
Medially it is bordered by the middle layer of deep cervical fascia known as the buccopharyngeal fascia which covers the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. The lateral border is comprised of the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia which covers the medial pterygoid muscle and the deep portion of the parotid gland.
Which anatomical structure limits the spread of infection between the spaces?
The hyoid bone is the main anatomical structure that limits the spread of infection between the spaces and for that reason they are categorised according to their position in relation to the hyoid bone. The three main groups of fascial spaces are known as the: suprahyoid. infrahyoid. fascial spaces that span the entire length of the neck.
Which space is more susceptible to infections that originate in Waldeyer’s disease?
The retropharyngeal space is more susceptible to infections that originate in Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring ...
Where is the retropharyngeal space?
The retropharyngeal space extends craniocaudally from the base of the skull to the posterior mediastinum and is enclosed by the buccopharyngeal and alar fascia. Retropharyngeal abscess is a suppurative collection within this space. Although infections of the prevertebral and alar spaces also can occur, infections of these anatomic spaces will not be discussed here.
When does retropharyngeal abscess occur?
Retropharyngeal abscess typically occurs in children between the ages of two and four years but can occur at any age.
What is the lateral neck x-ray?
Lateral neck radiographs are typically the imaging study of choice in the initial evaluation of suspected retropharyngeal abscess, especially in young children. Lateral neck radiographs have the benefit of lower radiation exposure and tend to be better tolerated by patients who are exhibiting signs of airway compromise. Lateral neck x-rays should be obtained during inspiration with the neck held in normal extension. Improper techniques in obtaining this imaging study can result in false positives for retropharyngeal infection. When the retropharyngeal infection is present, the depth of the prevertebral space will be increased on the lateral neck x-ray. In healthy individuals, the upper limit of normal prevertebral space is 7 mm at C2 and 14 mm at C6 in children. In healthy adults, the upper limit of normal prevertebral space is 7 mm at C2 and 2 mm at C6. A width of 30 mm at C6 indicates abscess collection.
What causes a retropharyngeal abscess?
Typically patients under the age of five have an antecedent upper respiratory tract infection leading to suppurative cervical lymphadenitis and eventually retropharyngeal abscess. In older children and adults, a retropharyngeal abscess can be caused by trauma to the posterior pharynx, which leads to inoculation of the retropharyngeal space and results in abscess formation. Primary infections of the tonsils and of the dentition can also evolve into retropharyngeal abscesses, though more commonly into peritonsillar (Quinsy) or parapharyngeal abscesses, respectively. Direct expansion from spinal discitis or osteomyelitis is a rare cause of a retropharyngeal abscess as well. As a retropharyngeal abscess grows in size, it can lead to upper airway obstruction and asphyxiation. Treatment of retropharyngeal abscess ranges from prolonged courses of intravenous antibiotics to surgical incision and drainage.[1][2][3]
Can retropharyngeal abscess cause death?
Although mortality from sepsis does occur in these patients, the number one cause of death in patients with retropharyngeal abscess remains upper airway occlusion. [9][10]
Can a retropharyngeal abscess cause airway obstruction?
Without proper treatment, retropharyngeal abscesses can lead to upper airway obstruction and asphyxiation. This activity reviews retropharyngeal abscesses and details important treatment considerations. This activity highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and managing this condition.
Can an oropharynx be examined?
The oropharynx of a patient with a suspected retropharyngeal abscess only should be thoroughly examined with palpation or probing by clinicians who are experienced in emergent airway management. Abscess rupture can occur during the examination of the posterior pharynx, leading to aspiration and potential asphyxiation. It has been suggested that this exam should be performed with patients in the Trendelenburg position to prevent aspiration in case of abscess rupture, and suction equipment should be readily available.

Overview
The retropharyngeal space (abbreviated as "RPS" ) is a potential space and deep compartment of the head and neck situated posterior to the pharynx. The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the prevertebral fascia, and laterally by the carotid sheath. It spans from the base of the skull superiorly to the mediastinum inferiorly. It contains the retropharyngeal lymph …
Anatomy
Superiorly, the retropharingeal space terminates at the base of the skull (more specifically, at the clivus ). Inferiorly, the true RPS terminates at a variable level along the upper thoracic spine with the fusion of alar fascia and visceral fascia; sources either give the inferior termination of the true RPS as occurring at approximately the vertebral level of T4 or at a variable level anywhere between the T1-T6. The danger space component of the RPS meanwhile extends further inferior-…
Clinical significance
A midline raphe may be present in this the RPS, making some infections appear unilateral. However without treatment infections can easily spread from one space to the adjacent space.
If more than half of the size of the C2 vertebra, it may indicate retropharyngeal abscess.
Additional images
• Retropharyngeal abscess
See also
• Parapharyngeal space
External links
• Anatomy figure: 31:01-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• MedEd at Loyola Radio/curriculum/Bones/Image476a.jpg