What types of DNA fragments can be assembled in vivo?
Fragment generation - Any linear DNA fragments can be assembled in vivo as long as they have homologous sequences at their termini. It doesn’t matter if the DNA is PCR amplified, restriction digested or even a synthesized gene.
What is in vivo?
In vivo is Latin for “within the living.” It refers to work that’s performed in a whole, living organism.
How do you use dsDNA to in vivo clone?
Using dsDNA to in vivo clone by gap repair. In this case, the linear substrate made by PCR contains an origin of replication and a drug-resistance marker as well as 50 bases of homology to the region to be cloned. In this case, three genes are being cloned onto a plasmid from the chromosome or a BAC.
Is bacterial in vivo cloning finally coming of age?
With these limitations no longer an issue, bacterial in vivo cloning is now able to come of age. In Vivo Assembly (IVA) cloning ( Garcia-Nafria et al ., 2016) uses the bacterial recombination pathway to allow any cloning procedure to be performed using a simple two-step, 2 hr protocol prior to transformation (Figure 1).

What is in vitro recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA (rDNA), or molecular cloning, is the process by which a single gene, or segment of DNA, is isolated and amplified. Recombinant DNA is also known as in vitro recombination.
How is DNA used in cloning?
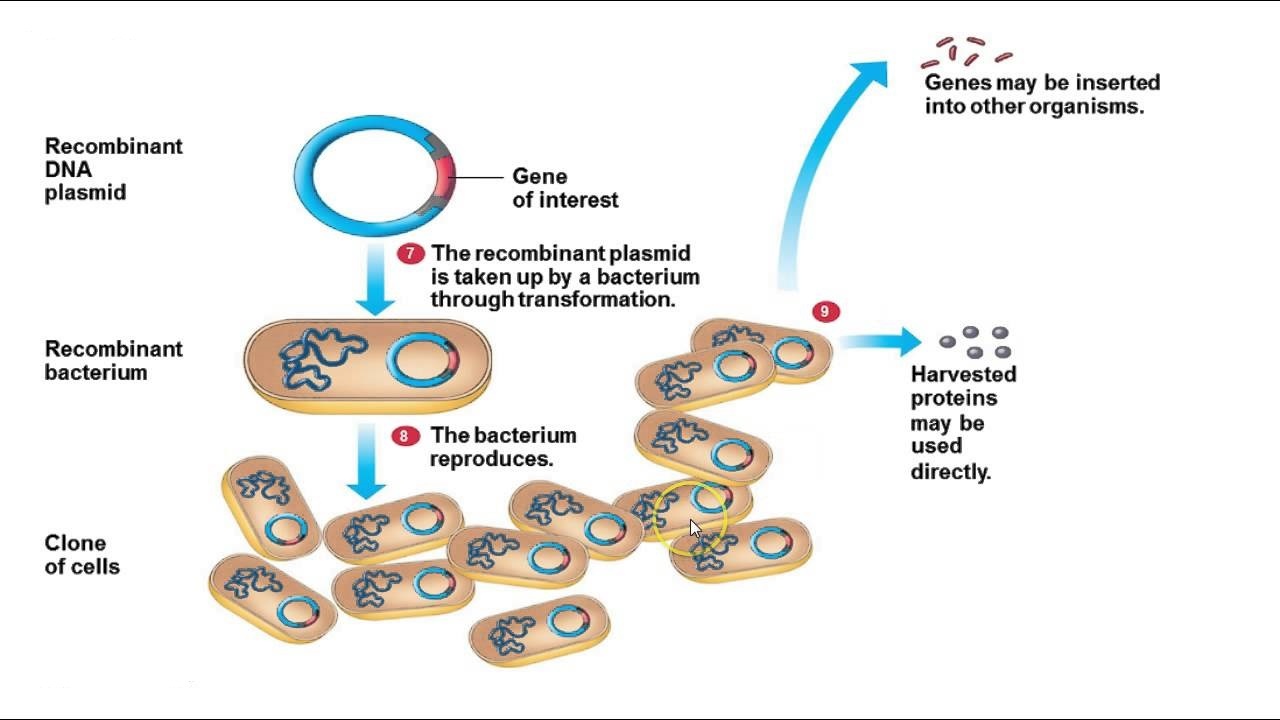
DNA cloning is the process of making multiple, identical copies of a particular piece of DNA. In a typical DNA cloning procedure, the gene or other DNA fragment of interest (perhaps a gene for a medically important human protein) is first inserted into a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid.
What is the purpose of bacterial transformation?
Bacterial transformation is a key step in molecular cloning, the goal of which is to produce multiple copies of a recombinant DNA molecule. Prior steps for creating recombinant plasmids are described in traditional cloning basics and involve insertion of a DNA sequence of interest into a vector backbone.
How do you confirm if there is an insert in a plasmid without sequencing?
For a simple way... take a vector specific primer with 3' end close to your insert and take another primer used to amplify your insert in such a way that you could get a amplification with PCR and done. If there is product from this PCR then you got your insert.
What are the 3 types of cloning?
There are three different types of cloning: Gene cloning, which creates copies of genes or segments of DNA. Reproductive cloning, which creates copies of whole animals. Therapeutic cloning, which creates embryonic stem cells.
What are the 4 steps in cloning?
In the classical restriction enzyme digestion and ligation cloning protocols, cloning of any DNA fragment essentially involves four steps:isolation of the DNA of interest (or target DNA),ligation,transfection (or transformation), and.a screening/selection procedure.
Why SOC medium is used in transformation?
SOC Medium is a rich medium used primarily to aid recovery of bacterial competent cells following transformation. Use of SOC medium improves the molecular uptake whilst stabilizing the cells rapidly and so maximizing the efficiency of competent cells.
What are the 5 steps of bacterial transformation?
MatchStep [1] Remove Plasmid from bacteria cell.Step [2] Isolate the gene of interest.Step [3] cut open plasmid with restriction enzymes, leaves "Sticky ends".Step [4] insert gene of interest.Step [5] Insert the Plasmid with Recombinant DNA into a new bacterium.Step [6]
Why is E. coli used for transformation?
E. coli is a preferred host for gene cloning due to the high efficiency of introduction of DNA molecules into cells. E. coli is a preferred host for protein production due to its rapid growth and the ability to express proteins at very high levels.
How can you tell if clones are positive?
Positive clones are identified by selecting against URA3. This method produces positive YAC recombinants at a frequency of ∼40%.
What are the 6 steps of cloning?
StepsChoice of host organism and cloning vector. ... Preparation of vector DNA. ... Preparation of DNA to be cloned. ... Creation of recombinant DNA with DNA ligase. ... Introduction of recombinant DNA into host organism. ... Selection of organisms containing vector sequences.More items...
How do you know if a gene is cloned?
One of the key elements required to identify a gene during cloning is a probe. A probe is normally a cloned piece of DNA that contains a portion of the sequence for which you are searching. You typically will make the probe radioactive and add it to a solution.
Why do people clone DNA?
The first motive for cloning genes may be to gain information about the nucleotide sequence of the gene. DNA sequencing or restriction enzyme cutting analysis can be used to study a gene or compare versions of a gene from different sources. A second motive would be to manipulate a gene.
Is DNA cloning possible?
The genes of an individual, the genome, can be cloned, but the individual itself cannot be cloned, as it will be made clear below. Cloning genes or, more generally, cloning DNA segments is routinely done in many genetics and pharmaceutical laboratories throughout the world (12, 31).
What is the purpose of DNA ligase in a cloning experiment?
In DNA replication, ligase's job is to join together fragments of newly synthesized DNA to form a seamless strand. The ligases used in DNA cloning do basically the same thing. If two pieces of DNA have matching ends, DNA ligase can join them together to make an unbroken molecule.
Why is DNA cloning considered an important technology?
Why is DNA cloning considered an important technology? DNA cloning allows for multiple genes to be copied, which can lead to the mass production/harvest of useful products.
Why is in vitro fertilization called in vitro?
Because fertilization occurs within a laboratory environment and not within the body (in vivo), the procedure is referred to as in vitro fertilization.
What is in vitro and in vivo?
In vitro and in vivo are two terms that you may encounter occasionally, particularly when reading about scientific studies. In vivo refers to when research or work is done with or within an entire, living organism. Examples can include studies in animal models or human clinical trials. In vitro is used to describe work that’s performed outside ...
What is in situ hybridization?
In situ methods can be used to observe things in their natural context, yet outside of a living organism. A good example of this is a technique called in situ hybridization (ISH). ISH can be used to look for a specific nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) within something like a tissue sample.
What is an in vitro experiment?
In vitro. In vitro methods used in a laboratory can often include things like studying bacterial, animal, or human cells in culture. Although this can provide a controlled environment for an experiment, it occurs outside of a living organism and results must be considered carefully.
What is a specialized probe?
Specialized probes are used to bind to a specific nucleic acid sequence that the researcher is looking to find. These probes are tagged with things like radioactivity or fluorescence. This allows the researcher to see where the nucleic acid is located within the tissue sample.
How do antibiotics affect bacteria?
They do this by disrupting the bacteria’s ability to grow or thrive. There are many types, or classes, of antibiotics and some bacteria are more sensitive to some classes than others. Additionally, bacteria can evolve to be resistant against antibiotics.
What is in vivo study?
In vivo. When a study is performed in vivo, it can include things like performing experiments in an animal model, or in a clinical trial in the case of humans. In this case, the work is taking place inside a living organism.
What are the drawbacks of in vitro drug testing?
An absence of biokinetics (how the body transports and metabolized drugs and toxins) is one of the significant drawbacks of in vitro studies. This, as well as several other factors, can make it very difficult to extrapolate the results of in vitro tests to what might be expected when the drug is used in vivo. 1
How do in vivo studies evaluate drugs?
An example of how in vivo studies are needed to evaluate drugs is with respect to drug absorption in the body. A new drug may appear to work in a dish, but not in the human body. It could be that the drug is not absorbed when it passes through the stomach, so it has little effects on humans.
Why is in vivo research important?
2 These studies allow researchers an opportunity to see how a drug works amid other bodily processes. Mice and humans have important differences.
Why do we do in vitro studies?
Studies are usually done in vitro first for ethical reasons. In vitro studies allow a substance to be studied safely, without subjecting humans or animals to the possible side effects or toxicity of a new drug.
Why is in vitro study important?
In vitro studies are important in that they allow more rapid development of new treatments —many drugs can be studied at one time (and they can be studied in a large number of samples of cells) and only those that appear to be efficacious go on to human studies.
What is an in vitro lab?
In vitro: The term in vitro refers to a medical study or experiment which is done in the laboratory within the confines of a test tube or laboratory dish.
What is in vivo study?
In contrast, in vivo studies are looking at the actual effect on an organism— whether a laboratory animal or a human.
