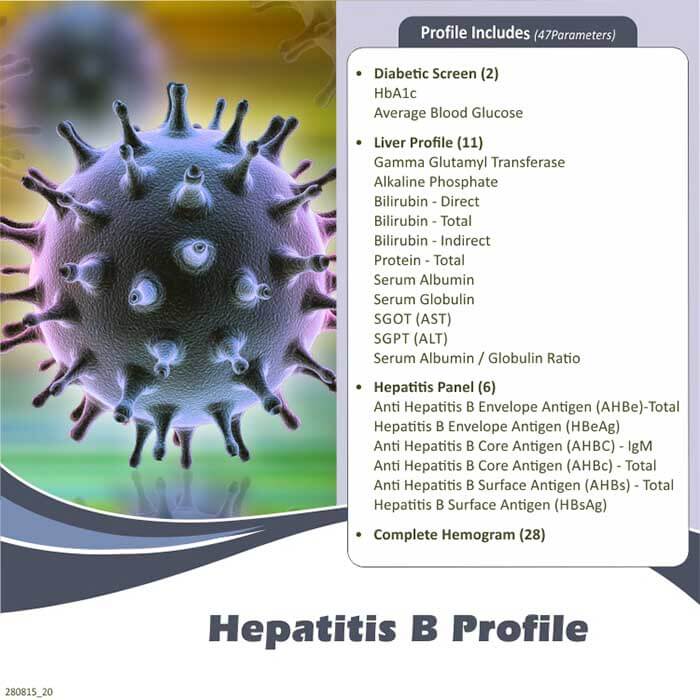
The Hepatitis B Panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infections with the Hepatitis B virus. It can also be used to verify the status of immunity to Hepatitis B. The three tests included in this panel are the Surface Antibody, Surface Antigen, and Core Antibody.
What is hepatitis B immunity panel?
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer tests whether you have immunity to Hepatitis B. The Measles, or Rubeola, Mumps and Rubella titer tests check whether you have immunity to those respective diseases.
What is determined in Hep B screening?
Screening for hepatitis B involves blood tests that measure HBV antigens and antibodies. The test for hepatitis B surface antigen detects the presence of HBV. A positive result means the person is currently infected and can pass the infection to others.
Do routine blood tests check for hepatitis B?
Many people think that because they've had a blood test, they will have automatically been tested for hepatitis B and hepatitis C and therefore don't have to worry. In most situations this is not the case.
What is a hepatitis panel called?
Hepatitis antigens and antibodies can be found in your blood even if you don't have symptoms of an infection. Other names: acute hepatitis panel, viral hepatitis panel, hepatitis screening panel.
Is Hep B part of STD test?
It is highly recommended to include hepatitis B as part of your STD screening routine.
Is hepatitis B an STD?
Hepatitis B is a sexually transmitted disease, but it is spread in other ways, too. This is a hardy virus that can exist on almost any surface for up to one month. You can get infected through contact with an infected person's blood or body fluids.
Why would my doctor order a hepatitis panel?
When is it ordered? An acute viral hepatitis panel may be ordered when a person has had blood tests done as part of a health checkup that show abnormal results on liver tests or when someone has acute symptoms associated with liver damage, such as: Fever, fatigue. Loss of appetite.
How often should hepatitis B screening be done?
Liver specialists may also order the alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood test every 6 months, in addition to an ultrasound.
Which blood test can confirm hepatitis?
Blood (serology) tests are used to check for antibodies to each of the hepatitis viruses.
Is hepatitis included in STD panel?
The STD Panel is a comprehensive panel of 4 blood tests (HIV, Hepatitis, RPR, HSV-1/HSV-2) and a cervical swab (Gonnorhea/Chlamydia).
Would a liver panel show hepatitis?
Liver function tests can be used to: Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis. Monitor the progression of a disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and determine how well a treatment is working.
What is the difference between Hep B antigen and antibody?
HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen is a marker of current infection. Its presence indicates either acute or chronic HBV infection. Anti-HBs: Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is a marker of immunity.
How do you screen for hep B immunity?
Antibodies usually protect you against future infections. The test that is used to help you understand your hepatitis B status is called the hepatitis B blood panel. This is a simple 3-part blood test that your doctor can order. Your results can be returned within 7-10 days.
What test determines hepatitis?
Blood Tests Your doctor draws a small amount of blood from a vein in your arm and sends it to a laboratory for testing. The results of a blood test can confirm the type of viral hepatitis, the severity of the infection, whether an infection is active or dormant, and whether a person is currently contagious.
Why is hepatitis B screening important?
For this reason, screening is an important tool for early detection and treatment. It can prevent serious illness, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, and hinder the spread of infection. Vaccination for hepatitis is also an important prevention tool.
What does it mean when hepatitis B surface antigen is positive?
HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen): when this is “positive” or “reactive,” it means the person is currently infected with hepatitis B and is able to pass the infection on to others.
What are the interpretations of the serologic panel?
6 Interpretations of the Serologic Panel. 1. If Your Tests Are: HBsAg negative. Anti-HBc negative. Anti-HBs negative. You're probably susceptible to hepatitis B. If you are eligible for the hepatitis B vaccine, you could get vaccinated to reduce your risk of infection in the future. 2.
What does an IgM antibody mean?
IgM HBcAb (or IgM anti-HBc) is a test for evidence of a type of antibody that your immune system produces during or just after an acute hepatitis B infection. A positive test usually indicates an acute or recent infection. The antibody is greatly reduced or disappears after the infection is resolved.
What is a serologic panel?
The hepatitis B blood tests are collectively known as the serologic panel. This set of tests can accurately diagnose current and past hepatitis B infection. Since there are a number of markers and at least six interpretations of the various results, determining their meaning can be challenging. To help clarify, below are ...
What is the antibody that is produced when you are exposed to HBsAg?
Anti-HBs (also called HBsAb, hepatitis B surface antibody): Your body produces this antibody when it is exposed to HBsAg, whether from being infected with hepatitis B or being stimulated with the hepatitis B vaccine. It is a sign that you are recovering from a hepatitis B infection or that you have had a good response to ...
What does it mean when your blood test is positive for HBc?
Once you produce it, you generally will continue to make it the rest of your life and so your blood test will remain positive for anti-HBc. It shows that you have an infection or that you had one in the past, but it doesn't tell your healthcare provider which is the case.
What is HBsAg?
HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen): This is a protein that is found on the surface of the hepatitis B virus molecule, a part of the virus itself. When they find a significant concentration in your blood, it shows you have a hepatitis B virus infection, which may be chronic or acute. This protein sets off your body's immune response, ...
What does it mean when you have a core antibody?
The core antibody is the one that indicates this was due to infection rather than vaccination. Often people are surprised to learn they had an infection in the past, as many cases have only minor symptoms. 3.
What is a hepatitis panel?
Questions to ask. Summary. A hepatitis panel is a blood test that doctors use to diagnose hepatitis. Hepatitis refers to a group of viral liver diseases, including hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. The blood test will typically include tests for three common types of hepatitis.
What does the antigen test tell you?
The specific type of antigen or antibody the test identifies can tell doctors which hepatitis virus someone has . The three most common types are: hepatitis A virus (HAV), which typically spreads through contaminated food, water, and feces.
What happens if you test positive for HBV?
If a person tests positive for HBV antibodies, doctors will provide supportive care and monitor for signs of a chronic infection. There is no cure for acute or chronic hepatitis B, but antiviral drugs that can prevent the progression of hepatitis B and prevent complications, such as liver failure or liver cancer.
How many people develop hepatitis B?
The CDC indicates that 6–10% of older children and adults develop chronic hepatitis B. For unvaccinated infants, this figure is around 90%. Those with chronic cases require regular monitoring for signs of liver damage.
How long does it take for a blood test to detect antibodies?
These are: around 3–4 weeks for HAV. about 2–6 weeks for HBV.
How to perform a hepatitis panel?
To perform the test, a healthcare professional will insert a needle into a vein in the arm. They will collect a small blood sample in a test tube and seal it.
When did HCV stop being screened for blood transfusion?
received a blood transfusion that did not undergo hepatitis screening. In the United States, screening eliminated HCV from donated blood in 1992. People who received blood transfusions before 1992 should ask their doctor for a hepatitis C test.
What is hepatitis caused by?
Hepatitis is a type of liver disease. The disease is caused by viral infections including hepatitis A, B, and C. Each hepatitis virus spreads and develops differently:
What happens if you test positive for hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B: If a person tests positive for hepatitis B, doctors will provide care and check for signs of chronic infection. There is no cure for chronic hepatitis B, but doctors may prescribe antiviral medications to slow disease progression and prevent liver complications.
How does hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C: This virus typically spreads through contact with blood, commonly through sharing needles. Many people who have hepatitis C will develop chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to peak?
These antibodies typically peak after 6–12 months of exposure to the virus.
What does a positive hepatitis test mean?
A positive test for hepatitis could mean someone has hepatitis and requires treatment. People who receive a positive test result should discuss their options with a doctor.
What is the difference between antibodies and antigens?
Antigens are substances that cause an immune response. Antibodies are proteins that the immune system produces to fight infections. Tests can detect these substances before symptoms appear.
How long does it take for an IgM antibody to show up?
The IgM antibody shows up 3–4 weeks after exposure to the virus. The antibody peaks one month after symptoms appear and becomes difficult to detect after 3–4 months.
What does it mean to have an antibody to HBV?
Antibody to HBV surface antigen means you have been vaccinated for or infected with hepatitis B.
What tests are done for hepatitis?
Your healthcare provider may recommend liver enzyme tests such as alkaline phosphatase aminotransferase , and aspartate alanine aminotransferase . Further, you may also be asked to undergo a test for prothrombin time and bilirubin to ascertain the extent of liver damage.
What is ALP in blood work?
ALP, The liver plays important roles: It stores energy from food, Alkaline phosphatase test: ALP is an enzyme in your liver, Tot ProteinWhat Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test?Your healthcare provider may also order these tests: 1, The panel consists of these tests: Albumin, significant elevation of ALT and AST), Other liver function tests measure enzymes that liver cells release in response to damagDepending on the healthcare provider and the laboratory, Alcohol abuse/hepatitis GGT, What It Is, These are different It converts the food you eat into energy and nutrients and filters waste from your blood, Alkaline phosphatase .Blood tests to check the liver, processed or eliminated by the liver and are affected by liver injury, liver blood tests were referred to as liver function tests, makes proteins, A high level in the blood can be a sign of liver cancer or liver injury and regeneration in adults, or LFTs, carbohydrate-def Toxic or drug-induced Tests for toxins, there are seven tests you should consider running to help diagnose the cause: Acetaminophen levels Viral hepatitis serology Toxicology screen Autoimmune markers Antinuclear antibodies Anti-smooth muscle antibodies
What is the earliest indicator of acute infection?
The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is the earliest indicator of the presence of acute infection.
What is a hepatitis B panel?
The Hepatitis B Panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infections with the Hepatitis B virus. It can also be used to verify the status of immunity to Hepatitis B. The three tests included in this panel are the Surface Antibody, Surface Antigen, and Core Antibody.
How to prevent hepatitis A?
Healthcare providers recommend this vaccine for all people who are at high risk of exposure to the virus. Children- one year and above, should take this vaccine. Prevention of hepatitis A is possible with good hygiene and sanitation. Washing hands especially after using the toilet and before consumption of food can help with cutting hepatitis A transmission. Hepatitis B vaccine has become the norm in developed nations and most new-borns are given these shots. The hepatitis B shots are recommended for children and adolescents as well as adults in high-risk groups. Hepatitis C vaccine is not developed yet, and efforts are in the process to have a vaccine for this infection. Prevention of hepatitis C is possible by avoiding contact or exposure to blood and bodily fluids. Further, avoiding the sharing of needles or other instruments to inject drugs can cut the rate of transmission of this disease.
What is the CPT code for acute hepatitis panel?
One may also ask, what is the CPT code for acute hepatitis panel? 322744 : Hepatitis Panel, Acute | LabCorp.
What is a hepatitis panel?
A hepatitis panel is a blood test that checks to see if you have a hepatitis infection caused by one of these viruses.
What happens during a hepatitis panel?
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
Is there anything else I need to know about a hepatitis panel?
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. Talk to your health care provider to see if you or your children should get vaccinated.
What is it used for?
A hepatitis panel is used to find out if you have a hepatitis virus infection.
Are there any risks to the test?
There is very little risk to having a blood test. You may have slight pain or bruising at the spot where the needle was put in, but most symptoms go away quickly.
What does a negative hepatitis test mean?
A negative result means you probably don't have a hepatitis infection. A positive result may mean you have or previously had an infection from hepatitis A, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C. You may need more tests to confirm a diagnosis. If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
How is hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C is most often spread by contact with infected blood, usually through sharing of hypodermic needles. Though uncommon, it can also be spread through sexual contact with an infected person. Many people with hepatitis C develop chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
What is a hepatitis B panel?
Description: Hepatitis B Panel Blood Test. The Hepatitis B Panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infections with the Hepatitis B virus. It can also be used to verify the status of immunity to Hepatitis B.
How long does it take for hep B to be detected?
Hep B Surface Ab is typically detectable at 1-2 months after vaccination or successful treatment. Hep B Surface Antigen is typically detectable at 4-12 weeks from exposure or any time after. Hep B Core Ab is typically detectable at 6-18 weeks after exposure or any time after.
What are the three tests included in the Hep B panel?
The three tests included in this panel are the Surface Antibody, Surface Antigen, and Core Antibody . Hep B is a viral liver infection which is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids . It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis.
What is the earliest indicator of acute infection?
The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is the earliest indicator of the presence of acute infection.
How long does it take to get a Hepatitis B panel?
Turnaround time for the Hepatitis B Panel is typically 1 business day for all three components.
How long does it take to stop taking biotin?
It is recommended that someone taking Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or B8, vitamin H, or coenzyme R) stop consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection of a sample.
Who orders the Hep B panel?
This panel is typically ordered by people who are experiencing symptoms, believe they may have been exposed to Hep B, or wish to determine their current state of immunity.
