What is a paresis and complete paralysis?
A paresis is an incomplete paralysis of a muscle, i.e. the muscle is weakened. If the muscle can no longer be moved at all, it is called a complete paralysis or plegia. Both forms are caused by damage to the afferent nerve.
What is incomplete paraplegia?
Incomplete paraplegia is an outcome of spinal cord injury that describes paralysis, and potentially loss of sensation, of the lower body. Because undamaged neural pathways exist when the injury is incomplete, it may be possible for individuals to recover weakened functions through intensive rehabilitation.
What is an incomplete spinal cord injury?
One of the terms you will hear often in reference to your spinal cord injury is complete or incomplete. An incomplete injury means that the ability of the spinal cord to convey messages to or from the brain is not completely lost.
What is the difference between an incomplete and a complete injury?
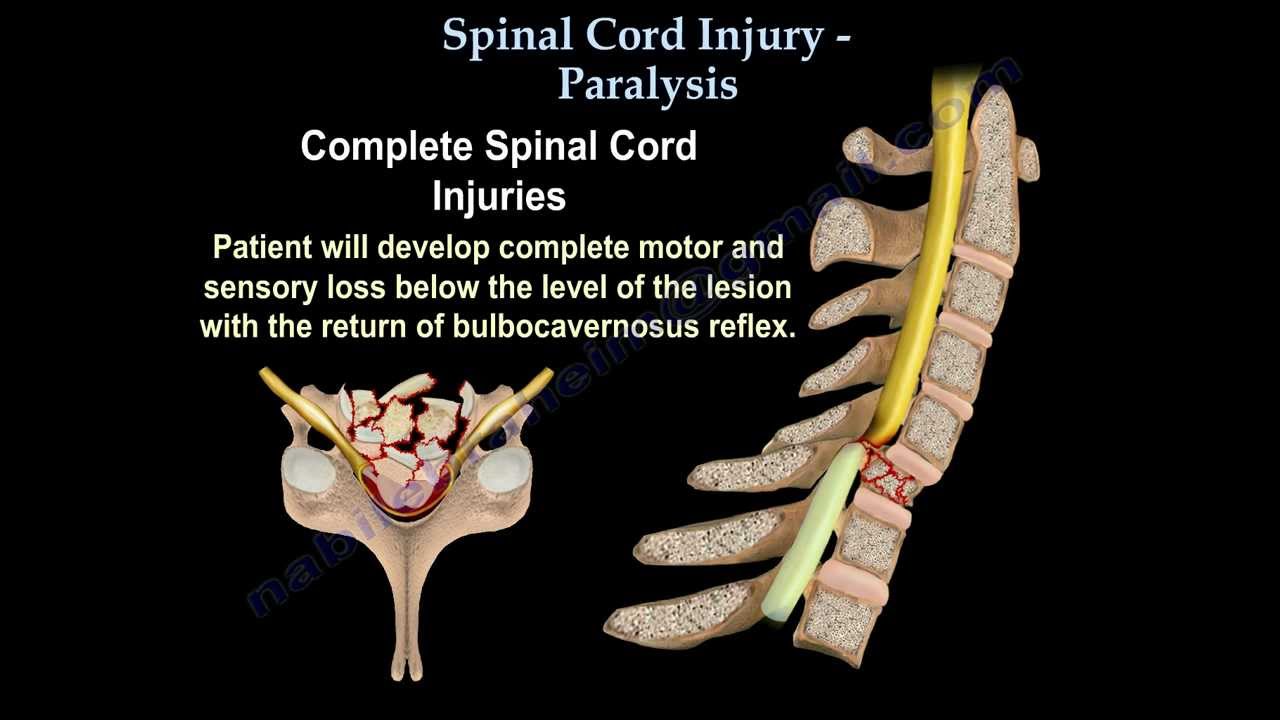
An incomplete injury means that the ability of the spinal cord to convey messages to or from the brain is not completely lost. Additionally, some sensation (even if it’s faint) and movement is possible below the level of injury. A complete injury is indicated by a total lack of sensory and motor function below the level of injury.
What is the difference between complete and incomplete paralysis?
People with a complete spinal cord injury cannot move or feel anything at or below the area where the trauma occurred. Those with an incomplete spinal cord injury may have some sensation and movement below the level of the injury.
Can you recover with incomplete paralysis?
Generally, the most recovery will occur within the first six months to a year following your SCI. After a traumatic event like spinal cord injury, the spinal cord experiences a heightened state of neuroplasticity, which makes it easier to relearn functions.
What are the four types of paralysis?
What Are the Four Types of Paralysis?Monoplegia.Hemiplegia.Paraplegia.Quadriplegia/tetraplegia.
What does incomplete spinal injury mean?
An incomplete injury means that the ability of the spinal cord to convey messages to or from the brain is not completely lost. Additionally, some sensation (even if it's faint) and movement is possible below the level of injury.
Can incomplete SCI walk again?
Approximately 80% of patients with incomplete spinal cord injury (SCI) can regain ambulatory ability after participation in a rehabilitation program. However, most of them can walk non-functionally and require a walking device.
Can someone with an incomplete spinal cord injury walk again?
Many factors play a role in regaining the ability to walk after a spinal cord injury. Fortunately, it is possible for many SCI survivors. There is potential to walk again after SCI because the spinal cord has the ability to reorganize itself and make adaptive changes called neuroplasticity.
What are the 5 types of paralysis?
The different types of paralysis are quadriplegia, paraplegia, monoplegia, diplegia, and hemiplegia.
What is partial paralysis called?
Partial or incomplete paralysis is when you still have some feeling in, and possibly control over, your paralyzed muscles. This is sometimes called paresis.
What are the three types of paralysis?
What are the types of paralysis?monoplegia, which affects only one arm or leg.hemiplegia, which affects one arm and one leg on the same side of your body.paraplegia, which affects both of your legs.quadriplegia, or tetraplegia, which affects both of your arms and both of your legs.
What is an example of an incomplete spinal cord injury?
Central Cord Syndrome Central cord syndrome is the most common type of incomplete spinal cord injury, making up about 15-25% of all incomplete SCIs. It most commonly occurs when there's damage to the middle region of the spinal cord from neck hyperextension.
Can an incomplete spinal cord injury get worse?
New research is suggesting that fatigue is a major issue for people with all kinds of spinal cord injuries the longer they have been injured. It won't go away on its own, and it's only likely to get worse, unless you do something about it – a change in your schedule, routine, or even the equipment you use might help.
Can a paralyzed person walk again?
A paralysed man with a severed spinal cord has been able to walk again, thanks to an implant developed by a team of Swiss researchers. It is the first time someone who has had a complete cut to their spinal cord has been able to walk freely.
Cervical Spinal Cord Injury C1-C8
Cervical level injuries cause paralysis or weakness in both arms and legs, resulting in quadriplegia (also known as tetraplegia). This area of the...
Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury T1-T12
Thoracic level injuries are less common because of the protection given by the rib cage. Thoracic injuries can cause paralysis or weakness of the l...
Lumbar Spinal Cord Injury L1-L5
Lumbar level injuries result in paralysis or weakness of the legs (paraplegia). Loss of physical sensation, bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction...
Sacral Spinal Cord Injury S1-S5
Sacral level injuries primarily cause loss of bowel and bladder function as well as sexual dysfunction. These injuries can cause weakness or paraly...
What percentage of spinal cord injuries result in incomplete paraplegia?
Incomplete Paraplegia: Frequently Asked Questions. Last updated on January 5, 2021. About 20% of all spinal cord injuries result in incomplete paraplegia, according to the National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. While incomplete paraplegia can affect your ability to walk and control bowel and bladder functions, ...
How Do I Exercise with Incomplete Paraplegia?
With incomplete paraplegia, arm exercise s are generally not a problem unless you have a thoracic SCI and experience balance difficulties due to weakened core muscles. In fact, many individuals with paraplegia end up over-using their arms to compensate for motor impairments in the legs. That being said, it is important to keep your upper body as strong as possible (without over-doing it), since you will be relying on your arms more than normal.
What Is Paraplegia?
When you break it down, ‘para’ means two and ‘plegia’ means paralysis. Therefore, paraplegia refers to the paralysis of two limbs, specifically the legs.
What Are Some Realistic Recovery Goals for People with Incomplete Paraplegia?
Individuals with incomplete paraplegia typically have a better recovery outlook than those with complete paraplegia, incomplete quadriplegia, and complete quadriplegia. This is because fewer functions will be affected.
What does it mean to have no control of the injury site?
In contrast, complete paraplegia means that you have no control or feeling below your injury site because all the neural pathways have been damaged.
How long can you walk with a walker with T1 paraplegia?
This study found that by using epidural stimulation for 15 weeks, a patient with T1 incomplete paraplegia was able to achieve overground walking with a walker and stand independently for about 50 minutes at a time.
Can incomplete paraplegia affect bladder function?
While incomplete paraplegia can affect your ability to walk and control bowel and bladder functions, it may be possible to recover these functions. To help you understand what to expect and how to recover, this article will answer frequently asked questions about incomplete paraplegia.
What happens if you have a paralysis?
If the cause of the nerve damage cannot be corrected , the continuous paralysis usually causes a loss of muscle mass (atrophy). It may also cause abnormalities of the connective tissue (fibrosis) in muscle fibres and increased fat deposits. The extent of atrophy and fibrosis is linked to the severity of the paralysis. Thus there is a relatively rapid loss of muscle mass in the case of severe paralysis.
What is a paresis?
A paresis refers to the incomplete paralysis of a skeletal muscle, as opposed to a plegia , which means complete paralysis. It is caused by damage to the afferent motor nerve. The neurological disorder manifests itself as decreased muscle strength.
What is it called when a muscle can't move?
the muscle is weakened. If the muscle can no longer be moved at all, it is called a complete paralysis or plegia. Both forms are caused by damage to the afferent nerve.
What causes paresis in the brain?
The paresis is caused by damage to the motor nerve which initiates muscle movement. The nerve can be damaged by pressure, accidents, infarctions or haemorrhages in the brain, or along its peripheral course. Pressure damage is often caused by tumours or herniated discs, which inhibit signal transmission via the spinal canal (vertebral canal).
Why does spastic paresis occur?
Depending on the extent of the paresis, spasticity (increased muscle tension) is seen in the case of central damage because the brain cannot adequately control the spinal cord. This is why multiple sclerosis or a stroke often causes spastic paresis . The stronger the paresis, the stronger the spasticity. The combination of diminished muscle strength and increased muscle tension usually causes limited joint mobility, which may result in joint stiffness (contractures) over time.
How is paresis diagnosed?
Paresis is diagnosed on the basis of a clinical examination, imaging technique, and specific additional tests which are optional.
How are pareses classified?
On the one hand, they can be classified according to the number of damaged nerves or affected limbs and, on the other hand, according to the location of nerve damage in the body.
What does it mean when your spinal cord is incomplete?
An incomplete injury means that the ability of the spinal cord to convey messages to or from the brain is not completely lost. Additionally, some sensation (even if it’s faint) and movement is possible below the level of injury.
What is complete injury?
A complete injury is indicated by a total lack of sensory and motor function below the level of injury.
What is spinal cord injury?
Spinal cord injury (SCI) occurs when the bony protection surrounding the cord is damaged by way of fractures, dislocation, burst, compression, hyperextension or hyperflexion.
What happens if you get a lumbar injury?
Lumbar level injuries result in paralysis or weakness of the legs (paraplegia). Loss of physical sensation, bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction can occur. However, shoulders, arms, and hand function are usually unaffected.
What happens after a neurological exam?
After a complete neurological examination, the doctor will assign a level of injury and determine if the injury is complete or incomplete. The initial level of injury and function may also change upon discharge to rehabilitation.
Can spinal cord be crushed?
The spinal cord does not have to be severed in order for a loss of function to occur. It can be bruised, stretched, or crushed.
Can you stabilize a cervical spinal cord injury?
Since the neck region is so flexible it is difficult to stabilize cervical spinal cord injuries. Individuals may be placed in a brace or stabilizing device. All regions of the body below the level of injury or top of the back may be affected.
What are the similarities between incomplete and complete SCIs?
There are many similarities between incomplete and complete SCIs. For example, both types of injury share many of the same causes, both impact the function of the body at and below the injury site, and therapy options for both types of injuries are often similar.
How do you know if you have an incomplete SCI?
The symptoms of an incomplete SCI can vary greatly from one injury to the next because of variables like: The location of the injury; The type of incomplete spinal cord injury that occurs; First aid delivered immediately following the injury; and. Quality of long-term care applied after an injury.
What is the C1-C7 vertebrae?
The cervical spine consists of the spinal cord and nerves located in the vertebrae of the neck. These are the C1-C7 vertebrae. There is an eighth spinal nerve section, labeled C8, which originates from the C7 vertebra.
What is a complete SCI?
A complete SCI is any injury that fully severs the spinal cord at the injury site. People who suffer a complete SCI lose all feeling and function for anything connected to nerves below the injury site. So, the higher up on the spinal cord an injury occurs, the more severe the symptoms tend to be.
What does spinal cord injury cause?
Injuries to the L1 and L2 spinal cord segments tend to cause symptoms like weakness in the hips and legs or problems with bladder and bowel control.
Does a complete SCI only partially severs the spinal cord?
Where a complete SCI fully severs the spinal cord at the site of the injury, an incomplete spinal cord injury only partially severs the spinal cord therefore allowing some signals to pass through the level of injury.
Can a person with a SCI be paraplegic?
For example, a person who suffers a complete SCI at the lower lumbar spine might lose feeling and function in their hips and legs, becoming paraplegic.
What is incomplete spinal cord injury?
What is an “incomplete” spinal cord injury? Doctors use the American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury when determining the classification of injuries. If there is evidence of any motor or sensory function in the area around the anus, one of four classifications is given ...
Is there a cure for SCI?
Recovery and Rehabilitation is important to returning to functioning back to normal. There is no cure for SCI but you can learn the potential areas for improvement. This and other fact sheets from the Model Systems Knowledge Translation Center provide useful health information that is based on research evidence and/or professional consensus and has been reviewed and approved by the SCI Model Systems editorial team of experts.
What is an Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury?
An incomplete spinal cord injury describes to damage to the spinal cord that partially disrupts the transmission of signals between the brain and muscles. The brain and body communicate by passing signals through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. When the neural pathways that transmit signals become damaged, signals can no longer reach their desired destination.
What happens when spinal cord injury is incomplete?
When a spinal cord injury is incomplete, some neural pathways at the level of injury are left unaffected. As a result, individuals may have some preserved sensation and/or motor control in areas below their level of injury.
What is the term for involuntary muscle contractions?
Additionally, many individuals with incomplete spinal cord injuries experience involuntary muscle contractions known as spasticity . This can pull the limbs into abnormal positions and negatively impact an individual’s form and posture. Wearing an orthotic device will help hold the spastic limb in place to prevent further contractures and gently stretch the spastic muscle.
What happens when you have incomplete spinal cord?
Individuals with this type of incomplete spinal cord injury generally experience loss of movement on the same side of the lesion, as well as decreased proprioception and vibration sense. Because the spinothalamic tracts cross at the middle of the spinal cord, pain and temperature sensations on the opposite side of the injury are often affected.
How does SCI affect the spinal cord?
This repetitive stimulation encourages spared neural pathways in the spinal cord to make adaptive changes and rewire functions affected by injury to healthy, unaffected regions.
What is anterior cord syndrome?
Anterior cord syndrome occurs when the front two-thirds of the spinal cord become damaged. It often results in the complete loss of motor function and altered sensation below your level of injury.
How does spinal cord injury affect mental health?
While an incomplete spinal cord injury directly affects motor control and sensation, it can also indirectly affect an individual’s mental health. Learning to cope after a spinal cord injury may be challenging as it can require some major lifestyle adjustments. By participating in psychotherapy, individuals can better understand their negative feelings and get the help they need to effectively cope and overcome them.
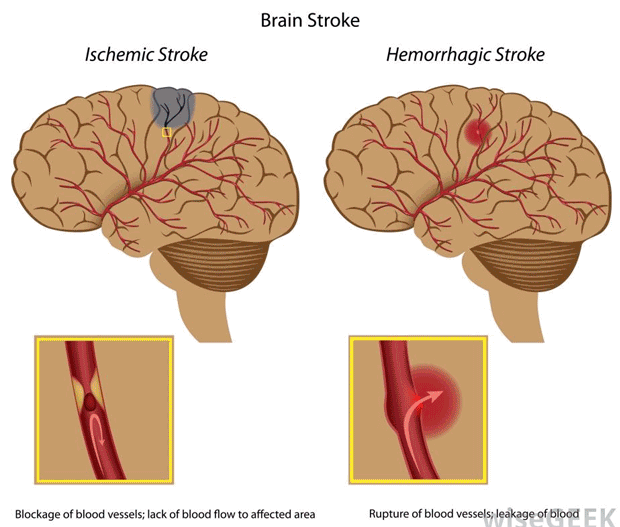
What causes paralysis in the brain?
Paralysis Caused by Conditions. Paralysis is most often caused by strokes, usually from a blocked artery in your neck or brain. It also can be caused by damage to your brain or spinal cord, like what can happen in a car accident or sports injury.
What is localized paralysis?
Localized paralysis affects just one specific area, like your face, hands, feet, or vocal cords.
What is the difference between monoplegia and diplegia?
Monoplegia is a kind of generalized paralysis that affects just one limb. Diplegia affects the same area on both sides, like both arms, both legs, or both sides of your face . Hemiplegia affects just one side of your body and is usually caused by a stroke, which damages one side of your brain. Quadriplegia (or tetraplegia) is when all four limbs are ...
What is it called when your muscles are jerky?
Paralysis can be stiff, or spastic, when your muscles are tight and jerky. Most people with cerebral palsy have spastic paralysis. It can also be floppy, or flaccid, when your muscles sag and eventually shrink.
What is the most common demyelinating disease?
There are several demyelinating diseases, but the most common is multiple sclerosis. Motor neuron diseases (MNDs). Motor neurons are the nerve cells that control the muscles you use to walk, breathe, speak, and move your limbs.
What happens when your nerve cells are damaged?
Demyelinating diseases. These happen when the protective coating around your nerve cells, called the myelin sheath, is damaged over time. That makes it harder for your neurons to send signals throughout your body. It weakens your muscles and eventually causes paralysis.
What is it called when you can't move your muscles?
Types of Paralysis . Complete paralysis is when you can’t move or control your paralyzed muscles at all. You also may not be able to feel anything in those muscles. Partial or incomplete paralysis is when you still have some feeling in, and possibly control over, your paralyzed muscles. This is sometimes called paresis.