- Independent Assortment Definition. Independent assortment is a genetic term that refers to the variation of chromosomes, or genetic information, during sex cell division.
- The Principle of Independent Assortment. ...
- Examples of Independent Assortment. ...
- Related Biology Terms. ...
- Quiz. ...
What do you mean by independent assortment?
independent assortment. noun. : formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair.
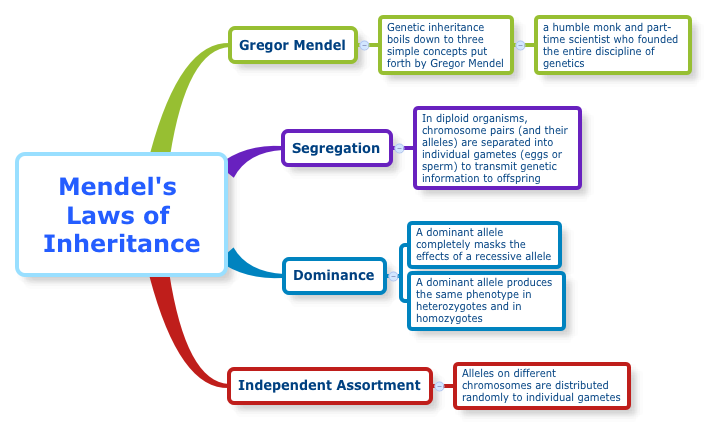
What is Mendel's law of independent assortment?
Mendel's law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene. Let's look at a concrete example of the law of independent assortment.
What is the law of Independent Assortment in biology?
The law of independent assortment states that the alleles for a trait separate when gametes are formed. These allele pairs are then randomly united at fertilization. Mendel arrived at this conclusion by performing monohybrid crosses.

What is Independent Assortment in simple terms?
Definition of independent assortment : formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair.
What is independent assortment in meiosis for kids?
Independent assortment is the process where the chromosomes move randomly to separate poles during meiosis. A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis, but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes.
What is Independent Assortment and why is it important?
Independent assortment is an important process for the production of new genetic combinations that contribute to the genetic diversity among individuals that reproduce sexually.
What is Independent Assortment and where does it occur?
Independent assortment occurs during the process of meiosis. This is a necessary part of sexual reproduction which allows two gamete cells to then fuse together to create a diploid zygote, containing all the DNA necessary to create a new organism.
What is the difference between segregation and independent assortment?
The law of segregation describes how alleles of a gene are segregated into two gametes and reunite after fertilization. The law of independent assortment describes how alleles of different genes independently segregate from each other during the formation of gametes.
What is the independent assortment of chromosomes a result of?
When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed to daughter cells, and different chromosomes segregate independently of each other. This called is called independent assortment. It results in gametes that have unique combinations of chromosomes.
What is the importance of independent assortment in meiosis?
Answer and Explanation: Independent assortment is important because it increases genetic diversity in offspring. During meiosis, four unique haploid gametes are formed. ...
How does independent assortment affect genetic diversity?
The Law of Independent Assortment states that separate genes for separate traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring. Together with random fertilization, more possibilities for genetic variation exist between any two people than the number of individuals alive today.
What is Independent Assortment biology quizlet?
independent assortment is the random assorting of chromosomes, during the making of gametes. it ends up being individual gametes.
What is Independent Assortment IB Biology?
Independent assortment describes how pairs of alleles separate independently from one another during gamete formation. According to independent assortment, the inheritance of one gene/trait is independent to the inheritance of any other gene/trait.
Does independent assortment occur in meiosis 1 or 2?
Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II. Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
During which phase of meiosis does independent assortment occur?
The law of independent assortment states that the random orientation of homologous chromosome pairs during metaphase I allow for the production of gametes with many different assortments of homologous chromosomes.
What is Independent Assortment Class 10?
According to the law of independent assortment, during the inheritance of two different traits, the alleles of both the traits assort and are inherited independently of one another during gamete formation. This gives both the trait equal chances of being inherited.
What is Mendel's independent assortment experiment?
Mendel's Independent Assortment Experiment. Mendel performed dihybrid crosses in plants that were true-breeding for two traits. For example, a plant that had round seeds and yellow seed color was cross-pollinated with a plant that had wrinkled seeds and green seed color.
How many alleles do diploids inherit?
They are separated during meiosis (process for the production of sex cells) and united at random during fertilization . Diploid organisms inherit two alleles per trait, one from each parent. Inherited allele combinations determine an organisms genotype (gene composition) and phenotype (expressed traits).
What are some examples of polygenic traits?
A common example of this in humans is ABO blood type. ABO blood types exist as three alleles, which are represented as (IA, IB, IO) . Further, some traits are polygenic, meaning that they are controlled by more than one gene. These genes may have two or more alleles for a specific trait.
How many genotypes are there in F2?
There were nine different genotypes in the F2 plants resulting from the dihybrid cross. The specific combination of alleles that comprise the genotype determines which phenotype is observed. For example, plants with the genotype of (rryy) expressed the phenotype of wrinkled, green seeds.
How did Mendel arrive at this conclusion?
Mendel arrived at this conclusion by performing monohybrid crosses. These cross-pollination experiments were performed with pea plants that differed in one trait, such as the color of the pod. Mendel began to wonder what would happen if he studied plants that were different with respect to two traits.
What is Mendel's law?
This law states that allele pairs separate independently during the formation of gametes. Therefore, traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another.
What generation did Mendel refer to as the F2 generation?
The F2 Generation: After observing the results of the dihybrid cross, Mendel allowed all of the F1 plants to self-pollinate. He referred to these offspring as the F2 generation .
How are gametes made?
Gametes are made by the process of meiosis 1, wherein chromosomes containing parent genes are randomly sorted and separated into the gamete cells. Before they are separated, though, the chromosomes undergo a process of crossing over, where the chromosomes basically swap genes with each other, leading to new chromosome configurations. This helps to ensure that independent assortment takes place. In the diagram, we see that the red and blue chromosomes undergo crossing over, and the result is a mix-match of color on each chromosome. These colors represent the genes that they have swapped. The resulting gametes each have a unique combination of the genes inherited by their parents, and thus, the genes will manifest themselves independently of each other.
What did Mendel use to test for genetics?
Among his test subjects, Mendel used peas in his genetic experiments that illustrated independent assortment. He could examine how one gene is passed on quite easily, usually with two different alleles, or variations of the gene. This Punnett Square shows a monohybrid cross, the crossing of two parents who differ by one gene of interest. This cross is examining the gene for color: yellow and green. This gene expresses yellow as a dominant allele and green as a recessive allele. The offspring (four, one in each box) receives one allele from each parent and will manifest their color based on which alleles they receive. If they receive two green alleles, they will be green. But if they receive one yellow and one green allele, they will be yellow, as yellow is the dominant allele.
What happens to chromosomes before they are separated?
Before they are separated, though, the chromosomes undergo a process of crossing over, where the chromosomes basically swap genes with each other, leading to new chromosome configurations. This helps to ensure that independent assortment takes place.
What happens if you have one yellow and one green allele?
But if they receive one yellow and one green allele, they will be yellow, as yellow is the dominant allele. With one gene of interest, this is pretty straightforward. But as you know, organisms have many, many genes that code for their diverse and complex characteristics.
What is Meredith's degree?
Meredith holds a B.S. in marine science with a minor in philosophy, as well as a master's of aeronautical science with a space science emphasis. She has taught subjects including marine science, biology, astronomy, math, and reading to students from kindergarten through high school.
Can genes for color and smoothness be passed on independently?
But, the bigger point here is that the gene for color and the gene for smoothness can be passed on independently of each other, leading to many different possibilities for the offspring. Due to the law of independent assortment, different genes are passed on to offspring independently of each other.
Is yellow a dominant or recessive allele?
This gene expresses yellow as a dominant allele and green as a recessive allele. The offspring (four, one in each box) receives one allele from each parent and will manifest their color based on which alleles they receive. If they receive two green alleles, they will be green.
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Independent assortment of genes and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 during his studies of genetics in pea plants.
What observation is explained by the Law of Independent Assortment?
Recessive trait forms are always hidden in the F 1 generation. Each pair of chromosomes separates on its own during meiosis. Dominant trait forms are always displayed in the F 1 generation.
What is Independent Assortment quizlet?
independent assortment. independent assortment is the random sorrting of chromosomes, during the making of gametes. it ends up being individual gametes. crossing over. crossing over is chromosomes come together and can become twisted, and they pull apart which causes them to break, rearange then reattach.
Why Law of Independent Assortment is not universal?
Many genes are located on one chromosome, i.e. they are linked. … Therefore, the law of independent assortment is applicable only for the traits which are located on different chromosomes. Thus, law of independent assortment is not universally applicable.
What is an example of independent assortment?
For example, a plant that had round seeds and yellow seed color was cross-pollinated with a plant that had wrinkled seeds and green seed color. … This means that the dominant traits of round seed shape and yellow color completely masked the recessive traits in the F1 generation.6 мая 2019 г.
How do you test for independent assortment?
The best way to generate such an example is through a dihybrid test cross, which considers two different genes during a cross between two heterozygote parents. Mendel’s principle of independent assortment predicts that the alleles of the two genes will be independently distributed into gametes.
How and at what stage is independent assortment accomplished?
Independent assortment is the process where the chromosomes move randomly to separate poles during meiosis. A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis, but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes.