What is meant by the induced fit model?
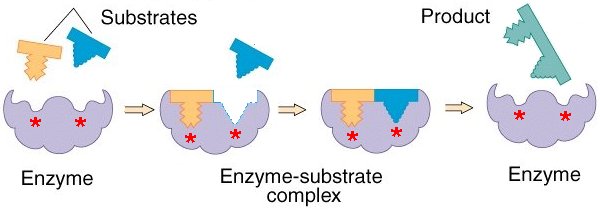
The induced fit model is a model for the interaction of enzymes and substrates. It states that only the appropriate substrate may cause the active site to align properly, allowing the enzyme to execute its catalytic activity. It also implies that the active site evolves until it is fully bonded to the substrate, at which time the final shape and charge are decided.
What is the induced fit theory?
induced-fit theory Quick Reference A variation of the lock-and-key theory of enzymatic function. It is proposed that the substrate causes a conformational change in the enzyme such that the active site achieves the exact configuration required for a reaction to occur. The overall effect would be a tighter binding for the substrate and enzyme.
What are the advantages of being induced?
- fewer infant deaths at or around the time of birth
- similar rates of admission to the neonatal intensive care unit
- slightly fewer babies born with Apgar scores below seven (an indication of poor health)
- fewer caesarean sections
- more vaginal births involving forceps or vacuum extraction
What is an induced fit hypothesis?
The induced fit model is one of the main models, describing the enzyme-substrate interaction. Also, Daniel Koshland suggested this model in 1958. Basically, according to the hypothesis, the active site of the enzyme does not have a rigid conformation. Therefore, the substrate does not completely fit into the active site of the enzyme.

What is meant by induced fit?
Induced fit indicates a continuous change in the conformation and shape of an enzyme in response to substrate binding. This makes the enzyme catalytic which results in the lowering of the activation energy barrier causing an increase in the overall rate of the reaction.
What happens during an induced fit?
In the induced fit model, both the substrate and the active site of the enzyme change in conformation until the substrate is completely bound to the enzyme, at which point the final shape and charge is determined. This activates the enzyme into performing its catalytic function.
What is induced fit in enzymes?
induced fit: Proposes that the initial interaction between enzyme and substrate is relatively weak, but that these weak interactions rapidly induce conformational changes in the enzyme that strengthen binding. catalyze: Cause or accelerate (a reaction) by acting as a catalyst.
Why is it called induced fit model?
The enzyme and the substrate will both change shape a little bit and bind to each other really strongly. And we call this the induced fit because both the enzyme and the substrate have changed their shape a little bit so that they bind together really tightly.
Why is induced fit better than lock and key?
The main difference between induced fit and lock and key model is that in the induced fit model, the active site of the enzyme does not completely fit to the substrate whereas in the lock and key model, the active site of the enzyme is the complement of the substrate and hence, it precisely fits to the substrate.
What kind of reaction take place during induced fit mechanism?
allosteric control …the basis of the so-called induced-fit theory, which states that the binding of a substrate or some other molecule to an enzyme causes a change in the shape of the enzyme so as to enhance or inhibit its activity.
How does induced fit lower activation energy?
Induced-Fit Theory Each enzyme has an active site where reactant molecules bind. The molecule that binds to the active site is called a substrate. The enzyme induces a change in the molecule which lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
What is meant by induced fit how is it shown in this figure?
How is it shown in this figure? An induced fit brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the chemical reaction: an enzyme is not a stiff structure locked into a given shape.
Why is the induced fit of an enzyme important as it binds its substrate?
Induced Fit and Enzyme Function As the enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a mild shift in the enzyme's structure that confirms an ideal binding arrangement between the enzyme and the substrate. This dynamic binding maximizes the enzyme's ability to catalyze its reaction.
Who gave induced fit theory?
KoshlandThe induced-fit model was first proposed by Koshland in 1958 to explain the protein conformational changes in the binding process.
What are the two types of enzyme models?
There are two models used to describe the way enzymes interact with substrates: The 'lock and key' model. The 'induced fit' model.
What are the types of enzyme specificity?
There are 4 types of specificity – absolute, group, linkage, and stereochemical.
How long does it take to dilate after being induced?
The time it takes to go into labor after being induced varies and can take anywhere between a few hours up to 2-3 days. In most healthy pregnancies, labor usually starts spontaneously between 37 and 42 weeks of pregnancy.
Are Inductions more painful?
Induced labour is usually more painful than labour that starts on its own, and you may want to ask for an epidural. Your pain relief options during labour are not restricted by being induced. You should have access to all the pain relief options usually available in the maternity unit.
How long does it take to give birth after being induced?
It can take from a few hours to as long as 2 to 3 days to induce labour. It depends how your body responds to the treatment. It is likely to take longer if this is your first pregnancy or you are less than 37 weeks pregnant.
How quickly does induction work?
Induction can take between 24 to 48 hours. The amount of time varies from person to person. Some people go into labour very quickly, in others, it takes time. Please be prepared that it could take 48 hours to get to a point that you are able to have your waters broken or get into labour.
How is the induced fit model different from lock and key?
The lock and key model proposes that the active site of an enzyme has a limited number of conformations. In contrast, the induced fit model propose...
Why is the induced fit model important?
The induced fit model is important because it is representative of what we observe experimentally. Further, it helps us to understand how the cell...
What is the induced fit model?
The induced fit model proposes that the shape (conformation) of the active site within enzymes is malleable and can be induced to fit the substrate...
What is an Enzyme Model?
Enzymes are proteins that can chemically modify a substrate. A substrate can be any biological molecule (e.g., sugars, fats, proteins). Enzymes can be either anabolic (i.e., the enzyme is built upon the substrate, creating a new product) or catabolic (i.e., the enzyme degrades the substrate into more basic molecules for reuse or elimination).
What Is the Induced Fit Model of Enzyme Action?
The induced fit hypothesis states that while an enzyme is in the unbound state (i.e., not binding to the substrate), the active site is not structurally optimal for substrate binding. The conformation (structure) of the active site in enzymes has been shown to be influenced by many factors including but not limited to:
What is the only noticeable effect of the induced fit?
Thus, the only noticeable effect of the induced fitis usually a flickering of the eyelids.
What is a conformational change in a macromolecule?
a conformational change in a macromolecule (for example, protein) as a result of multiple weak interactions with a ligand or substrate.
