
Fertilizers
- Types of Fertilizers. Inorganic fertilizers are chemical fertilizers that contain nutrient elements for the growth of crops made by chemical means.
- Advantages of Fertilizers. They are easy to transport, store, and apply. ...
- Disadvantages of Fertilizers. They are expensive. ...
- Uses of Fertilizers. ...
- Importance of Fertilizers. ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of organic fertilizer?
Improve the soil structure
- The use of organic fertilizers helps to retain nutrients from the soil.
- They allow to take advantage of organic waste.
- They allow the fixation of carbon in the soil and improve the capacity to absorb water.
- They usually need less energy for their elaboration.
- They maintain the necessary humidity in the soil for each type of plantations.
What is the difference between organic and non organic fertilizer?
• Inorganic fertilizers contain synthetic materials but, organic fertilizers contain naturally degradable compounds. • Generally, high application rates are necessary for organic fertilizer but,comparatively fewer amounts are needed for inorganic fertilizer.
How do you apply inorganic fertilizer?
Vegetable Gardening: Applying Fertilizer
- When to Fertilize. Regular fertilizer applications keep plants vigorous and productive. ...
- Types of Fertilizer. There are many options for how you convey nutrients to your plants. ...
- Preventing Pollution. To prevent water pollution from nutrient leaching and runoff, always follow these steps when fertilizing your vegetable garden.
How does inorganic fertilizer destroy soil?
- Manure helped keep soil pH—a measure of acidity or alkalinity—in a healthy range for crops. ...
- Manure increased soil organic carbon for all the measured soil depths compared to inorganic fertilizer and control treatments. ...
- Manure significantly increased total nitrogen compared to fertilizer treatments. ...
- Manure increased water-stable aggregates. ...
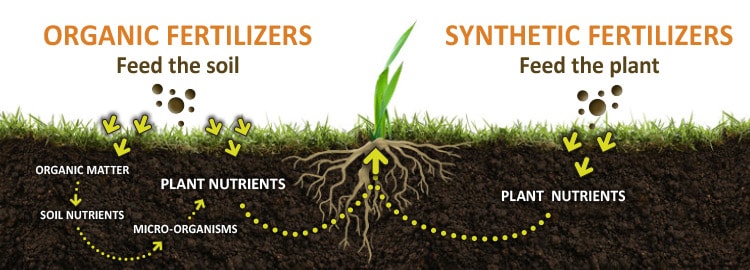
What is inorganic fertilizer and give examples?
Examples of manufactured or chemically-synthesized inorganic fertilizers include ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate, and superphosphate, or triple superphosphate.
What is the other name for inorganic fertilizer?
Inorganic fertilizer, also referred to as synthetic fertilizer, is manufactured artificially and contains minerals or synthetic chemicals. For example, synthetic nitrogen fertilizers are typically made from petroleum or natural gas.
What are the 3 types of inorganic fertilizers?
Types of Inorganic FertilizersNitrogen Fertilizers. Many different chemical and physical forms of nitrogen (N) fertilizers exist. ... Phosphorous Fertilizers. ... Potassium Fertilizers. ... Sulfur, Calcium, and Magnesium Fertilizers. ... Micronutrient Fertilizers.
What are the 5 example of inorganic fertilizer?
Fertilizer FormulationsNFormSodium nitrate16SolidTriple superphosphate0SolidUrea45–46SolidUrea-ammonium nitrate28–32Liquid15 more rows
What is the best inorganic fertilizer?
Potassium Fertilizers Muriate of potash is the most commonly used potassium fertilizer. In some cases, plants may be sensitive to chloride. If a plant is sensitive to chloride, potassium sulfate, also known as sulfate of potash, is a better choice, as it does not contain chloride.
What's the difference between organic and inorganic fertilizer?
Inorganic fertilizers are manufactured, concentrated, and inexpensive, but often lack trace elements. Organic fertilizers are made from natural products such as worm castings, seaweed, or compost. They cost more but are safer to apply and offer a wider range of nutrients.
Is NPK inorganic fertilizer?
Inorganic fertilization is commonly used by farmers such as the implementation of NPK fertilizer in the form of Urea, SP 36, and KCl. N, P, and K nutrients are essential nutrients for plants, it must always be available in the soil. The farmers implement fertilization oftenly in an excessive amount.
Why do farmers use inorganic fertilizers?
Farmers turn to fertilizers because these substances contain plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Fertilizers are simply plant nutrients applied to agricultural fields to supplement required elements found naturally in the soil. Fertilizers have been used since the start of agriculture.
Is urea an inorganic fertilizer?
Urea is an example of organic fertilizer. Urea is an example of organic fertilizer.
Is urea organic or inorganic?
organic compoundUrea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH 2) 2.
What is organic fertilizer example?
Processed organic fertilizers include compost, humic acid, grain meal, amino acids, and seaweed extracts. Other examples are natural enzyme-digested proteins. Decomposing crop residue (green manure) from prior years is another source of fertility.
What are the examples of organic and inorganic fertilizers?
Organic fertilizer examples- include green manures, livestock manure, compost, household waste, crop residues, woodland litter etc.; inorganic fertilizers include phosphate, lime, rock, potash etc.
Is NPK inorganic fertilizer?
Inorganic fertilization is commonly used by farmers such as the implementation of NPK fertilizer in the form of Urea, SP 36, and KCl. N, P, and K nutrients are essential nutrients for plants, it must always be available in the soil. The farmers implement fertilization oftenly in an excessive amount.
What is DAP fertilizer?
DAP 18-46-0 IFFCO's DAP (Diammonium phosphate) is a concentrated phosphate-based fertilizer. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient along with Nitrogen and plays a vital role in the development of new plant tissues and the regulation of protein synthesis in crops.
Is NPK organic fertilizer?
Green and Pure Bio NPK is 100% Organic Fertilizer. It is a Powder based NPK biological consortium. It contains Azotobactor(N), PSB(P) and Frateuria aurantia (K) in equal proportions. It is highly effective in results and prove highly favorable for plant growth.
Is urea an inorganic fertilizer?
Urea is an example of organic fertilizer. Urea is an example of organic fertilizer.
What is the process of immobilizing nitrates in the unsaturated zone?
Crop uptake and microbial assimilation are the dominant processes that immobilize nitrate in the unsaturated zone. Immobilization by soil microorganisms may be offset by the opposing process of mineralization, both of which generally occur continuously (Keeney, 1986 ).
Does manure reduce nitrogen?
The concentration and storage of manure also increases nitrogen losses to the atmosphere (Lander et al., 1998). This loss to the atmosphere of nitrogen will not likely reduce the non-point source load of nitrogen because the deficit will be made up with inorganic fertilizer applications.
Fertilizer
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this articleFertilizer, natural or artificial substance containing the chemical elements that improve growth and productiveness of plants.
The Importance Of Using Chemical Fertilizers
The proper use of chemical fertilizers represents one of the most cost-effective ways to boost plant production. Some chemical fertilizers, for example, are “nitrogenous” — containing nitrogen — while others are phosphate-based.
Chemical Fertiliser - an overview
HISTORICAL REVIEW OF SOIL FERTILITY MANAGEMENTTraditional farming systems generally included a period of fallow in the cropping sequence to help restore soil fertility. The biblical injunction, for example, required fallowing the land every seventh year to let the land rejuvenate (Deuteronomy 15).
Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their
Present study investigated the effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impacts on soil physico-chemical characteristics. In comparison to sole application of organic manure, combined application of both organic and inorganic manures showed lower values for C: N ratio.
Revisiting the original reasons for excluding inorganic fertilizers in
This paper reviews the original reasons of the organic farming movement for excluding mineral (inorganic) fertilizers. In this paper, their theories and decision criteria for excluding use of inorganic fertilizers in crop production were revisited.
Organic Fertilizer - an overview
5.3.1 Organic fertilizersAn organic fertilizer is a fertilizer that is derived from organic sources, including organic compost, cattle manures, poultry droppings and domestic sewage.
Co-incorporation of manure and inorganic fertilizer improves leaf
A 1 g soil sample was taken along with the tin and weighed as W2. NTa is the total aboveground N accumulation at anthesis, and NT stem,m , NT leaf,m , and NT chaff,m are the total N accumulation of stems, leaves, and chaff at physiological maturity.
Organic Fertilizer - an overview
5.3.1 Organic fertilizersAn organic fertilizer is a fertilizer that is derived from organic sources, including organic compost, cattle manures, poultry droppings and domestic sewage.
Bio-organic fertilizer with reduced rates of chemical fertilization
CF: 100% chemical fertilizer; BF: 75% chemical fertilizer + bio-organic fertilizer; OF: 75% chemical fertilizer + organic fertilizer. CF: 100% chemical fertilizer; BF: 75% chemical fertilizer + bio-organic fertilizer; OF: 75% chemical fertilizer + organic fertilizer; SS: 75% chemical fertilizer + spore suspension.
Effect of compost and inorganic fertilizer on organic carbon and
The accumulation pattern of organic C mainly depends on the characteristics of aggregates and the different types of organic C that accumulate in different aggregates [7]. And soil organic C can be distinguished from intermediate and passive organic C pools into different active C pools through fractionation [9].
Water: Use organic fertilizer instead of inorganic
A replicated, randomized, controlled study in 1995–1999 in arable farmland in southern Turkey found more water in soils with organic fertilizer, compared to inorganic fertilizer. Water availability: More available water was found in soils with organic fertilizer, compared to inorganic fertilizer (0.14–0.17 vs 0.09 cm3 water/cm3 soil).
The effects of organic and inorganic fertilizer applications to
IntroductionBecause of an increasing interest in renewable energy crops, several trials have investigated the potential of perennial grass crops, but little is known about their husbandry, in particular their nutrient requirements.
Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their
Present study investigated the effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impacts on soil physico-chemical characteristics. In comparison to sole application of organic manure, combined application of both organic and inorganic manures showed lower values for C: N ratio.
What happens when you use inorganic fertilizer?
Inorganic fertilizers are perfectly measured out shots of nutrients exactly when you need them most but at significant cost. They can easily upset the entire ecosystem, create a toxic buildup of chemicals, and long-term use changes the pH of the soil, increases a pest problem, and releases greenhouse gases.
Why do we need organic fertilizer?
Given time, they make your soil and plants healthier and hardier. Organic fertilizers carry little risk of a toxic overdose of chemicals, but they require a breakdown of microorganisms to release nutrients, limiting their seasonal effectiveness and potentially increasing the amount of time they take to feed your plants.
What is the best fertilizer for a garden?
Organic fertilizer vs. inorganic is mainly a question of nutrient needs. Both organic and inorganic fertilizers provide the necessary nutrients for growth, but where inorganic fertilizers deliver a rapid dose of nutrients, organic moves slower, more naturally and healthily.
What is fertilizer?
Fertilizers, no matter the kind, provide your plants with the macronutrients they need that might be in short supply in your soil. Organic and inorganic fertilizers deliver these nutrients in different ways.
What are the minerals in fertilizer?
Most of the minerals in inorganic fertilizer are mined from the earth, and balanced inorganic fertilizers are high in all three macronutrients and can contain ammonium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, and potassium chloride.
Is organic fertilizer natural?
Organic fertilizers are natural, in that the nutrients they possess are strictly comprised of plant- or animal-based materials. Either byproducts or end products of natural processes. Cow manure, decaying leaves, and food compost are all forms of organic fertilizer. Inorganic fertilizer is synthetic, comprised of minerals and synthetic chemicals.
Is organic fertilizer cheaper than inorganic fertilizer?
In bag form, organic fertilizer is significantly more expensive than inorganic, but there are cheaper alternatives to bags . And the environmental factor is important to consider. If you want healthier plants, a healthier you, and a healthier environment, organic is your best bet. ORGANIC FERTILIZER VS. INORGANIC: ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY LAWN CARE.
What are the ingredients in inorganic fertilizer?
While the specific ingredients in inorganic fertilizer depend on the manufacturer, it could include ammonium hydroxide, urea, ammonium nitrate, phosphoric acid, and potassium hydroxide.
What is the difference between organic fertilizer and synthetic nitrogen?
Synthetic nitrogen decimates the diversity of beneficial microorganisms in the soil that would otherwise break down organic matter into nutrients to support your plants. Inorganic fertilizer also cuts down on the amount of organic matter in the soil, which means more erosion and more compaction. Organic fertilizers, especially composts, add organic ...
How much does it cost to apply organic fertilizer?
Other organic fertilizers can be more expensive, like fish emulsion. According to Fixr, it costs between $50 – $95 to have a lawn care company apply organic fertilizer or $25 – $80 to apply inorganic. The price depends on the type of inorganic fertilizer.
What to do when applying fertilizer?
Always wear a mask and protective clothing when applying synthetic fertilizers. Cause salt-buildup in the soil, as most of the components are salt types, especially when there’s little rain. Add greenhouse gases, and nitrates are just as harmful as carbon dioxide.
Does organic fertilizer affect the environment?
Organic fertilizer typically positively impact salt types of the environment, supporting the food web in your soil and reusing kitchen and yard scraps instead of sending them to the garbage dump. In contrast, inorganic has a negative impact, to say the very least. Inorganic fertilizers:
Do vegetables need iron?
If all your vegetables get is NPK, and whatever leftover micronutrients linger in the soil, then your vegetables will not be full of iron or calcium or other healthy human micronutrients.
Is organic fertilizer the same as certified organic?
Organic fertilizer is not the same as certified organic, a certification process that farmers and other companies undergo to ensure their products follow national guidelines. Organic fertilizer may be certified organic, but it isn’t always. Your backyard compost or vermicompost is still considered organic fertilizer.
What is the difference between organic and inorganic fertilizer?
Before that, fertilizers are substances normally used for improving the plant nutrients. The success of farming mainly depends on the growth of a crop. There are a number of factors that influenced the crop growth. Plant nutrients are an important group out of them. It is important to supply an adequate quantity of a particular nutrient for plant growth and it depends on both the behavior of that nutrient in the soil as well as the utilizing capacity of the crop root system. If these elements are not available in an optimum amount to the plant that will adversely affect to the plant growth and quantity and quality of the yield. One of the main characters of fertilizers is that it can replace the chemical elements taken from the soil by previous crops. This may lead to enhancing the natural fertility of the soil.
What is organic fertilizer?
Organic fertilizers are fertilizers derived from animal or vegetable matter as well as human excreta. It contains all essential plant nutrients and the nutrients release is enhanced by the warm and moisture levels of the soil.
What happens when manure decomposes?
When the decomposition starts the parts of its organic manure first degrade into primary nutrients and further decomposition results in secondary nutrients too.
What is integrated farming?
This is a new approach to plant nutrition by obtaining the nutrients from both inorganic and organic sources to maintain and sustain soil fertility and enhance crop productivity.
Why is it important to consider the concentration of inorganic fertilizers?
When applying the inorganic fertilizers, it is important to consider about its concentration because high nutrient levels increase the risk of burning the plant. Another disadvantage of inorganic fertilizer is the rapid release of elements, which reach deeply into the soil and water, but plants cannot access them.
Why is it important to supply nutrient to plants?
Plant nutrients are an important group out of them. It is important to supply an adequate quantity of a particular nutrient for plant growth and it depends on both the behavior of that nutrient in the soil as well as the utilizing capacity of the crop root system.
Why use chemical fertilizer and organic fertilizer together?
Use of both chemical and organic fertilizers together gives more benefits than applying them separately which increase physical and microbiological properties of the soil. This will increase the availability of nutrients as well.
