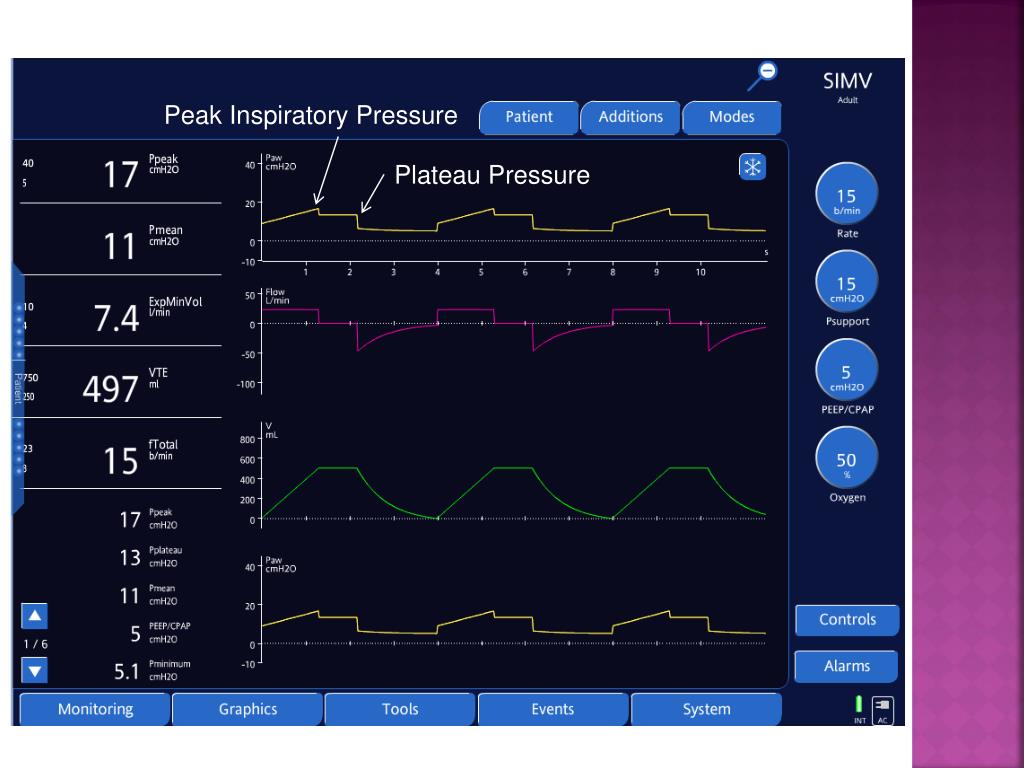
The inspiratory rise time (IRT) determines the time to reach the selected airway pressure. A short IRT results in a high peak inspiratory flow and a short time to reach that peak, but is also associated with the development of turbulent flow, resulting in increased WOB.
What is inspiratory rise time and why is it important?
The inspiratory rise time (IRT) determines the time to reach the selected airway pressure. A short IRT results in a high peak inspiratory flow and a short time to reach that peak, but is also associated with the development of turbulent flow, resulting in increased WOB.
What is rise time on a BiPAP?
The speed at which inspiratory pressure increases to the set target pressure is known as the rise time on most BiPAPs. Adjustments in rise time can improve patient comfort/tolerability with BiPAP. Rise times generally go from 100ms to 600ms, with settings of 1 through 5. A setting of 1 is the fastest while a setting of 5 is the slowest.
What is the inspiratory time constant?
The inspiratory time constant is the amount of inspiratory time required for the alveolar pressure to reach the pressure control level, and can be expressed as airway resistance multiplied by static compliance. Inspiratory time should be 3-5 times the inspiratory time constant.
Does rise time and cycling criteria affect inspiratory parameters during pressure support?
CONCLUSIONS: Significant differences in exhaled tidal volume, inspiratory time, and peak flow were observed by adjusting rise time and cycling criteria. This research demonstrates that during pressure support ventilation strategy, adjustments in rise time and/or cycling criteria can produce changes in inspiratory parameters.

What is rise time on ventilator?
What is Rise Time? The speed at which inspiratory pressure increases to the set target pressure is known as the rise time on most BiPAPs. Adjustments in rise time can improve patient comfort/tolerability with BiPAP. Rise times generally go from 100ms to 600ms, with settings of 1 through 5.
What is a normal inspiratory time?
The inspiratory time constant is typically short (approximately 0.05 seconds) in RDS and relatively long (0.25 seconds) in infants with normal lungs. For practical purposes, an expiratory time equivalent to three time constants must be provided to allow 95% of inspired tidal volume to be expelled (Harris 1996).
Is rise time the same as inspiratory time?
An inspiratory pause is a period during inspiration during which flow ceases. Inspiratory rise time is the rate at which the ventilator achieves the pressure control variable.
What does increasing inspiratory time do?
Abstract. Rationale: Increasing the inspiratory time and thereby the inspiratory/expiratory ratio (I:E ratio) during mechanical ventilation may improve oxygenation but may also be harmful as the absolute stress over time increases.
How do you measure inspiratory time?
1:366:12Total Cycle Time, Ti (Inspiratory Time) and Te (Expiratory Time) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd it's kind of like this this is the formula for your TI is equal to total cycle time minus te andMoreAnd it's kind of like this this is the formula for your TI is equal to total cycle time minus te and TE is equal to total cycle. Time minus TI we can also then say that the total cycle time. It also
What is normal rise time on BiPAP?
100 ms to 600 msMost BiPAP devices allow for adjustment of the rise time (angle of the pressure change) from 100 ms to 600 ms.
What is inspiratory time in mechanical ventilation?
The inspiratory time is the time taken for inhalation. For ventilators, the inspiratory time is the amount of time it takes to deliver the tidal volume of air to the lung. The ratio of inspiratory time to expiratory time is a vital indication of respiration quality and is directly related to the respiration rate.
What is normal I E ratio?
Normal inspiratory to expiratory ratios (I:E) on spontaneously breathing patients are usually around 1:3 to 1:5. Meaning, the ratio of time in expiration is 3 to 5 times longer than the ratio of time in inspiration. Think logically about the time you take when you breathe to inhale and exhale.
What is inspiratory flow rate?
Flow rate, or peak inspiratory flow rate, is the maximum flow at which a set tidal volume breath is delivered by the ventilator. Most modern ventilators can deliver flow rates between 60 and 120 L/min. Flow rates should be titrated to meet the patient's inspiratory demands.
Does increasing I time increase tidal volume?
If the inspiratory flow does not return to baseline, an increase in inspiratory time will generally result in an increased tidal volume and should be considered as long as increasing inspiratory time does not result in shortening expiratory time, causing AutoPEEP, or result in patient-ventilator asynchrony.
What is a normal PIP?
Normal peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is 25-30 cm H2O. Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) should be kept below 20 to 25 cm H2O whenever positive-pressure ventilation is required, especially if pneumothoraces, or fresh bronchial or pulmonary suture lines, are present.
What does 50 on a ventilator mean?
A FiO2 of . 5 means the patient will be receiving 50% oxygen, and FiO2 of 1.0 means the patient will be receiving 100% oxygen. ◆ Respiratory rate The rate at which the ventilator is set to provide respirations per minute.
What is the normal inspiration to expiration ratio?
1:2Inspiration/expiration ratio The normal inspiration/expiration (I/E) ratio to start is 1:2. This is reduced to 1:4 or 1:5 in the presence of obstructive airway disease in order to avoid air-trapping (breath stacking) and auto-PEEP or intrinsic PEEP (iPEEP).
What is inspiratory flow rate?
Flow rate, or peak inspiratory flow rate, is the maximum flow at which a set tidal volume breath is delivered by the ventilator. Most modern ventilators can deliver flow rates between 60 and 120 L/min. Flow rates should be titrated to meet the patient's inspiratory demands.
What is the normal minute ventilation?
between 5 and 8 L per minuteNormal minute ventilation is between 5 and 8 L per minute (Lpm). Tidal volumes of 500 to 600 mL at 12–14 breaths per minute yield minute ventilations between 6.0 and 8.4 L, for example. Minute ventilation can double with light exercise, and it can exceed 40 Lpm with heavy exercise.
What are normal ventilator settings?
Ventilator settings Sensitivity adjusts the level of negative pressure required to trigger the ventilator. A typical setting is –2 cm H2O. Too high a setting (eg, more negative than –2 cm H2O) causes weak patients to be unable to trigger a breath.
COVID patients
Anyone else seeing young (20s-40s) patients die from covid left and right? Mostly obese, unvaccinated, younger people at my hospital.
Burn out after a month
Hey, I am a new grad and I’ve been working for a little over a month now.
Public health and respiratory therapy programs
Hello, everyone. I am a public health graduate with a bachelor's degree, is it possible that I can study respiratory therapy for my master's? If so, please help me with the best programs in the US for Internationals. Thank you!
Passed TMC
Got through the TMC today, on the first attempt, fortunately. 117/140. A lot of folks here have been quite helpful. No celebrating yet, still got work to do. Onto the next one. - Any tips on preparing for the sims? I have both tutorial systems membership and kettering.
Introduction
Pressure support ventilation is widely used in patients in the ICU. Matching the patient's respiratory needs with adequate ventilator settings is necessary to ensure a low work of breathing (WOB) and maximal patient comfort. The inspiratory rise time (IRT) determines the time to reach the selected airway pressure.
Methods
We performed a prospective, single-blind cohort study in patients on pressure support ventilation. Ten healthy adult patients admitted to the ICU after elective facial or neck surgery were included.
Results
An interim analysis was performed on four of a total of 10 patients. The WOB increased from 0.25 ± 0.11 J/l at 0% IRT to 0.48 ± 0.01 J/l at 5% IRT and 0.59 ± 0.21 J/l at 10% IRT (values expressed as mean ± SD).
Conclusion
With increasing IRT the WOB increases and patient comfort decreases. In this category of patients we therefore suggest using the shortest IRT (0%).