
Integrated pest management (IPM
Integrated pest management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as Integrated Pest Control (IPC) is a broad-based approach that integrates practices for economic control of pests. IPM aims to suppress pest populations below the economic injury level (EIL).
Full Answer
What are the principles of Integrated pest management?
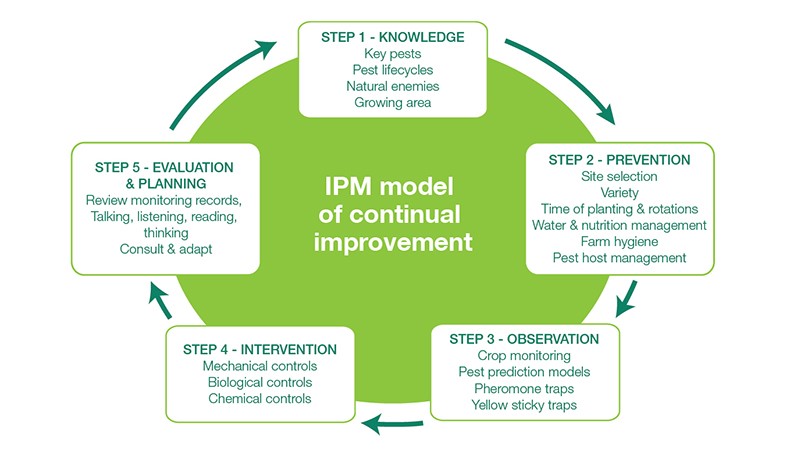
Principles of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Identify pests, their hosts and beneficial organisms before taking action. The cause of the problem and associated plant or animal species must be correctly identified. ...
- Establish monitoring guidelines for each pest species. ...
- Establish an action threshold for the pest. ...
- Evaluate and implement control tactics. ...
- Monitor, evaluate and document the results. ...
What are the benefits of Integrated pest management?
Some of the benefits of an integrated approach:
- Promotes sound structures and healthy plants
- Promotes sustainable bio-based pest management alternatives.
- Reduces environmental risk associated with pest management by encouraging the adoption of more ecologically benign control tactics
- Reduces the potential for air and ground water contamination
What does integrated pest management stand for?
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) is a broad-based approach that integrates practices for economic control of pests.IPM aims to suppress pest populations below the economic injury level (EIL). The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of ...
What is involved in integrated pest management?
- prevent unacceptable levels of pest damage;
- minimize the risk to people, property, infrastructure, natural resources, and the environment; and
- reduce the evolution of pest resistance to pesticides and other pest management practices.
What is Integrated Pest Management explain?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management that relies on a combination of common-sense practices. IPM programs use current, comprehensive information on the life cycles of pests and their interaction with the environment.
What is Integrated Pest Management and what are some examples?
One or several control methods may be coordinated into an Integrated Pest Management program to target a certain pest or several pests. Examples are: Cultural preventative methods. Resistant varieties, crop rotation, pruning, plant nutrition and sanitation. Physical and mechanical methods.
What is the main focus of Integrated Pest Management?
The approach known as Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an integrated, systematic approach to managing pests. Public agencies must invest time and money to increase employee knowledge of pest ecology and biology and reduced-risk control strategies.
What are the 5 components of IPM?
Five general types of single component control methods may be used in IPM programs in stored ecosystems. These are: chemical control, physical and mechanical methods, biological control, host plant resistance and regulatory control.
What are 5 methods of IPM?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) TacticsCultural methods. Suppress pest problems by minimizing the conditions they need to live (water, shelter, food). ... Physical methods. ... Genetic methods. ... Biological methods. ... Chemical methods. ... Regulatory.
What are the benefits of IPM?
Benefits of IPMPromotes sound structures and healthy plants.Promotes sustainable bio-based pest management alternatives.Reduces environmental risk associated with pest management by encouraging the adoption of more ecologically benign control tactics.Reduces the potential for air and ground water contamination.More items...
What are the 4 main factors to IPM?
a s this review concentrates on practices associated with IPM, it focuses on factors that influence environmental and consumer risks. These include biological factors such as pest biology, the sustainability of crop production, pesticide resistance, and natural control by biological control agents.
What are the 4 goals of IPM?
Successful IPM programs use this four-tiered implementation approach: Identify pests and monitor progress. Set action threshholds. Prevent.
What are the 3 main IPM strategies?
Pest-Resistant Crops. One of the mainstays of integrated pest management is the use of crop varieties that are resistant or tolerant to insect pests and diseases. ... Cultural Control. ... Physical and Mechanical Control. ... Chemical Control.
What are the 3 main principles of an integrated pest management system?
The principles of IPM include: Identify pests, their hosts and beneficial organisms before taking action. Establish monitoring guidelines for each pest species. Establish an action threshold for the pest.
What are the 4 steps of integrated pest management?
Successful IPM programs use this four-tiered implementation approach:Identify pests and monitor progress.Set action threshholds.Prevent.Control.
How Do IPM Programs Work?
IPM is not a single pest control method but, rather, a series of pest management evaluations, decisions and controls. In practicing IPM, growers wh...
How Do You Know If The Food You Buy Is Grown Using IPM?
In most cases, food grown using IPM practices is not identified in the marketplace like organic food. There is no national certification for grower...
If I Grow My Own Fruits and Vegetables, Can I Practice IPM in My Garden?
Yes, the same principles used by large farms can be applied to your own garden by following the four-tiered approach outlined above. For more speci...
For More Information on IPM
1. Pesticides and Food: What "Integrated Pest Management" Means 2. EPA is encouraging the innovation of biological pesticides, also known as biopes...
What is traditional pest control?
Traditional pest control involves the routine application of pesticides. IPM, in contrast:
When is pest control required?
Pest control is required if action thresholds are exceeded. IPM programs use the most effective, lowest risk options considering the risks to the applicator, building occupants, and environment. Control methods include:
Why is IPM important?
Smart because IPM creates a safer and healthier learning environment by managing pests and reducing children’s exposure to pests and pesticides. Sensible since practical strategies are used to reduce sources of food, water and shelter for pests in school buildings and grounds.
What is IPM in school?
IPM is an effective and environmentally-sensitive approach that offers a wide variety of tools to reduce contact with pests and exposure to pesticides. The website focuses on providing vital information in the school setting to parents, school administrators, staff and pest management professionals.
Why is IPM limited?
Preventive pesticide application is limited because the risk of pesticide exposure may outweigh the benefits of control , especially when non-chemical methods provide the same results.
What is an IPM program?
Put simply, IPM is a safer and usually less costly option for effective pest management in the school community.
What is IPM in landscaping?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an environmentally friendly, common sense approach to controlling pests. The IPM principles and benefits described below apply to any type of structure and landscaping.
What does IPM mean in pest control?
Rather than simply eliminating the pests you see right now, using IPM means you'll look at environmental factors that affect the pest and its ability to thrive. Armed with this information, you can create conditions that are unfavorable for the pest.
What is monitoring a pest?
Monitoring means checking your field, landscape, forest, or building—or other site—to identify which pests are present, how many there are, or what damage they've caused. Correctly identifying the pest is key to knowing whether a pest is likely to become a problem and determining the best management strategy.
How Does IPM Work?
With IPM, you take actions to keep pests from becoming a problem, such as by growing a healthy crop that can withstand pest attacks, using disease-resistant plants, or caulking cracks to keep insects or rodents from entering a building.
What is IPM in ecology?
IPM is an ecosystem-based strategy that focuses on long-term prevention of pests or their damage through a combination of techniques such as biological control, habitat manipulation, modification of cultural practices, and use of resistant varieties. Pesticides are used only after monitoring indicates they are needed according to established guidelines, and treatments are made with the goal of removing only the target organism. Pest control materials are selected and applied in a manner that minimizes risks to human health, beneficial and nontarget organisms, and the environment.
What are the components of IPM?
These IPM principles and practices are combined to create IPM programs. While each situation is different, six major components are common to all IPM programs: 1 Pest identification 2 Monitoring and assessing pest numbers and damage 3 Guidelines for when management action is needed 4 Preventing pest problems 5 Using a combination of biological, cultural, physical/mechanical and chemical management tools 6 After action is taken, assessing the effect of pest management
What is a pest?
A pest can be a plant (weed), vertebrate (bird, rodent, or other mammal), invertebrate (insect, tick, mite, or snail), nematode, pathogen (bacteria, virus, or fungus) that causes disease, or other unwanted organism that may harm water quality, animal life, or other parts of the ecosystem.
When are pesticides used?
Pesticides are used only after monitoring indicates they are needed according to established guidelines, and treatments are made with the goal of removing only the target organism. Pest control materials are selected and applied in a manner that minimizes risks to human health, beneficial and nontarget organisms, and the environment. What is a pest?
What is IPM pest control?
IPM is a comprehensive, systems-based approach to pest management with the goal of providing the safest, most effective, most economical, and sustained remedy to pest infestations. IPM reduces the risk from pests while also reducing the risk from the overuse or inappropriate use of hazardous chemical pest-control products.
What is the foundation of IPM?
The foundation of IPM is managing the environment to eliminate pest access to food, water, and shelter. Using control techniques that focus on eliminating at least two of these essentials that
What is IPM pest control?
IPM is not a single pest control method but rather an integration of pest management strategies and good agronomical practices.
What is IPM in agriculture?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a philosophy of agricultural pest control that looks to reduce the use of harmful chemical pesticides by incorporating a system of preventative cultural, physical, biological and chemical controls. The aim of the philosophy is to grow crops sustainably while protecting the health of the consumers, ...
What is IPM philosophy?
The IPM philosophy not only focuses on existing pests challenges but also on reducing pest invasions, emergence and resident populations. This approach takes into account past and future crops as a part of the crop protection strategy.
What is the importance of IPM?
An important part of the IPM philosophy is that it not only focuses on existing pests challenges but also on reducing pest invasions, emergence and resident populations. A successful IPM program focuses on the following implementation approach:
What is synthetic pesticide?
Synthetic chemical pesticides are used only when needed and play more of a supportive role, assisting in more effective, long-term management of pest populations. Examples include:
How does spraying with pesticides affect plants?
Spraying with synthetic pesticides stresses plants and reduces photosynthetic activity and plant growth. With fewer sprays in the crops there is an increase in production and quality; bigger, shinier, more disease-resistant leaves, and better post-harvest storage characteristics.
What is the purpose of IPM?
The aim of the philosophy is to grow crops sustainably while protecting the health of the consumers, workers and the environment. Dudutech offers a range of these IPM products for use on a wide variety of farm types. By using IPM, growers help to make agriculture safer for consumers, farmworkers and the environment alike.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
Integrated Pest Management in schools and day care centers involves cooperation between school staff and pest control personnel (e.g., commercial pest management professionals or in-house staff).
Why implement an IPM program in schools and day care centers?
Children are different than adults. Proportionally, they have greater surface area, a higher respiratory rate, and they eat/drink more than adults. Children have a natural tendency to put objects in their mouths and they inhabit spaces closer to the ground (and pesticide-treated surfaces) than do adults.
What is integrated pest management?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) has become the very foundation of virtually all pest management programs. According to an article by Texas A&M University, “The concept and impetus for IPM grew out of the discontent with using a purely insecticidal approach to insect control in many areas in the 1950s.” Pesticide overuse was resulting in insect resistance and environmental damage, so the concept of integrated control, which emphasized the use of selective insecticides, was developed.
What is IPM pest control?
So, what is IPM? IPM is a holistic approach to pest management, involving a partnership between the pest management company and the commercial facility, for the control of insects, rodents, and other problem pests. It is a method advocated as “an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management that relies on a combination of common-sense practices,” by the EPA. They describe IPM as using current, comprehensive information on the life cycles of pests and their interaction with the environment, in combination with available pest control methods to manage pest damage by the most economical means, and with the least possible hazard to people, property, and the environment.
What is the focus of a pest control plan?
The initial focus will be on physical and mechanical methods, similar to the exclusion and sanitation methods of prevention, as well as trapping and other applicable non-chemical measures. Although pesticides are used in an Integrated Pest Management program, they are used only when necessary.
What is integrated control?
Pesticide overuse was resulting in insect resistance and environmental damage, so the concept of integrated control, which emphasized the use of selective insecticides, was developed. It was later expanded into what we know today as IPM; that is, what A&M describes as: “What began 30 years ago as a lofty notion to partner with nature ...
What is the purpose of identification in pest control?
Identification. From the inspection, an identification is made of existing pests to determine the extent of the population, cause of their presence, and the most effective method of control. Prevention.
How does IPM impact the environment?
Finally, IPM empowers you to impact the future of our environment. Agriculture was the first to adopt IPM principles. Government and some industries have followed them. In Connecticut, homeowners manage more land and many apply more pesticides than agriculture and government combined. You can do your part to restore balance to the ecosystem by supporting farms, businesses and government agencies that use IPM. Also, you can take the socially and environmentally responsible action of using IPM in and around your own home.
How do pests develop resistance?
Think of resistance as "speeded-up natural selection" or as "artificial selection." Natural selection is the process nature uses to select the most fit individuals for survival. Successful individuals pass on genes to their offspring, which are encoded with a certain trait that helps them overcome some specific environmental adversity or hardship. Repeated applications of the same pesticide "artificially selects" for the individuals from the pest population that can detoxify, tolerate or avoid a specific poison. Individuals susceptible to the poison perish, leaving those with resistant genes to reproduce and pass on the beneficial trait. After several generations and repeated exposures, you simply "weed out" all susceptible individuals, and are left with a resistant population. This selection process happens with any type of biotic pest including insects, diseases, and weeds. Resistance develops quickly for pests that have many generations per year, reproduce rapidly, and have few susceptible individuals migrating in from other areas or from wild hosts.
How to control potato beetles in Colorado?
If a simple trench trap will prevent most Colorado Potato Beetles from reaching your garden, using floating row covers to enhance early potato development and to prevent potato beetles from feeding on the emerging potatoes raises the effectiveness of control to nearly 100 percent -- all without the use of pesticides.
How to prevent resistance to pesticides?
The use of multiple control methods helps prevent the development of resistance. For example, you can slow or manage resistance by alternating between pesticides that use different modes of action (for example, a stomach and a nerve poison). The individual pests lucky enough to possess a gene that can detoxify one material are unlikely to tolerate a second toxin that works differently.
What materials are considered soft pesticides?
If problems continued, use of the "soft" pesticides would be considered. These materials include highly specific materials such as growth regulators and more general materials, like repellants, soaps and oils. Low human toxicity and a minimal impact on the environment characterize all these materials. Many also have little impact on beneficial organisms that may be present.
Is IPM a common sense approach?
IPM has been called the common sense approach to pest management. It surely is. IPM costs no more than conventional pest management methods yet it protects the environment, helps maintain or restore the ecological balance while maintaining the productivity, appearance and quality of our environment and adds to our quality of life.
