What are the four types of cellular junctions?
Cell junctions also act as a barrier against stress to the cell itself. In this article, we define five different types of cell junctions: Gap Junctions, Adherens Junctions, Hemisdesmosomes, Desmosomes, and Tight Junctions. See Also: Types of Chemical Reactions. Table of Contents. Types of Cell Junctions. 1.
What are the four types of junctions?
Types of Junctions: Overview
- Turning left from a main road into a side road
- Turning right form a main road into a side road
- Emerging from an open T-junction
- Emerging from a closed T-junction
What are cell junctions and their function?
Cell-cell junctions link cells to each other in tissues, and regulate tissue homeostasis in critical cell processes that include tissue barrier function, cell proliferation, and migration. Defects in cell-cell junctions give rise to a wide range of tissue abnormalities that disrupt homeostasis and are common in genetic abnormalities and cancers.
What are the three types of junctions between cells?
- Tight junctions: Impermeable junctions that prevent molecules from passing through the intercellular space.
- Desmosomes: Anchoring junctions that bind adjacent cells together and help form an internal tension-reducing network of fibers.
- Gap junctions: Communicating junctions that allow ions and small molecules to pass for intercellular communication.

What is meant by intercellular junction?
Intercellular junctions are specialized regions of contact between the plasma membranes of adjacent cells. They are essential to any multicellular organism, providing the structural means by which groups of cells can adhere and interact.
What are the 3 types of intercellular junctions?
Three are different types of connecting junctions, that bind the cells together.occluding junctions (zonula occludens or tight junctions)adhering junctions (zonula adherens).desmosomes (macula adherens). ... Gap junctions.
What are examples of intercellular junctions?
Different types of intercellular junctions, including plasmodesmata, tight junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes.
What are the different types of intercellular junctions and functions?
Three different types of intercellular junctions can be distinguished according to their function: Tight or occluding junctions. Adherent or anchoring junctions, including desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. Gap junctions.
What is tight junction and gap junction?
Tight junction refers to a specialized connection of two adjacent animal cell membranes, such that, space usually lying between them is absent while a gap junction refers to a linkage of two adjacent cells consisting of a system of channels extending across a gap from one cell to the other, allowing the passage.
What are the four intercellular junctions?
Intercellular junctions are complex structures formed by the assembly of transmembrane and cytoplasmic/cytoskeletal protein components. At least four different types of endothelial junctions have been described: tight junctions, gap junctions, adherence junctions, and syndesmos.
What is the difference between intracellular and intercellular?
Intercellular space is space located between two near by or neighboring cells. Intracellular space is space located inside or with in the cell.
Where are gap junctions found?
Gap junctions are found in many places throughout the body. This includes epithelia, which are the coverings of body surfaces, as well as nerves, cardiac (heart) muscle, and smooth muscle (such as that of the intestines). Their primary role is to coordinate the activity of adjacent cells.
How many cell junctions are there?
In vertebrates, there are three major types of cell junction: Adherens junctions, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes (anchoring junctions) Gap junctions (communicating junction) Tight junctions (occluding junctions)
How do you remember intercellular junctions?
0:171:29Gap Junctions MCAT Mnemonic Preview - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it's like a gap Junction. Remember gap Junction for drawbridge gap speaking of between theMoreSo it's like a gap Junction. Remember gap Junction for drawbridge gap speaking of between the junction. Look at all that water rushing between the drawbridge arms. It's like a channel with water.
Do all cells have gap junctions?
Gap junctions occur in virtually all tissues of the body, with the exception of adult fully developed skeletal muscle and mobile cell types such as sperm or erythrocytes. Gap junctions are not found in simpler organisms such as sponges and slime molds. A gap junction may also be called a nexus or macula communicans.
What are the different types of intercellular junctions quizlet?
what are the 3 types of intercellular junctions?... Zonula Adherens. Desmosomes or Macula Adherens. Hemidesmosomes.
What are the different types of intercellular communication?
There are four basic categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, autocrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and signaling by direct contact.
How do you remember intercellular junctions?
0:171:29Gap Junctions MCAT Mnemonic Preview - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it's like a gap Junction. Remember gap Junction for drawbridge gap speaking of between theMoreSo it's like a gap Junction. Remember gap Junction for drawbridge gap speaking of between the junction. Look at all that water rushing between the drawbridge arms. It's like a channel with water.
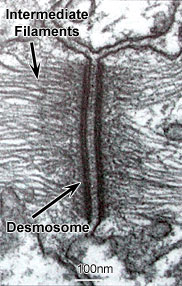
What is desmosome Junction?
Summary. Desmosomes are adhesive intercellular junctions that mechanically integrate adjacent cells by coupling adhesive interactions mediated by desmosomal cadherins to the intermediate filament cytoskeletal network.
What are the intercellular junctions between ECs?
Intercellular junctions between ECs, mediated by adherens junctions and tight junctions, stabilize the vascular endothelial monolayer. These junctions need to be destabilized to allow sprouting ECs to migrate from existing microvessels in response to angiogenic inducers. ECs uniquely express the adherens junction transmembrane protein vascular endothelial-cadherin (VE-cadherin), which contains five extracellular Ig-like domains, a single-pass transmembrane helical sequence and C-terminal intracellular region. VE-cadherins from adjacent ECs are thought to form a zipper-like structure between them. Although the VE-cadherin crystal structure shows overlap between the N-terminal Ig-like domains on VE-cadherins from opposing directions, they are also thought to be able to generate narrower adherens junctions by overlapping multiple Ig-like domains as illustrated in Figure 7. VE-cadherin binds near the membrane to p120 that influences VE-cadherin retention and spatial organization at the cell surface. The C-terminal tail of VE-cadherin binds β-catenin that in turn binds α-catenin, which attaches to actin thereby linking cell surface intercellular junctions to intracellular cytoskeleton microfilaments ( Bravi et al., 2014 ).
What are the adherens junctions?
Adherens junctions: Transmembrane proteins called cadherins (see Fig. 30.5) link neighboring cells and connect to actin filaments in the cytoplasm.
How does VEGF affect intercellular junctions?
The stability of the intercellular junctions is controlled by phosphorylation. VEGFR2, acting through endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) generation of nitric oxide, can nitrosylate β-catenin promoting its dissociation from VE-cadherin. VEGFR2-activated signaling pathways also phosphorylate VE-cadherin tyrosines in the binding sites for p120 and β-catenin, inhibiting adherens junction complex formation and promoting the internalization and degradation of VE-cadherin. Either the same or a different pool of β-catenin migrates to the nucleus and interacts with additional transcription factors to downregulate expression of the tight junction protein claudin-5. VEGF also induces serine phosphorylation of occludin, which increases ubiquitination that marks it for proteasome degradation. In addition to destabilizing EC intercellular junctions, growth factor-induced Rho GTPase activity promotes actin cytoskeleton contraction-mediated opening of the gaps between ECs. In contrast, Ang1-activated Tie2 signaling can inhibit VEGF-mediated EC junction destabilization, a process that can be functionally inhibited by the Tie2 weak agonist Ang2 ( Goddard and Iruela-Arispe, 2013; Bravi et al., 2014 ). Therefore, as denoted in Figure 7, VEGF-induced destabilization of both adherens and tight junctions not only increases vascular permeability but also inhibits intercellular adhesion facilitating EC migration.
How do epithelial cells establish polarity?
From left to right, maturation of primordial junctions into distinct TJs and AJs during epithelial cell polarization. The process requires the exclusion of Par3 through the localized activation of Rac1 GTPase at intermediate stages of polarization. Upon phosphorylation by aPKC, Par3 accumulates at TJs. The Par and Crb complexes establish the apical and the apical/lateral membrane, whereas the Scrib complex defines the basolateral plasma membrane domain. On the right, overview of the antagonistic interactions between the Par complex (orange), the Crumbs complex (red), and the Scribble complex (green).
Which proteins are involved in the formation of tight junctions?
Narrower tight junctions (bottom) are formed by occludin (dark blue) and claudin (orange), two types of integral membrane proteins, each of which probably multimerizes and forms long ribbons that prevent diffusion of all but small molecules between ECs.
What are tight junctions?
Tight junctions are composed of linear strands consisting of multiple proteins including occludins, EC-specific claudin-5, junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs), and zona occludens-1 (ZO-1), which links it to the actin cytoskeleton. VE-cadherin/β-catenin, acting through the PI3K/Akt pathway, expels a claudin-5 transcriptional repressor from the nucleus, effectively upregulating claudin-5 transcription and facilitating EC tight junction formation ( Bravi et al., 2014 ).
How are synapses different from other cell junctions?
The most striking difference of synapses from other cell–cell junctions is the asymmetry of structures on both sides of the synaptic junction. Such asymmetry implies that two compartments must respond differently to the signal (s) that initiate synaptogenesis. This asymmetry is partially achieved through differential distribution of synaptic components to axonal and dendritic compartments within a neuron. Asymmetric interaction of cell adhesion molecules can also account for triggering divergent cascades of downstream events and induction of pre- and postsynaptic sites. However, it is important to note that despite this asymmetry the sizes of the structures on both sides of the synaptic cleft are all correlated, suggesting that the structural synapse assembly is significantly coordinated across the cleft.
What are gap junctions?
Gap Junctions. Video Animation of the Inner Life of the Cell. Cells can also communicate with each other via direct contact, which we refer to to as intercellular junctions. However, there are some differences in the ways that plant and animal cells do this. Plasmodesmata are junctions between plant cells, whereas animal cell contacts include tight ...
How do gap junctions work?
Gap junctions develop when a set of six proteins (called connexins) in the plasma membrane arrange themselves in an elongated donut-like configuration called a connexon. When the pores (“doughnut holes”) of connexons in adjacent animal cells align, a channel between the two cells forms. Gap junctions are particularly important in cardiac muscle. The electrical signal for the muscle to contract passes efficiently through gap junctions. This allows the heart muscle cells to contract in tandem.
What is the channel between the cell walls of two adjacent plant cells?
A plasmodesma is a channel between the cell walls of two adjacent plant cells. Plasmodesmata allow materials to pass from the cytoplasm of one plant cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell. Image Attribution: OpenStax Biology.
Why are gap junctions important?
Gap junctions are particularly important in cardiac muscle. The electrical signal for the muscle to contract passes efficiently through gap junctions. This allows the heart muscle cells to contract in tandem.
What are short proteins that connect to the plasma membrane called?
Also found only in animal cells are desmosomes, which act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells ( see image below ). Short proteins called cadherins in the plasma membrane connect to intermediate filaments to create desmosomes. In fact, the cadherins join two adjacent cells together and maintain the cells in a sheet-like formation in organs and tissues that stretch, like the skin, heart, and muscles.
Where are tight junctions found?
This tight adherence prevents materials from leaking between the cells; tight junctions are typically found in epithelial tissues that line internal organs and cavities, and comprise most of the skin.
Who made the inner life of the cell?
The Inner Life of the Cell was produced by XVIVO for Harvard University . In 2006, Harvard University teamed up with XVIVO to develop an animation that would take their cellular biology students on a journey through the microscopic world of a cell.
When did we find no intercellular junctions between the cells of the stomach remnant?
In the early stages of restoration, on days 1-2 after autotomy, we found no intercellular junctionsbetween the cells of the stomach remnant.
Which cellular margins contribute to adhesion?
specializations of the cellular margins that contribute to the adhesion or allow for communication between cells; they include the macula adherens (desmosome), zonula adherens, zonula occludens, and nexus (gap junction).
Do coelothelial cells retain their differentiation?
It is worth noting that although the coelothelial cells have lost their differentiated phenotype, they remain connected to one another via typical intercellular junctions. Moreover, dividing cells are also connected to their neighbors with intercellular junctionsand retain SLSs or short bundles of tonofilaments in their cytoplasm (Fig.
Do enterocytes retain polarity?
The cells lose their connections to the basal lamina and perhaps to each other, since we found no intercellular junctions. On the other hand, the enterocytes obviously retain polarity, as their apical regions with microvilli are directed toward the interior of the aggregation (Fig.
Is an intercellular junction present in desmosomes?
Intercellular junctionswere seen, but well-formed desmosomes were not present.
What Are Cell Junctions?
Cellular junctions, or cell junctions, are the connections between cells. They are multiprotein complexes that are found in the cell membrane of animal cells. These complexes help anchor animal cells to each other, as well as the environment called the extracellular matrix. There are different types of cell junctions that serve different functions between cells. Cell junctions are also called intercellular junctions.
How many types of cell junctions are there?
There are four main types of cell junctions:
What is the purpose of gap junctions?
They are protein complexes that create a channel between two animal cells. This allows for the passage of cytoplasm, water, nutrients, and signaling molecules.
What is the gap junction made of?
Gap junctions are made of a protein called connexins. Six connexins form a half channel called a connexon. Two connexons come together to form a full channel that creates the gap junction. The gap junction spans across both cell membranes and the extracellular space between them.
What is the function of adhesion junctions?
The main function of adhesion junctions is to connect cells together. They are typically found near tight junctions and help anchor cells to each other. Adhesion junctions help epithelial tissue resist mechanical stress and create an intact membrane.
Which junctions allow for transport of materials between cells?
3. Gap junctions and plasmodesmata - allow for transport of materials between cells
Which type of junctions tightly connect the membrane of two cells together?
1. Occluding junctions - also known as tight junctions in epithelial cells, these junctions tightly connect the membrane of two cells together
What is the ureteropelvic junction?
ureteropelvic junction the area where the renal pelvis meets the ureter.
What is the junction between the cementum and the enamel?
cementoenamel junction the line at which the cementum covering the root of a tooth meets the enamel covering the crown.
What is the synonym for the junction of dentin and cementum?
The interface of dentin and cementum of the tooth. Synonym: dentinocemental junction
What is the site of junction of a motor nerve fiber and a skeletal muscle fiber that innervates?
myoneural junction ( neuromuscular junction) the site of junction of a motor nerve fiber and a skeletal muscle fiber that it innervates. The discoid expansion of the terminal branch of the axon forms the motor end plate, the neurotransmitter that diffuses across the synapse is acetylcholine.
What is the plane between the dentin of the tooth and the enamel crown?
The plane or interface between the dentin of the tooth and the enamel crown; histological sections show it to be a scalloped boundary at the site of the basement membrane which separated the cell layers that formed the calcified enamel and dentin. Synonym: amelodentinal junction
What is the definition of juncture?
The point, line, or surface of union of two parts, mainly bones or cartilages. Synonym (s): juncture (2)
What does "adjunct" mean?
a place of meeting or coming together. adj., adj junc´tional.
What is the tight junction between two adjacent cells?
Instead, tight junctions create a watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells. At the site of a tight junction, cells are held tightly against each other by many individual groups of tight junction proteins called claudins, each of which interacts with a partner group on the opposite cell membrane.
What are the junctions in animal cells called?
Desmosomes. Animal cells may also contain junctions called desmosomes, which act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells. A desmosome involves a complex of proteins. Some of these proteins extend across the membrane, while others anchor the junction within the cell.
How do gap junctions form?
In vertebrates, gap junctions develop when a set of six membrane proteins called connexins form an elongated, donut-like structure called a connexon. When the pores, or “doughnut holes,” of connexons in adjacent animal cells align, a channel forms between the cells. (Invertebrates also form gap junctions in a similar way, ...
What is the gap junction in animal cells?
Functionally, gap junctions in animal cells are a lot like plasmodesmata in plant cells: they are channels between neighboring cells that allow for the transport of ions, water, and other substances. Structurally, however, gap junctions and plasmodesmata are quite different.
What are tight junctions?
The tight junctions are like rivets, and they are arranged in multiple strands that form lines and triangles. Image credit: OpenStax Biology. Modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal.
Why are gap junctions important?
Gap junctions are particularly important in cardiac muscle: the electrical signal to contract spreads rapidly between heart muscle cells as ions pass through gap junctions, allowing the cells to contract in tandem.
How do molecules move through the plasmodesmal channel?
Molecules below a certain size (the size exclusion limit) move freely through the plasmodesmal channel by passive diffusion. The size exclusion limit varies among plants, and even among cell types within a plant. Plasmodesmata may selectively dilate (expand) to allow the passage of certain large molecules, such as proteins, although this process is poorly understood.