What do the intercostal arteries supply?
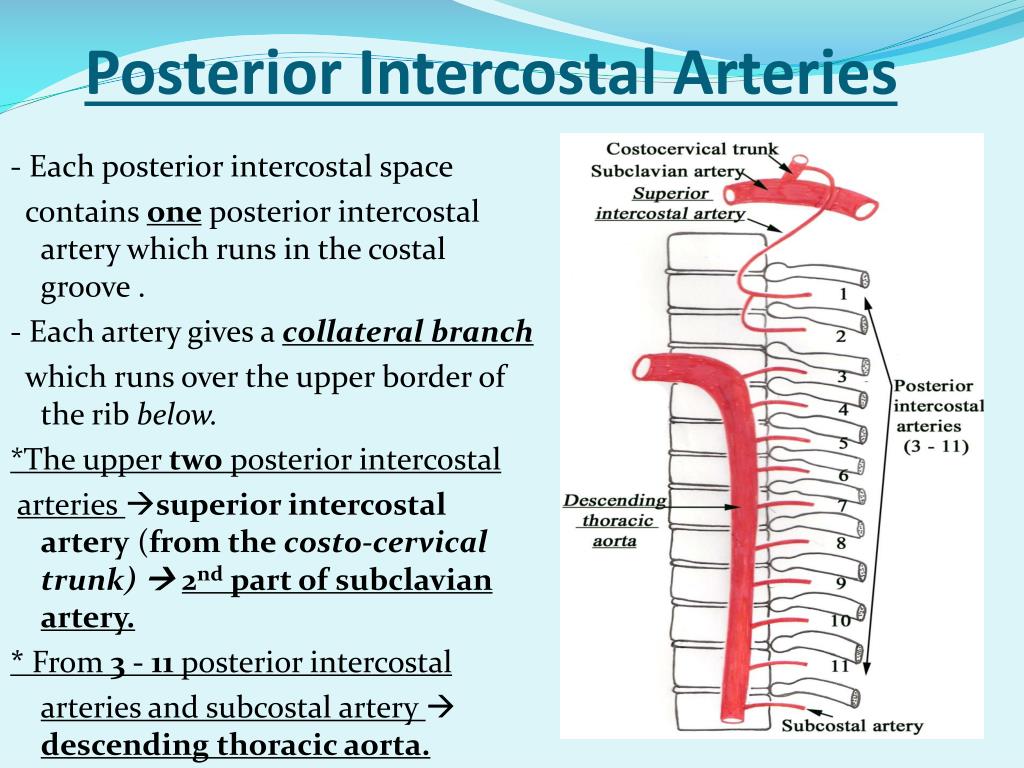
The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the superior intercostal artery (upper two spaces) and the descending aorta (lower nine spaces). They supply the chest wall, parietal pleura, and, through their dorsal branches, the skin and muscles of the back and the spine and its contents.
How many intercostal arteries are there?
eleven posteriorThere are eleven posterior intercostal arteries and they arise from two sources: The first and second posterior intercostal arteries originate from the superior (supreme) intercostal artery, a branch of the costocervical trunk.
Where is the intercostal nerve artery and vein located?
The intercostal artery, vein, and nerve run along the inferior aspect of each rib, occasionally running underneath a ledge in the costal groove.
Where does the intercostal artery branch from?
costocervical trunkThe superior intercostal artery is the descending branch of the costocervical trunk, which arises from the second part of the subclavian artery 2. It enters the thorax anterior to the neck of the first rib with the sympathetic trunk on its medial side.
Where do anterior intercostal arteries come from?
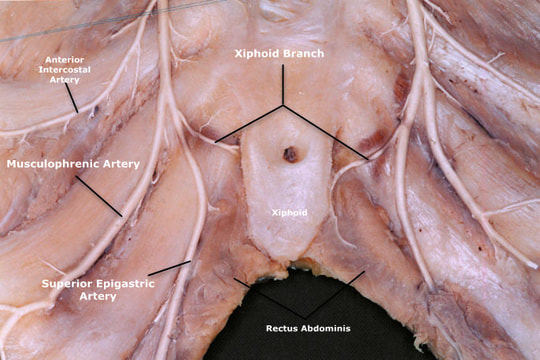
Gross Anatomy The 1st to 6th anterior intercostal arteries arise directly from the lateral aspect of the internal thoracic artery. The 7th to 9th arise from the musculophrenic artery, a branch of the internal thoracic artery.
What does the intercostal nerve control?
Unlike the nerves from the autonomic nervous system that innervate the visceral pleura of the thoracic cavity, the intercostal nerves arise from the somatic nervous system. This enables them to control the contraction of muscles, as well as provide specific sensory information regarding the skin and parietal pleura.
What does the intercostal nerve do?
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, aiding in the contraction of muscles and the return of sensory information from the skin and parietal pleura. The intercostal nerves arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11 and are situated between adjacent ribs.
What is the function of the intercostal muscles?
Internal intercostals assist with exhalation and moving the ribs and chest cavity back to their original position. These muscles combine to fill in the space between each rib and provide support for the respiratory system.
How many intercostal veins are there?
(Intercostals visible at right.) There are eleven posterior intercostal veins on each side. Their patterns are variable, but they are commonly arranged as: The 1st posterior intercostal vein, supreme intercostal vein, drains into the brachiocephalic vein or the vertebral vein.
Where do intercostal veins drain to?
The intercostal veins run above the intercostal arteries, which run above the intercostal nerves. The posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein (right side), and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins (left side). The latter two veins ultimately drain into the azygos vein.
What do intercostal nerves and vessels supply?
They supply the rectus abdominis muscle and terminate as anterior cutaneous branches of the abdomen supplying the cutaneous sensation to the anterior abdominal wall. The lower intercostal nerves also supply the intercostal muscles and anterior abdominal wall musculature.
Which artery gives off intercostal branches?
It gives off intercostal branches to the seventh, eighth, and ninth intercostal spaces; these diminish in size as the spaces decrease in length, and are distributed in a manner precisely similar to the intercostal arteries from the internal thoracic arter y . The musculophrenic artery also gives branches to the lower part of the pericardium, ...
How many posterior intercostal arteries are there?
The posterior intercostal arteries are arteries that supply blood to the intercostal spaces. There are eleven posterior intercostal arteries on each side. The 1st and 2nd posterior intercostal arteries arise from the supreme intercostal artery, a branch of the costocervical trunk of the subclavian artery. The lower nine arteries are the aortic ...
What is the name of the artery that supplies the area between the ribs?
Intercostal arteries. The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. The highest intercostal artery ( supreme intercostal artery or superior intercostal artery) is an artery in the human body that usually gives rise to the first and second posterior intercostal ...
What are the lower nine arteries?
The lower nine arteries are the aortic intercostals, so called because they arise from the back of the thoracic aorta.
Where is the musculophrenic artery located?
The musculophrenic artery arises from the internal thoracic artery, directed obliquely downward and laterally, behind the cartilages of the false ribs; it perforates the diaphragm at the eighth or ninth costal cartilage, and ends, considerably reduced in size, opposite the last intercostal space .
Which artery supplies blood to the corresponding intercostal space?
The highest intercostal artery ( supreme intercostal artery or superior intercostal artery) is an artery in the human body that usually gives rise to the first and second posterior intercostal arteries, which supply blood to their corresponding intercostal space.
Which vein runs backwards?
The left aortic intercostals run backward on the sides of the vertebrae and are covered by the left lung and pleura; the upper two vessels are crossed by the left superior intercostal vein, the lower vessels by the hemiazygos ve in .
What is the intercostal artery?
Intercostal arteries are posterior branches along the length of the descending thoracic aorta and provide segmental arterial blood supply to the spinal cord. From: Atlas of Cardiac Surgical Techniques (Second Edition), 2019. Download as PDF.
What are the two groups of intercostal arteries?
The intercostal arteries are arranged in two groups, anterior and posterior. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic (upper six spaces) and musculophrenic (seventh to ninth spaces) arteries. The lowest two spaces do not receive an anterior supply. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches ...
Which arteries cross the thoracic vertebral bodies to reach the right?
Because the thoracic aorta lies to the left of the thoracic spine, the right intercostal arteries must cross over the thoracic vertebral bodies to reach the right intercostal spaces. This results in the right intercostal arteries being longer than the left ones.
Where do the third and eleventh intercostal arteries originate?
The third through eleventh intercostal arteries originate from the thoracic aorta and course laterally along the inferior aspect of the corresponding rib (see Figs. 6-11 and 6-13, A ). The artery that courses below the twelfth rib is known as the subcostal artery because it lies inferior to the twelfth rib and not between two ribs. The first two intercostal arteries arise from the highest intercostal artery. The highest intercostal artery is a branch of the costocervical trunk, which arises from the subclavian artery.
Which artery supplies the wall of the right mainstem bronchus?
Graphic depicts a common variation of the anatomy of the bronchial arteries. In this illustration, the right bronchial artery arises from the right intercostal artery and supplies the wall of the right mainstem bronchus. Superior and inferior left bronchial arteries arise from the descending thoracic aorta and supply the wall of the left mainstem bronchus.
Which artery does not receive anterior supply?
The lowest two spaces do not receive an anterior supply. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the superior intercostal artery (upper two spaces) and the descending aorta (lower nine spaces). They supply the chest wall, parietal pleura, and, through their dorsal branches, the skin and muscles of the back and the spine and its contents.
Which artery gives rise to dorsal and lateral branches that supply the dorsal (including deep?
Each posterior intercostal artery gives rise to dorsal and lateral branches that supply the dorsal (including deep back muscles) and lateral aspects of the intercostal spaces, respectively.
What are the subcostal arteries?
The subcostal arteries are direct branches of the thoracic aorta. They are analogous to the posterior intercostal artery, so if there was a 12th intercostal space, they would be the 12th intercostal arteries. Like its preceding counterparts, each subcostal artery gives the anterior and posterior branches that travel along with the subcostal space below the twelfth rib. On the left side, the artery passes behind the accessory hemiazygous vein, while on the right side it passes in front of the twelfth thoracic vertebra and behind the thoracic duct and azygous vein. On either side, the arteries are posteriorly related to the sympathetic trunk, diaphragm, and adjacent pleura.
Where do the first and second posterior intercostal arteries originate?
The first and second posterior intercostal arteries originate from the superior (supreme) intercostal artery, a branch of the costocervical trunk. Third to eleventh posterior intercostal arteries arise directly from the posterior surface of the thoracic aorta.
What is the internal thoracic vein?
The internal thoracic veins accompany the internal thoracic arteries. They unite at about the third costal cartilage to form a single internal intercostal vein that is medial to the accompanying artery.Like most veins in the body, the internal thoracic vein has several valves along its length to promote the unidirectional flow of blood. It receives segmental tributaries at each intercostal level (similar to the points at which the corresponding arteries emerge). The pericardiophrenic vein also drains deoxygenated blood by way of the internal thoracic veins. The internal thoracic vein eventually drains directly into the ipsilateral brachiocephalic vein .
How many pairs of intercostal veins are there?
Intercostal veins. There are eleven pairs of posterior intercostal veins, ni ne pairs of anterior intercostal and one pair of subcostal veins supplying the thoracic wall. Each posterior intercostal vein forms an anastomosis with the ipsilateral anterior intercostal veins.
Why are the internal thoracic arteries called the internal mammary arteries?
The internal thoracic arteries were once referred to as the internal mammary arteries because they indirectly supply the breasts. They stem from the subclavian artery and contribute to supplying the intercostal muscles, skin and parietal pleura associated with the first six intercostal spaces.
Why is it important to know the arteries and veins of the chest wall?
Knowledge of the arteries and veins that supply the chest wall is not only important for passing exams, but also for certain emergency situations that pop up during clinical practice. This article will discuss the arteries and veins of the thoracic wall. However, a brief review of the intercostal space and the chest wall anatomy will also be included.
How many branches does the internal thoracic artery have?
The internal thoracic artery gives off five sets of branches :
Which artery runs between the ribs?
Any of the nine pairs of arteries that originate from the dorsal side of the thoracic aorta and run horizontally between the ribs to supply blood to the skin, muscles, and bones of the chest wall. These aortic intercostal arteries run in interspaces 3 to 11. The intercostal arteries of the first two interspaces are branches of the superior intercostal artery (a branch of the costocervical trunk of the subclavian artery). The anterior (sternal) segments of the upper nine intercostal spaces receive their blood supplies from the anterior intercostal arteries, which are branches of the internal mammary artery.
What artery is the feeding artery in the right T5?
The highly vascularised tumour had a feeding artery branch from the right T5 intercostal artery and a dilated draining tortuous vein within the dural sac After considering pre- or postpartum surgery, the surgeons decided that an urgent operation was required.
What type of collateral vessel develops in the intercostal artery?
In addition, transpleural systemic collateral vessels ( intercostal arteries) also develop.
Which arteries are located in the thoracic wall?
See: anterior intercostal branches of internal thoracic artery, first and second posterior intercostal arteries, posterior intercostal arteries 3-11, supreme intercostal artery.
Which artery runs obliquely after crossing the first rib?
In contrast to mammals with a circular thorax (primates), in mammals with a major ventrodorsal axis (quadrupeds) the internal intercostal artery runs obliquely after crossing the first rib and emits a branch that runs ventrally in parallel to the sternal border and that supplements the anterior intercostal arteries. The specialization of the upper extremity in prehensile function and the circular expansion of the thorax explain this difference between quadrupeds and primates.
Which arteries are responsible for bleeding?
According to the statistics, the main responsible vessels for bleeding are right bronchial arteries, left bronchial arteries, combined right and left bronchial trunk, right intercostal arteries. In different etiologies, the rate of abnormal arteries is coincidence with the result.
What is the grid-like arrangement of transverse arteries?
The basic grid-like arrangement is fundamental to understanding all vascular anatomy of brain and spine. The picture above shows the power of conceptualizing this homologous system.
Which artery supplies vertebrae?
This important artery participates in supply of upper thoracic vertebral elements located above the aortic arch. Below the arch, while we have the aorta, each metamere (osseous, neural, muscular — vertebrae, nerve roots, ribs etc) is supplied usually by its dedicated segmental artery. These transverse arteries are connected by numerous longitudinal anastomoses — like pretransverse, post-transverse, etc. The basic grid-like arrangement is fundamental to understanding all vascular anatomy of brain and spine. The picture above shows the power of conceptualizing this homologous system. The vert is homologous to the prevertebral anastomosis, the median sacral to the aorta below iliac bifurcation, the lateral sacral arteries are homologs of prevertebral anastomoses below aortic bifurcation, the iliac and / subclavian vessels are just really large segmental arteries supplying legs and arms, etc. In this system, the supreme intercostal is the homolog of pretransverse anastomoses above the arch. Injecting this artery allows one to see supply to the upper thoracic vertebral bodies. Its important, as various embo targets such as fistulas and tumors can be supplied by it.
What is the color of the ipsilateral subclavian injection?
An ipsilateral supreme interconstal (red) injection demonstrates extensive additional tumor, which is not apparent from the subclavian injection. The vert is labeled in light blue.
Which artery shows transient opacification of the vert?
An injection of the right deep cervical artery shows transient opacification of the vert (arrow) via the C2 muscular anastomosis; we know the vert is there
Is the vert a prevertebral anastomosis?
The vert is homologous to the prevertebral anastomosis, the median sacral to the aorta below iliac bifurcation, the lateral sacral arteries are homologs of prevertebral anastomoses below aortic bifurcation, the iliac and / subclavian vessels are just really large segmental arteries supplying legs and arms, etc.
What is intercostal neuralgia?
Intercostal neuralgia is neuropathic pain involving the intercostal nerves. These are the nerves that arise from the spinal cord, below the ribs. Intercostal neuralgia tends to cause thoracic pain, which affects your chest wall and upper trunk.
How long does an intercostal nerve block last?
Your doctor will use an X-ray to guide the injection into the area just under your rib cage. While it can take a few days to start working , intercostal nerve blocks can last for several months.
How does intracoastal neuralgia affect people?
Intracoastal neuralgia can affect people in very different ways. You doctor can give you a better idea of what to expect based on your symptoms and how well they respond to different treatments. Untreated chronic pain can lead to several complications, including insomnia, low appetite, anxiety, and depression.
What is it called when you have a thoracotomy?
nerve entrapment or pressure. injury from a surgical procedure that involved opening your chest to access your throat, lungs, heart, or diaphragm ( thoracotomy) Sometimes, intercostal neuralgia doesn’t have a clear cause. In this case, it’s called idiopathic intercostal neuralgia.