
Intermittent monitoring. This is done using a handheld battery-operated device known as a Doppler sonicaid, which is held against your abdomen to listen to your baby's heartbeat. When you are pushing in the second stage of labor, the fetal heart needs to be monitored more frequently.
How long will I be monitored intermittently during labor?
In most practices in which intermittent monitoring is an option, your provider may still want to connect you to the monitor for an initial 20- to 30-minute check when you're admitted to the hospital in labor. If you're laboring in a birth center or at home, you'll definitely be monitored intermittently.
What is Intermittent fetal monitoring?
Intermittent monitoring is done with an electronic fetal monitor, a handheld Doppler device, or a fetoscope. If you have a high-risk pregnancy or are having your labor induced or augmented with medication, you'll likely be hooked up to an electronic fetal monitor continuously throughout labor.
What kind of monitoring is done during labor?
All the information about your labor is recorded on a chart, called a labor graph (see External fetal monitoring). Intermittent monitoring. This is done using a handheld battery-operated device known as a Doppler sonicaid, which is held against your abdomen to listen to your baby's heartbeat.
What is the PMCID for Intermittent fetal monitoring during labour?
PMCID: PMC6619817 PMID: 31291375 Intermittent auscultation fetal monitoring during labour: A systematic scoping review to identify methods, effects, and accuracy
How often is intermittent fetal monitoring?
They defined intermittent EFM as being on the monitor for 10 to 30 minutes every two to two-and-a-half hours during the active first stage of labor plus the use of hands-on listening every 15-30 minutes in between EFM periods.
What is the difference between intermittent and continuous fetal monitoring?
Even if your pregnancy and labor are low risk, chances are high you'll receive continuous fetal monitoring. Intermittent auscultation is more labor intensive for hospital staff, so hospitals and practitioners generally prefer continuous fetal monitoring for all laboring women, regardless of risk factors.
What is the purpose of intermittent auscultation and uterine contraction?
Simultaneous evaluation of the maternal pulse provides additional reassurance that the FHR is being monitored. Just before and during intermittent auscultation, a hand is placed on the uterine fundus to determine the timing of uterine contractions and to detect fetal movements.
What are the different types of fetal labor monitoring?
There are two methods of fetal heart rate monitoring in labor. Auscultation is a method of periodically listening to the fetal heartbeat. Electronic fetal monitoring is a procedure in which instruments are used to continuously record the heartbeat of the fetus and the contractions of the woman's uterus during labor.
What are the benefits of intermittent auscultation?
Advantages of intermittent auscultation It facilitates the assessment of other physical parameters such as maternal skin tone, temperature, breathing patterns, direct palpation of fetal movements, and maternal contractions.
When is intermittent auscultation used?
Intermittent auscultation (IA) is the technique of listening to and counting the fetal heart rate (FHR) for short periods during active labour and continuous cardiotocography (CTC) implies FHR monitoring for longer periods.
How often is intermittent auscultation?
Opinion is forwarded that intermittent auscultation should be performed for 60 seconds before and after three contractions over about 10 min every half an hour in the first stage of labour.
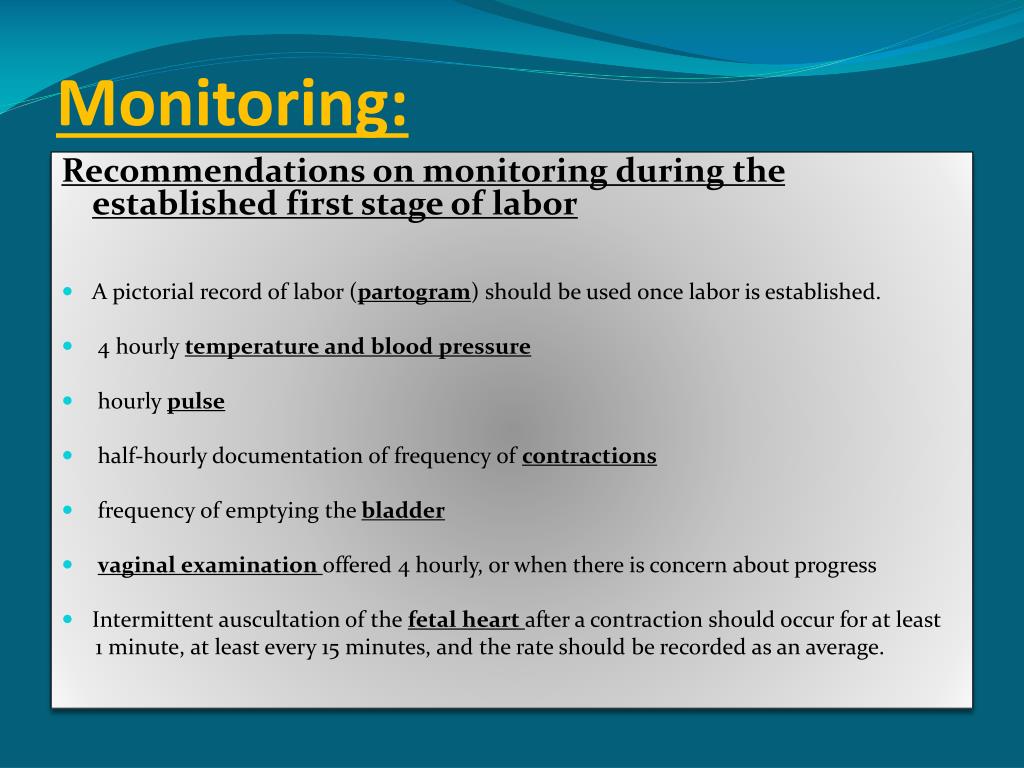
What is Partogram in labour?
The partograph (sometimes known as partogram) is usually a pre‐printed paper form on which labour observations are recorded. The aim of the partograph is to provide a pictorial overview of labour, and to alert midwives and obstetricians to deviations in maternal or fetal well‐being and labour progress.
Can you refuse fetal monitoring?
External fetal monitoring As a result, most hospitals suggest intermittent fetal monitoring. Although you can refuse monitoring entirely, the staff may be unhappy about this and ask you to sign a form or statement releasing them from liability if anything goes wrong during the labor and birth.
Why do they do fetal monitoring?
Fetal heart rate monitoring measures the heart rate and rhythm of your baby (fetus). This lets your healthcare provider see how your baby is doing. Your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor.
Is continuous fetal monitoring required?
EFM can also be done with internal monitors as well. Research is showing that routine continuous electronic fetal monitoring for healthy women is unnecessary in many circumstances, and intermittent auscultation will provide all the information needed.
How do you monitor labor contractions?
The monitoring is usually performed in a doctor's office or hospital. A nurse will wrap a belt around your waist and attach it to a machine called a tocodynamometer. The machine records the frequency and length of your contractions. Your doctor may also recommend monitoring your contractions at home.
What is intermittent monitoring?
Intermittent monitoring is done with an electronic fetal monitor, a handheld Doppler device, or a fetoscope. If you have a high-risk pregnancy or are having your labor induced or augmented with medication, you'll likely be hooked up to an electronic fetal monitor continuously throughout labor. If your pregnancy is low-risk ...
What is fetal monitoring?
Fetal monitoring is when your healthcare practitioner and nurse keep tabs on your baby's heart rate during labor. They do this to check how he's doing and see how he's tolerating your contractions. The monitoring is typically done with one of these devices: an electronic fetal monitor. a handheld Doppler device (like the one your caregiver used ...
What are the conditions that require continuous electronic fetal monitoring?
You'll have continuous electronic fetal monitoring if: You have pregnancy complications or develop any during labor. You have a preexisting medical condition, such as chronic hypertension, diabetes or heart disease. You get an epidural.
What is the name of the device that monitors the heart rate of a baby?
a stethoscope-like device called a fetoscope. Your health provider will check your baby's heart rate either continuously with an electronic fetal monitor, or periodically (this is called intermittent auscultation). Intermittent monitoring is done with an electronic fetal monitor, a handheld Doppler device, or a fetoscope.
What to watch for during labor?
Throughout labor, your practitioner will evaluate your baby's heart rate frequently and watch for anything that could signal a problem. Even if someone is not present with you in your room, don't worry. Most hospitals have central monitoring where providers and nurses can watch fetal heart rates from afar. ACOG. 2018.
How often do you check your heartbeat?
This might happen every 15 to 30 minutes in the active phase of the first stage of labor, and every five to 15 minutes during the second (pushing) stage.
What is the device that monitors the heartbeat of a baby called?
An electronic device called a transducer that is attached to wide, stretchy bands will be placed around your abdomen. This device monitors your baby's heartbeat. Another device that tracks your contractions is usually attached to a second band around your abdomen.
What is the best way to monitor a baby's heart rate?
There are two methods used to monitor your baby's heart rate: periodic assessments, called intermittent auscultation (IA) or continuous assessment with an electronic fetal monitor (EFM). IA is done using a handheld Doppler device, a stethoscope-like device called a fetoscope, or one part of the electronic fetal heart monitor.
Can EFM be done with internal monitors?
EFM can also be done with internal monitors as well. Research is showing that routine continuous electronic fetal monitoring for healthy women is unnecessary in many circumstances, and intermittent auscultation will provide all the information needed.
What is fetal monitoring?
Electronic fetal monitoring. In this type of fetal monitoring, two devices monitor your baby's heart rate and the strength and frequency of your contractions. Your baby's heart rate is monitored with a circular ultrasound-like device. If you want, you can hear the heartbeat, or ask that the volume be turned down if this is distracting.
Why is my baby's heartbeat monitored during labor?
Your baby's heartbeat and your contractions are monitored during labor to check for progress and to ensure your and your baby's well-being. Get the facts on intermittent monitoring, electronic fetal monitoring, and labor graphs.
What is the name of the monitoring of a baby's heart rate?
Your baby's heart rate is an indication of how well your baby is dealing with labor and it is monitored at regular intervals, called intermittent monitoring. If a problem is found or you have a high-risk pregnancy, then you may be advised to have fetal electronic monitoring, in which your baby's heart rate and your contractions are monitored ...
How to monitor contractions?
Your contractions are monitored with a small plastic circular device. One or two elastic belts are placed around your abdomen to secure the monitors. You should be able to stand, sit, or squat with the monitors in place, and some hospitals have monitors that allow you to walk around and be monitored by radio signal.
What is the device used to monitor the heartbeat of a baby?
Intermittent monitoring. This is done using a handheld battery-operated device known as a Doppler sonicaid, which is held against your abdomen to listen to your baby's heartbeat. When you are pushing in the second stage of labor, the fetal heart needs to be monitored more frequently. Electronic fetal monitoring.
What is labor graph?
A labor graph is a large chart that contains several graphs which provide information on your labor, allowing the doctor to monitor the progress of your labor. One of the most useful tools in this chart is a graph showing your labor curve.
What is recorded with a baby's heart rate?
Also recorded with your baby's heart-rate monitoring are your blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and the rate of your contractions, as well as your pain levels. An illustrated daily countdown to motherhood, from conception to childbirth and beyond.
What is the procedure of fetal monitoring?
Electronic fetal monitoring is a procedure in which instruments are used to continuously record the heartbeat of the fetus and the contractions of the woman's uterus during labor. The method that is used depends on the policy of your ob-gyn or hospital, ...
What is the purpose of fetal heart rate monitoring?
Fetal heart rate monitoring may help detect changes in the normal heart rate pattern during labor. If certain changes are detected, steps can be taken to help treat the underlying problem. Fetal heart rate monitoring also can help prevent treatments that are not needed.
What is an OB gyn?
Obstetrician–Gynecologist (Ob-Gyn): A physician with special skills, training, and education in women’s health. Vacuum-Assisted Delivery: The use of a special instrument attached to the baby’s head to help guide it out of the birth canal during delivery. ACOG does not endorse companies or products.
What is the device used to check the heart rate of a fetus?
Auscultation is done with either a special stethoscope or a device called a Doppler transducer. When the transducer is pressed against your abdomen, you can hear your fetus's heartbeat. When auscultation is used, your ob-gyn or other health care professional will check the heart rate of the fetus at set times during labor.
Where is the heart rate monitor placed?
It is placed on the part of the fetus closest to the cervix, usually the scalp. This device records the heart rate. Uterine contractions also may be monitored with a special tube called an intrauterine pressure catheter that is inserted through the vagina into your uterus.
Do you need to stay in bed during electronic monitoring?
You may need to stay in bed during both types of electronic monitoring, but you can move around and find a comfortable position. How is external monitoring performed? With this method, a pair of belts is wrapped around your abdomen. One belt uses Doppler to detect the fetal heart rate.
Is it acceptable to use the OB-GYN method?
The method that is used depends on the policy of your ob-gyn or hospital, your risk of problems, and how your labor is going. If you do not have any complications or risk factors for problems during labor, either method is acceptable.
Why is admission during latent labor important?
Admission during the latent phase of labor may be necessary for a variety of reasons, including pain management or maternal fatigue 9 10.
When women are observed or admitted for pain or fatigue in latent labor, what are the techniques?
When women are observed or admitted for pain or fatigue in latent labor, techniques such as education and support, oral hydration, positions of comfort, and nonpharmacologic pain management techniques such as massage or water immersion may be beneficial 11 12.
How long does it take for a woman to go into labor after a rupture of the membrane?
When membranes rupture at term before the onset of labor, approximately 77–79% of women will go into labor spontaneously within 12 hours, and 95% will start labor spontaneously within 24–28 hours 13 14. In the TERMPROM trial, a RCT of labor induction versus expectant management of rupture of membranes at term, the median time to delivery for women managed expectantly was 33 hours; 95% had delivered by 94–107 hours after rupture of membranes 15. A 2017 Cochrane review that compared immediate induction with expectant management did not find a difference in cesarean delivery or definite early-onset neonatal sepsis, but did find a decreased risk of chorioamnionitis or endometritis, or both (relative risk [RR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.33–0.72), a decreased risk of definite or probable early-onset neonatal sepsis (RR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.58–0.92), and a decreased risk of neonatal admission to a special or intensive care unit (RR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.66–0.85) in the induction group 16. The Cochrane authors commented that the quality of evidence to support reduced risk of maternal and probable neonatal infection remains low and that “women should be appropriately counselled in order to make an informed choice between planned early birth and expectant management for PROM at 37 weeks’ gestation or later.” However, given the available evidence, obstetrician–gynecologists and other obstetric care providers should recommend labor induction to pregnant women with term PROM who are candidates for vaginal birth, although the choice of expectant management for a limited time may be considered after appropriate counseling.
What is the evidence for labor care practices that facilitate a physiologic labor process and minimize intervention for appropriate women who
This Committee Opinion reviews the evidence for labor care practices that facilitate a physiologic labor process and minimize intervention for appropriate women who are in spontaneous labor at term. The desire to avoid unnecessary interventions during labor and birth is shared by health care providers and pregnant women. Obstetrician–gynecologists, in collaboration with midwives, nurses, patients, and those who support them in labor, can help women meet their goals for labor and birth by using techniques that require minimal interventions and have high rates of patient satisfaction 1. This Committee Opinion has been revised to incorporate new evidence for risks and benefits of several of these techniques and, given the growing interest on the topic, to incorporate information on a family-centered approach to cesarean birth.
What are the techniques used to help women with pain during labor?
When women are observed or admitted for pain or fatigue in latent labor, techniques such as education and support, oral hydrat ion, positions of comfort, and nonpharmacologic pain management techniques such as massage or water immersion may ...
Why do we change positions during labor?
Frequent position changes during labor to enhance maternal comfort and promote optimal fetal positioning can be support ed as long as adopted positions allow appropriate maternal and fetal monitoring and treatments and are not contraindicated by maternal medical or obstetric complications.
What is the process of shared decision making in obstetrics?
For women who are in latent labor and are not admitted to the labor unit, a process of shared decision making is recommended to create a plan for self-care activities and coping techniques.
