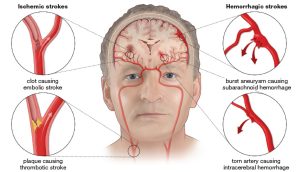
What is internal stroke? An internal capsule stroke is caused by interruption of blood supply in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) or one of its small branches. An ischemic
Ischemic Colitis
A condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestines results from inadequate blood supply.
What is the difference between internal and ischemic stroke?
An internal capsule stroke is caused by interruption of blood supply in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) or one of its small branches. An ischemic internal capsule stroke is caused by an embolic blood clot coming from elsewhere in the body and blocking one of the small branches of the MCA.
What is the pathophysiology of internal capsule stroke?
An internal capsule stroke is caused by interruption of blood supply in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) or one of its small branches. Usually, an ischemic internal capsule stroke is caused by an embolic blood clot coming from elsewhere in the body and blocking one of the small branches of the MCA.
What is a small stroke in the brain?
More in Stroke. An internal capsule stroke is a relatively small stroke that can cause profound weakness of one side of the body. The internal capsule is a region in the brain, and a stroke that affects the internal capsule causes characteristic symptoms.
What is a stroke and what causes it?
A stroke occurs when an artery in the brain gets blocked (ischemic stroke) or bursts (hemorrhagic stroke). The arteries in the internal capsule are very small, which increases the likelihood of clotting that can lead to a stroke. Blood is rich in oxygen and other essential nutrients that fuel brain activity.

What are the symptoms of internal capsule stroke?
Symptoms and Diagnosis An internal capsule stroke can cause arm, hand, leg, or foot weakness, described as hemiparesis or hemiplegia. You might have some strength left in the affected area (hemiparesis,) or you might not be able to move it at all (hemiplegia.)
What are the three types of strokes?
What are the types of stroke?Ischemic stroke. Most strokes are ischemic strokes. ... Hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke happens when an artery in the brain leaks blood or ruptures (breaks open). ... Transient ischemic attack (TIA or “mini-stroke”) ... CDC. ... Million Hearts® and CDC Foundation. ... Other organizations.
Which type of stroke is worse?
Hemorrhagic strokes are less common, making up about 15 percent of stroke cases, but they are often deadlier, Sozener says.
What are the four different types of strokes?
What Are the Types of Strokes?Ischemic Stroke.Hemorrhagic Stroke.Transient Ischemic Attack (Mini-Stroke)Brain Stem Stroke.Cryptogenic Stroke (stroke of unknown cause)
Which medicine is best for stroke?
An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.
Are there warning signs days before a stroke?
- Warning signs of an ischemic stroke may be evident as early as seven days before an attack and require urgent treatment to prevent serious damage to the brain, according to a study of stroke patients published in the March 8, 2005 issue of Neurology, the scientific journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
What is a Level 1 stroke?
A Level 1 stroke alert is a patient with LKN 0-8 hours prior, and results in the Vascular Neurology team responding immediately to the emergency department.
Do stroke patients sleep alot?
Causes of Excessive Sleeping After Stroke Although sleep is a crucial part of stroke recovery, many patients develop a problem known as excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS). Excessive daytime sleeping usually decreases after a few weeks. However, in about 30 percent of stroke patients, EDS can last for over six months.
What time of day do strokes usually occur?
Ischaemic stroke, similar to myocardial infarction and sudden death, occurs most often after awakening in the morning hours. A meta-analysis of 31 publications reporting the circadian timing of 11 816 strokes found a 49% increase in stroke of all types between 06 00 and 12 00.
What are the three main causes of strokes?
CausesHigh blood pressure. Your doctor may call it hypertension. ... Tobacco. Smoking or chewing it raises your odds of a stroke. ... Heart disease. This condition includes defective heart valves as well as atrial fibrillation, or irregular heartbeat, which causes a quarter of all strokes among the very elderly. ... Diabetes.
Which side of the brain is worse to have a stroke?
Left-hemispheric ischemic strokes appear to be more frequent and often have a worse outcome than their right-hemispheric counterparts.
How long do you stay in hospital after a stroke?
The typical length of a hospital stay after a stroke is five to seven days. During this time, the stroke care team will evaluate the effects of the stroke, which will determine the rehabilitation plan.
What is pure motor stroke?
Pure motor stroke is when the effects of the stroke are strictly related to movement. In other words, there is weakness or paralysis in the face, upper and/or lower limb, but no other symptoms are present such as cognitive, language, or sensory deficits. This is the most common secondary effect of internal capsule strokes. 2.
How to restore sensation after stroke?
To restore sensation, stroke survivors should work on sensory reeducation exercises. They help stimulate the brain to promote the rewiring of sensory processing for properties like texture and temperature. This may be part of your occupational therapy treatment as well, if necessary. Visual Restoration Therapy.
What is the internal capsule?
An internal capsule stroke affects the tiny blood vessels deep within the brain. Many motor, sensory, and cognitive fibers run through the internal capsule as they travel between the cerebral cortex (the outer layer of the brain) and the brainstem (the lower area of the brain that connects to the spinal cord).
What is the term for the auditory fibers that run through the sublenticular segment of the internal capsule?
Hearing Impairments. Auditory fibers run through the sublenticular segment of the internal capsule. These auditory fibers are called auditory radiations, and they connect auditory signals from the thalamus to the auditory cortex. A stroke in this area of the internal capsule can result in hearing deficits. 6.
What to do if you have a capsule stroke?
Speech Therapy. If internal capsule stroke has left you with facial weakness, speech therapy can help. A speech-language pathologist will help guide you through exercises specifically designed to strengthen the muscles around the mouth so that you can chew, swallow, and speak more effectively. Occupational Therapy.
What is the recovery process after a capsule stroke?
Although every stroke is unique, recovery from any type of stroke ultimately relies on neuroplasticity.
What side of the body does damage to the internal capsule affect?
Damage to the left internal capsule will affect movement and sensation on the right side of your body, and damage to the right internal capsule will affect the left side of your body. The internal capsule is a V-shaped structure that consists of 5 regions: Anterior Limb (the upper portion)
What happens if you have a stroke?
If one arm begins to fall, you may be having a stroke. Also, one side of your mouth may droop when you try to smile. Problems seeing in one or both eyes. You may suddenly have blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes, or you may see double.
How to prevent a stroke?
Prevention. Knowing your stroke risk factors, following your doctor's recommendations and adopting a healthy lifestyle are the best steps you can take to prevent a stroke. If you've had a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA), these measures might help prevent another stroke.
What is the most common type of stroke?
Ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain. A blood clot often forms in arteries damaged by the buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis). It can occur in the carotid artery of the neck as well as other arteries. This is the most common type of stroke.
How does a stroke affect your speech?
Difficulty talking or swallowing. A stroke might affect control of the muscles in your mouth and throat, making it difficult for you to talk clearly, swallow or eat. You also may have difficulty with language, including speaking or understanding speech, reading, or writing. Memory loss or thinking difficulties.
What is a TIA?
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) — sometimes known as a ministroke — is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those you'd have in a stroke. A TIA doesn't cause permanent damage. They're caused by a temporary decrease in blood supply to part of your brain, which may last as little as five minutes.
What happens when a blood vessel in your brain leaks or ruptures?
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in your brain leaks or ruptures. Brain hemorrhages can result from many conditions that affect your blood vessels. Factors related to hemorrhagic stroke include:
What happens when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes. A stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and other complications.
What is a pure motor stroke?
Known as one of the classic types of lacunar infarcts, a pure motor stroke is the result of an infarct in the internal capsule. Pure motor stroke caused by an infarct in the internal capsule is the most common lacunar syndrome. Since both motor and sensory fibers are carried in the internal capsule, a stroke to the posterior limb ...
What is a mixed sensorimotor stroke?
Mixed sensorimotor stroke. Since both motor and sensory fibers are carried in the internal capsule, a stroke to the posterior limb of the internal capsule (where motor fibers for the arm, trunk and legs and sensory fibers are located) can lead to contralateral weakness and contralateral sensory loss. If a patient has weakness +/- sensory deficits, ...
What is the internal capsule?
The internal capsule is one of the subcortical structures of the brain. Subcortical structures: internal capsule, caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, thalamus, brainstem. The anterior limb of the internal capsule separates the caudate nucleus and lenticular nucleus.
Ischemic stroke vs. hemorrhagic stroke
During an ischemic stroke, arteries to your brain get blocked or become narrowed by a blood clot. Ischemic strokes can be classified as either thrombotic or embolic, depending on where the blood clot forms.
TIAs – Not something to ignore
Often referred to as a “mini stroke,” a transient ischemic attack (or TIA) happens when a blockage in a blood vessel stops the flow of blood to part of your brain.
How to prevent a stroke
Now that you know what’s happening inside the body during a stroke, you’re probably wondering how you can prevent one.
Stroke signs and symptoms to look for
When someone has a stroke, get medical help as soon as possible to restore blood flow to the brain or stop the bleeding. These symptoms signal that someone may be having a stroke:
Introduction
The internal capsule (IC), a white matter structure, is a unique location where a large number of motor and sensory fibers travel to and from the cortex. Damage of any kind in this location will cause some relatively unique findings that can allow you to localize the lesions to the internal capule by exam alone.
Structure
The internal capsule is a deep subcortical structure that contains a concentration of afferent and efferent white matter projection fibres. Anatomically, this is an important area because of the high concentration of both motor and sensory projection fibres.
Anatomy
Location: The internal capsule is one of the subcortical structures of the brain. Subcortical structures include: internal capsule, caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, thalamus, brainstem
IC CVA
The internal capsule is prone to cerebrovascular accidents because the perforating arteries that supply the region are predisposed to occlusion or rupture due to their small diameter.
Lacunar strokes
Lacunar strokes primarily affect the deep structures of the brain, such as the putamen, caudate nucleus, thalamus, and internal capsule. Depending on the location of a lesion, the symptoms of lacunar strokes will require differentiation from cortical strokes.
Rehabilitation After Internal Capsule Stroke
Rehabilitation after internal capsule stroke requires an individualized approach and will depend on what kind of secondary effects you experience.
What causes a stroke?
A stroke can be caused by bleeding, known as a hemorrhagic stroke, or blocked blood flow called an ischemic stroke. A clot typically causes blocked blood flow strokes. These are the most common, causing nearly 90 percent of all strokes.
How does a stroke affect the brain?
Depending on which area of the brain is damaged , a stroke can have an effect on a variety of different muscle groups. These changes can range from major to minor, and will usually require rehabilitation to improve.
What side of the brain does a stroke affect?
A stroke normally effects one side of the brain. The left side of the brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. If there’s a lot of damage to the left side of the brain, you may experience paralysis on the right side of the body. When messages can’t travel properly from ...
What is it called when you have a stroke and you can't swallow?
Damage to the area of your brain that controls eating and swallowing can cause you to have trouble with these functions. This is called dysphagia. It is a common symptom following a stroke, but often improves with time. If the muscles in your throat, tongue, or mouth aren’t able to direct food down the esophagus, ...
Why do people wear braces after stroke?
A brace might also be helpful. There is some overlap between the areas of the brain and their function. Damage to the front part of the brain may cause changes in intelligence, movement, logic, personality traits , and thinking patterns . If this area is affected following a stroke it may also make planning difficult.
What happens if you have a stroke on the left side of your brain?
Damage to the left side of the brain can cause difficulty speaking and understanding language, memory problems, trouble reasoning, organizing, thinking mathematically/analytically, and behavior changes. Following a stroke, you’re also at a higher risk ...
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves throughout the body. This system sends signals back and forth from the body to the brain. When the brain is damaged, it doesn’t receive these messages correctly.