What is good qualitative research?
What is good qualitative research? A first step towards a comprehensive approach to judging rigour/quality. Qualitative research has an enormous amount to contribute to the fields of health, medicine and public health but readers and reviewers from these fields have little understanding of how to judge its quality.
What are the different types of qualitative research?
Types of Qualitative Research
- Case study. The case study is a study that focuses on discussing a particular event or phenomenon. ...
- Oral History. Oral history is a process of obtaining, collecting, recording, analyzing, presenting, and interpreting historical or current information based on personal experiences and opinions of some members of ...
- Focus Groups. ...
- Participant Observation. ...
What are the fundamentals of qualitative research?
These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys: distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
What are qualitative research questions?
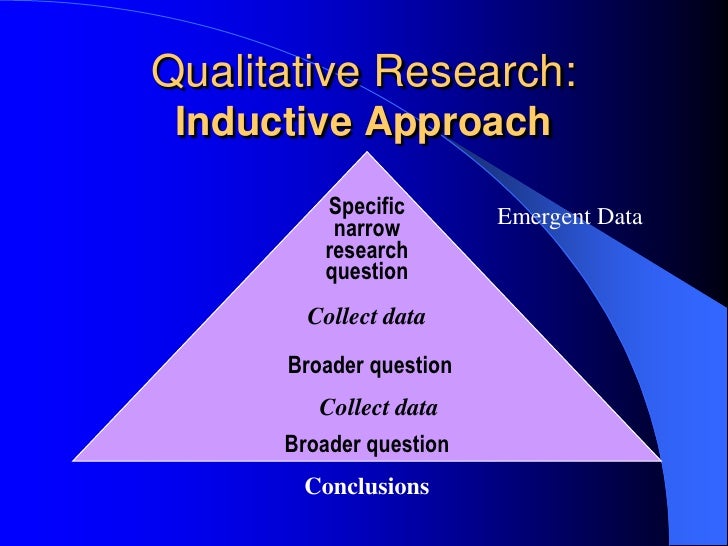
Questions in qualitative research can be described as an inverted pyramid, beginning with a broad, overarching question and narrowing down to focus on the “why” and “how” of the specific phenomenon (Agee, 2008).

What is interpretive approach in research?
Interpretive approaches encompass social theories and perspectives that embrace a view of reality as socially constructed or made meaningful through actors' understanding of events. In organizational communication, scholars focus on the complexities of meaning as enacted in symbols, language, and social interactions.
Is interpretive research qualitative or quantitative?
qualitativeInterpretative approaches are usually associated with qualitative social science but are equally applicable to the analysis of quantitative data. In interpretive quantitative research, statistics are used to shed light on the unobservable data generating processes that underlie observed data.
What type of research is interpretive?
Interpretive research is a framework and practice within social science research that is invested in philosophical and methodological ways of understanding social reality.
What is interpretive?
serving to interpret; explanatory. deduced by interpretation. made because of interpretation: an interpretive distortion of language. of or relating to those arts that require an intermediary, as a performer, for realization, as in music or theater.
What is interpretive research question?
Interpretive Questions: Look to gather feedback on a certain topic or concept without influencing the outcome. For example, testing new product concepts and understanding how messaging claims are interpreted would fall under this type.
Why is interpretive research important?
Interpretive research provides flexibility in terms of the chance of reformulation of the researcher's priori knowledge and understandings during the research process. Thus, data generation and data analysis are intertwined in interpretive research.
Is quantitative research Interpretive?
Quantitative research rests on a background of appreciation of meanings. Whether they acknowledge it or not, researchers draw freely on this background; they do not come up with procedures that explicate it. Therefore, quantitative research is an interpretive process.
Why do Interpretivists prefer qualitative data?
Surveys are unlikely to be completed honestly, and offer little scope for respondents to reveal unexpected truths about themselves. For this reason interpretivists prefer qualitative methods. Unstructured interviews and participant observation allow more genuine two-way interaction to take place.
What is interpretive research?
Interpretive research is a research paradigm ( see Chapter 3) that is based on the assumption that social reality is not singular or objective. Rather, it is shaped by human experiences ...
Why is interpretive research important?
First, it is well-suited for exploring hidden reasons behind complex, interrelated, or multifaceted social processes— such as inter-firm relationships or inter-office politics—where quantitative evidence may be biased, inaccurate, or otherwise difficult to obtain. Second, it is often helpful for theory construction in areas with no or insufficient a priori theory. Third, it is also appropriate for studying context-specific, unique, or idiosyncratic events or processes. Fourth, interpretive research can also help uncover interesting and relevant research questions and issues for follow-up research.
How to determine if interpretive research is reliable?
Dependability. Interpretive research can be viewed as dependable or authentic if two researchers assessing the same phenomenon, using the same set of evidence, independently arrive at the same conclusions, or the same researcher, observing the same or a similar phenomenon at different times arrives at similar conclusions. This concept is similar to that of reliability in positivist research, with agreement between two independent researchers being similar to the notion of inter-rater reliability, and agreement between two observations of the same phenomenon by the same researcher akin to test-retest reliability. To ensure dependability, interpretive researchers must provide adequate details about their phenomenon of interest and the social context in which it is embedded, so as to allow readers to independently authenticate their interpretive inferences.
What is temporal nature of interpretive research?
Temporal nature: Interpretive research is often not concerned with searching for specific answers, but with understanding or ‘making sense of’ a dynamic social process as it unfolds over time. Hence, such research requires the researcher to immerse themself in the study site for an extended period of time in order to capture the entire evolution of the phenomenon of interest.
What is qualitative versus quantitative research?
However, qualitative versus quantitative research refers to empirical or data-oriented considerations about the type of data to collect and how to analyse it. Qualitative research relies mostly on non-numeric data, such as interviews and observations, in contrast to quantitative research which employs numeric data such as scores and metrics. Hence, qualitative research is not amenable to statistical procedures such as regression analysis, but is coded using techniques like content analysis. Sometimes, coded qualitative data is tabulated quantitatively as frequencies of codes, but this data is not statistically analysed. Many puritan interpretive researchers reject this coding approach as a futile effort to seek consensus or objectivity in a social phenomenon which is essentially subjective.
What is interpretive interpretation?
Interpretive interpretations tend to focus on language, signs, and meanings from the perspective of the participants involved in the social phenomenon, in contrast to statistical techniques that are employed heavily in positivist research.
Why do interpretive researchers interpret social reality?
Because interpretive researchers view social reality as being embedded within—and therefore impossible to abstract from—their social settings, they ‘interpret’ the reality though a ‘sense-making’ process rather than a hypothesis testing process.
What is interpretive description?
Interpretive description: a noncategorical qualitative alternative for developing nursing knowledge. Despite nursing's enthusiastic endorsement of the applicability of qualitative research approaches to answering relevant clinical questions, many nurse researchers have been hesitant to depart from traditional qualitative research methods.
Is a non-categorical description a methodological alternative?
The authors present the point of view that a non-categorical description, drawing on principles grounded in nursing's epistemological mandate, may be an appropriate methodological alternative for credible research toward the development of nursing science.
Is nursing a qualitative research?
Thus, as many nurse researchers have discovered, nursing's unique knowledge mandate may not always be well served by strict adherence to traditional methods as the "gold standard" for qualitative nursing research. The authors present the point of view that a non-categorical description, drawing on principles grounded in nursing's epistemological ...
What are qualitative methods?
Qualitative research methods today are a diverse set, encompassing approaches such asempirical phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, protocol analysis and dis-course analysis. By one common definition (Polkinghorne, 1983), all these methodsrely on linguistic rather than numerical data, and employ meaning-based rather thanstatistical forms of data analysis. Distinguishing between measuring things with wordsand measuring them in numbers, however, may not be a particularly useful way ofcharacterising different approaches to research. Instead, other distinctive features ofqualitative research may turn out to be of far greater importance (Elliott, 1999):
Why are self-report questionnaires used less in qualitative research?
Self-report questionnaires are used much less in qualitative research, because theytyp ically do not stimulate the needed level of elaboration sought by the qualitativeresearcher. However, given time and space constraints, questionnaires may be used aswell. In that case they naturally consist of open-ended questions and ask respondentsfor elaboration, examples, etc. A good practice is to build in the opportunity to follow-up on questionnaires by phone interview (Hill et al., 1997) or email correspondence, asresponses often do not provide enough elaboration to understand the respondents’point.
Is the validity of the analysis assessed throughout the study?
The validity of the analysis is assessed throughout the study, as previously noted. Toaccomplish this, a constructively sceptical process of independent auditing is recom-mended. Although it is best for researchers to employ careful internal auditingthroughout the analysis, the major auditing step typically occurs after a complete draftanalysis has been produced.

Distinctions from Positivist Research
Benefits and Challenges of Interpretive Research
- Interpretive research has several unique advantages. First, they are well-suited for exploring hidden reasons behind complex, interrelated, or multifaceted social processes, such as inter-firm relationships or inter-office politics, where quantitative evidence may be biased, inaccurate, or otherwise difficult to obtain. Second, they are often helpful for theory construction in areas with …
Characteristics of Interpretive Research
- All interpretive research must adhere to a common set of principles, as described below. Naturalistic inquiry: Social phenomena must be studied within their natural setting. Because interpretive research assumes that social phenomena are situated within and cannot be isolated from their social context, interpretations of such phenomena must be grounded within their soci…
Interpretive Data Collection
- Data is collected in interpretive research using a variety of techniques. The most frequently used technique is interviews (face-to-face, telephone, or focus groups). Interview types and strategies are discussed in detail in a previous chapter on survey research. A second technique is observation . Observational techniques include direct observation , where the researcher is a ne…
Interpretive Research Designs
- Case research . As discussed in the previous chapter, case research is an intensive longitudinal study of a phenomenon at one or more research sites for the purpose of deriving detailed, contextualized inferences and understanding the dynamic process underlying a phenomenon of interest. Case research is a unique research design in that it can be used in an interpretive mann…
Distinctions from Positivist Research
Benefits and Challenges of Interpretive Research
Characteristics of Interpretive Research
Interpretive Data Collection
Interpretive Research Designs
Rigor in Interpretive Research
- While positivist research employs a ‘reductionist’ approach by simplifying social reality into parsimonious theories and laws, interpretive research attempts to interpret social reality through the subjective viewpoints of the embedded participants within the context where the reality is situated. These interpretations are heavily contextualised, a...