INTERSTITIAL GROWTH IN GROWING LONG BONES. Even in a tissue of such firm consistency as cartilage, it is found that its increase in size is due to the multiplication and growth of the individual cells. This form of interstitial growth also takes place in the cartilaginous forerunner of bone, but it is questionable whether it occurs after...
What is interstitial growth in growing long bones?
INTERSTITIAL GROWTH IN GROWING LONG BONES. Even in a tissue of such firm consistency as cartilage, it is found that its increase in size is due to the multiplication and growth of the individual cells. This form of interstitial growth also takes place in the cartilaginous forerunner of bone, but it is questionable whether it occurs after...
What is the difference between interstitial growth and appositional growth?
Interstitial growth allows bones to grow in length, while appositional growth allows bones to grow in diameter. Moreover, interstitial growth occurs within lacunae while appositional growth happens on the surface of pre-existing cartilage.
What causes interstitial growth in cartilage?
Even in a tissue of such firm consistency as cartilage, it is found that its increase in size is due to the multiplication and growth of the individual cells. This form of interstitial growth also takes place in the cartilaginous forerunner of bone, but it is questionable whether it occurs after...
What happens to interstitial growth during adolescence?
As a result of interstitial growth, long bones continue to lengthen. Interstitial growth happens, and bones continue to grow in length until early adulthood. At the end of adolescence, when chondrocytes stop dividing by mitosis, interstitial growth ceases. What is Appositional Growth?

What causes interstitial growth?
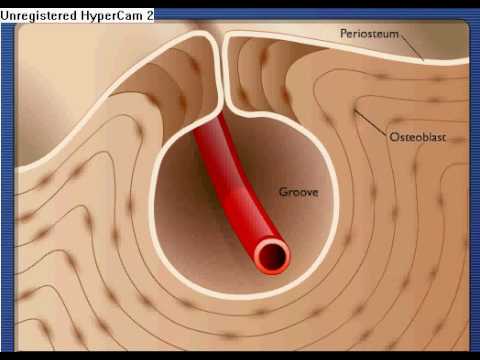
3:2311:44Bone Growth and Remodeling: Appositional and Interstitial GrowthYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt occurs within the periosteum which is the lighting on the outside of the bone. You have boneMoreIt occurs within the periosteum which is the lighting on the outside of the bone. You have bone matrix that is deposited within layers perla to its surface. So if this is the edge of your bone.
What does interstitial growth mean in anatomy?
Interstitial growth is the process that adds or removes solid mass at locations inside a solid material. For this process to occur, there must be interstitial space within this material to allow atoms or molecules to bind to the underlying substrate.
What age does interstitial growth occur?
This growth can be commonly observed after birth of an individual but generally in the first trimester that is around fourth or fifth week the development of bones and stops growing at the age of 21 for males and comparatively in female at lesser age of 18.
What is interstitial growth vs Appositional growth?
Appositional growth occurs when chondroblasts secrete new matrix along existing surfaces and this causes the cartilage to expand and widen. In interstitial growth, chondrocytes secrete new matrix within the cartilage and this causes it to grow in length.
Does interstitial growth ever stop?
Interstitial growth happens, and bones continue to grow in length until early adulthood. At the end of adolescence, when chondrocytes stop dividing by mitosis, interstitial growth ceases.
What are the steps of interstitial growth?
Cartilage formationInterstitial growth which includes: Cell division of the chondrocytes. Synthesis of the extracellular matrix. Expansion of the cartilage matrix from within.Appositional growth which includes: Differentiation of the chondroblasts or perichondrial cells. Synthesis of the extracellular matrix.
What are the stages of bone growth?
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines, they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation, called proliferation, maturation of matrix, and mineralization.
Do bones undergo interstitial growth?
In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage. Activity in the epiphyseal plate enables bones to grow in length (this is interstitial growth). Appositional growth allows bones to grow in diameter.
What hormones affect bone growth?
The female hormone estrogen and the male hormone testosterone both have effects on bone in men and women (Falahati-Nini, Riggs et al. 2000). The estrogen produced in children and early in puberty can increase bone growth.
What is Appositional growth of bone?
Appositional growth is the process by which old bone that lines the medullary cavity is reabsorbed and new bone tissue is grown beneath the periosteum, increasing bone diameter.
What is interstitial growth quizlet?
interstitial growth (bone) growth from within the middle. cartilage increases with length, dies off, and replaced by bone.
What does Appositional growth mean?
Definition. Growth by forming new layers on the surface of pre-existing layers; process of increasing in thickness rather than length. Supplement. In bones, this method of growth is accomplished by the addition of newly formed cartilage on the surface of the previously formed cartilage.
What is interstitial growth quizlet?
interstitial growth (bone) growth from within the middle. cartilage increases with length, dies off, and replaced by bone.
Where do interstitial and appositional growth of cartilage occur?
0:268:05Ch 6: Interstital Growth VS Appositional Growth - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo with our appositional growth this is growth from the outside. So more of the periphery ofMoreSo with our appositional growth this is growth from the outside. So more of the periphery of cartilage in this case or if we were talking about bone would be the outside of the bone close to that
What does Appositional growth mean?
Definition. Growth by forming new layers on the surface of pre-existing layers; process of increasing in thickness rather than length. Supplement. In bones, this method of growth is accomplished by the addition of newly formed cartilage on the surface of the previously formed cartilage.
What are the two types of cartilage growth?
In hyaline cartilage, type II collagen makes up 40% of its dry weight. Elastic cartilage also contains elastic fibers, and fibrocartilage contains more collagen than hyaline cartilage.
What is Interstitial Growth?
Interstitial growth is a bone growth which results in the lengthening of the bone. This growth occurs within the lacunae. It happens due to the cell division in the proliferative zone and the maturation of cells in the zone of maturation. Cartilage lengthens and is replaced by bone tissue during interstitial growth.
What is the Difference Between Interstitial and Appositional Growth?
Interstitial growth is the increase in the length of bones by the cartilage lengthening and is replacing by bone tissue while appositional growth is the increase in the diameter of bones by the addition of bony tissue at the surface of the pre-existing bone. So, this is the key difference between interstitial and appositional growth. Interstitial growth allows bones to grow in length, while appositional growth allows bones to grow in diameter. Moreover, interstitial growth occurs within lacunae while appositional growth happens on the surface of pre-existing cartilage.
What is Appositional Growth?
Appositional growth is the second type of growth which increases the bone width or diameter. This growth occurs as a result of depositing new bone tissue on the endosteal and periosteal surfaces. Therefore, new layers are formed on the surface of pre-existing bones, increasing the thickness of the bone.
What happens during appositional growth?
During the appositional growth, both bone formation and reabsorption take place. Osteoclasts resorb old bone while osteoblasts produce new bone tissue. Appositional growth not only increases the diameter of the diaphysis but also increases the diameter of the medullary cavity.
Can bones grow?
Bones can grow. They can increase in length as well as in diameter or thickness. Moreover, they are highly active organs which can repair themselves when injured. Bones are formed from cartilages. We call this process ossification. Soft cartilages gradually turn into hard bones.