
What is a normal PR interval measurement?
- PR interval: measuring the distance between the start of the P-wave and the start of the QRS complex
- QT interval: the distance between the start of the QRS complex and the end of the T wave
- ST interval: the distance between the end of the QRS complex and the end of the T wave
What is the difference between interval and ratio data?
Third, that said:
- Categorical variables can only take a certain number of values
- Continuous variables can take any real number.
- Nominal variables are just names
- Ordinal variables have order
- Interval variables have equal intervals
- Ratio variables have a meaningful 0
What are the seven units of measurement?
What are the seven fundamental units of Measurement?
- Mass –. The basic fundamental unit of mass is “ Kg”. ...
- Time –. The basic fundamental unit of Time is “Sec (s)”. ...
- Electric Current –. The basic fundamental unit of Electric Current is “Ampere (A)”.
- Amount of Substance –. Amount of Substance is a dimensionless expression of the number of particles in a particle or object.
- Illumination. ...
- Distance. ...
- Temperature. ...
What is an example of ordinal level of measurement?
What is an example of ordinal measurement? Examples of ordinal variables include: socio economic status (“low income”,”middle income”,”high income”), education level (“high school”,”BS”,”MS”,”PhD”), income level (“less than 50K”, “50K-100K”, “over 100K”), satisfaction rating (“extremely dislike”, “dislike”, “neutral”, “like”, “extremely like”).
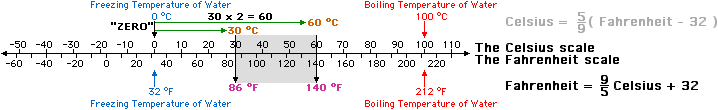
What is an example of interval level of measurement?
An interval scale is one where there is order and the difference between two values is meaningful. Examples of interval variables include: temperature (Farenheit), temperature (Celcius), pH, SAT score (200-800), credit score (300-850).
What is an example of an interval question?
When you ask someone to select a meal from a menu, you're using a nominal scale. When you ask someone to rate their meal on a scale of one to ten, you're using an interval scale.
What does interval level data mean?
Interval data is a type of data which is measured along a scale, in which each point is placed at an equal distance (interval) from one another. Interval data is one of the two types of discrete data. An example of interval data is the data collected on a thermometer—its gradation or markings are equidistant.
What is ratio level of measurement?
The ratio level is the highest of four hierarchical levels of measurement. The levels, or scales, of measurement indicate how precisely data is recorded. The higher the level, the more complex the measurement is. The ratio level contains all of the features of the other 3 levels.
Is age an interval or ratio?
Age, money, and weight are common ratio scale variables. For example, if you are 50 years old and your child is 25 years old, you can accurately claim you are twice their age.
Is age interval or ordinal?
Age can be both nominal and ordinal data depending on the question types. I.e “How old are you” is used to collect nominal data while “Are you the firstborn or What position are you in your family” is used to collect ordinal data. Age becomes ordinal data when there's some sort of order to it.
What are examples of interval and ratio?
Examples of interval level data include temperature and year. Examples of ratio level data include distance and area (e.g., acreage). The scales are similar in so far as units of measurement are arbitrary (Celsius versus Fahrenheit, Gregorian versus Islamic calendar, English versus metric units).
Is age an example of interval data?
Interval-level variables are continuous, meaning that each value of the variable is one increment larger than the previous and one smaller than the next value. Age, if measured in years, is a good example; each increment is one year.
What is the difference between ordinal and interval data?
Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized and ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
Is salary a ratio or interval?
Example: salary data for is often recorded as interval data (i.e. just a number).
What are examples of interval variables?
Arithmetic operations can also be performed on the numerical values of the interval variable. These arithmetic operations are, however, just limited to addition and subtraction. Examples of interval variables include; temperature measured in Celsius or Fahrenheit, time, generation age range, etc.
Is height an interval or ratio?
ratio scalesPhysical characteristics of persons and objects can be measured with ratio scales, and, thus, height and weight are examples of ratio measurement.
What is an interval scale question?
Interval rating scale questions are the most common type of survey question, and we use them to capture the level of feelings the respondent has about the topic of interest. The level of feelings is captured by presenting a multiple point scale to the respondent and asking them where they fall on the scale range.
What does interval mean example?
1 : a period of time between events or states : pause a three-month interval the interval between elections. 2 : a space between things the interval between two desks. 3 : difference in pitch between tones.
What is an example of a ordinal question?
Examples of ordinal scales This popular form of survey question offers respondents an ordered range of answers from one extreme to another. Take, for example, these questions from our Employee Satisfaction Survey Template: How meaningful is your work? How challenging is your job?
How do you write an interval?
Intervals are written with rectangular brackets or parentheses, and two numbers delimited with a comma. The two numbers are called the endpoints of the interval. The number on the left denotes the least element or lower bound. The number on the right denotes the greatest element or upper bound.
Why is interval measurement important?
Interval data is especially useful in business, social, and scientific analysis and strategy because it is straightforward and quantitative.
Why is interval scale preferred?
The interval scale is preferred to nominal scaleor ordinal scalebecause the latter two are qualitative scales. The interval scale is quantitative in the sense that it can quantify the difference between values.
What is the 3rd quantitative level of measurement where the difference between 2 variables is meaningful?
The interval scale is defined as the 3rd quantitative level of measurement where the difference between 2 variables is meaningful.
What is the third level of measurement after the nominal scale?
The measures used to calculate the distance between the variables are highly reliable. The interval scale is the third level of measurement after the nominal scale and the ordinal scale. Understanding the first two levels will help you differentiate interval measurements. A nominal scale is used when variables do not have a natural order or ranking.
What does zero degrees mean on the Celsius scale?
Zero degrees on the Fahrenheit (and Celsius) scale is not a universal constant but instead assigned to represent the temperature at which brine made from equal parts of ice, water, and salt freezes. Let’s not get too wrapped up in the particulars of temperature, though. Your surveys will likely focus on other variables.
Why is the sentiment scale used in statistics?
This is a preferred scale in statistics because you can assign a numerical value to any arbitrary assessment, such as feelings and sentiments.
When to use nominal scale?
A nominal scale is used when variables do not have a natural order or ranking. You can include numbered or unnumbered variables, but common survey examples include gender, location, political party, pets, and so on.
What are the levels of measurement?
This is what’s known as the level of measurement. There are four main levels of measurement: Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
What is the difference between interval scale and ordinal scale?
Unlike the ordinal scale, however, the interval scale has a known and equal distance between each value on the scale (imagine the points on a thermometer).
What is ordinal level?
The ordinal level of measurement groups variables into categories, just like the nominal scale, but also conveys the order of the variables. For example, rating how much pain you’re in on a scale of 1-5, or categorizing your income as high, medium, or low.
What determines the type of analysis you can perform on your data?
As already mentioned, the level of measurement determines the type of analysis you can perform on your data. Let’s take a look at the appropriate descriptive statistics and statistical tests for nominal data.
What is nominal scale?
The nominal scale is the first level of measurement, and the simplest. It classifies and labels variables qualitatively. In other words, it divides them into named groups without any quantitative meaning. It’s important to note that, even where numbers are used to label different categories, these numbers don’t have any numerical value.
What does a ratio scale mean?
Just like the interval scale, the ratio scale is a quantitative level of measurement with equal intervals between each point. What sets the ratio scale apart is that it has a true zero. That is, a value of zero on a ratio scale means that the variable you’re measuring is absent. Population is a good example of ratio data.
How to find the mean of a central tendency?
So, to calculate the mean, add all values together and then divide by the total number of values.
What is the nicest thing about interval scale data?
The nice thing about interval scale data is that it can be analyzed in more ways than nominal or ordinal data. For example, researchers could gather data on the credit scores of residents in a certain county and calculate the following metrics:
What is the next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables?
Interval. The next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is an interval scale . Interval scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order and a quantifiable difference between values, but no “true zero” value. These variables have a natural order.
What type of scale is used to label variables?
The next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is an ordinal scale. Ordinal scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order, but no quantifiable difference between values. Some examples of variables that can be measured on an ordinal scale include:
What is the last type of measurement scale?
The last type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is a ratio scale . Ratio scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order, a quantifiable difference between values,and a “true zero” value. Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
What are some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale?
Some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale include: Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero. Weight: Can be measured in kilograms, pounds, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
How is nominal scale data collected?
The most common way that nominal scale data is collected is through a survey. For example, a researcher might survey 100 people and ask each of them what type of place they live in.
How many different data measurement scales are there?
In statistics, we use data to answer interesting questions. But not all data is created equal. There are actually four different data measurement scales that are used to categorize different types of data:
What does interval scale measure?
The interval scale cannot measure scales such as money, weight or temperatures other than Fahrenheit. 4. Ratio. The ratio measurement level classifies numbers on a scale and the value difference between them, including zero. The ratio measurement acknowledges true zero, or the absence of a variable.
How does interval measurement help in statistics?
Interval measurement can help create statistical data analysis. It can use mean, median and mode to calculate variable tendencies. Researchers can use the interval scale to evaluate variable number differences. Interval scales can process averaging data, unlike ordinal and nominal scales. Researchers also use interval data to determine numerical values from statistics results. For example, if half of the survey participants choose answer "A" instead of answer "B," researchers can use interval measurement to calculate what percentage gave each answer.
Why are levels of measurement important?
Levels of measurement are important because they help researchers decide how to interpret the data from a variable. For example, if researchers assign three people the labels "one," "two" and "three," understanding the level of measurement can show observers what those labels mean. If the measure is nominal, then the numbers are placeholders. If the measure is ordinal, the people have ranks from one to three.
What is ordinal scale?
Since ordinal measurement defines items based on rank, ordinal scales can evaluate rank-based or value-based questions in surveys. For example, an ordinal question may ask, "Rank these three from your highest value to your lowest: love, money and respect." Both label and order value apply to ordinal data, making these questions useful for feedback surveys. Researchers can present ordinal data through graph or comparison formats.
Why do researchers use interval data?
Researchers also use interval data to determine numerical values from statistics results. For example, if half of the survey participants choose answer "A" instead of answer "B," researchers can use interval measurement to calculate what percentage gave each answer.
Why use nominal scales in surveys?
Researchers can use nominal scales in surveys to categorize customer data. Nominal research is useful for research where only labels are significant. For example, a nominal question in a survey can ask "What's your favorite season?" The question helps gather labeling data for a group by showing how many selected each season, and which season had the most votes.
What is nominal level?
The nominal level of measurement uses letters, words or numbers to label variables into different categories. Nominal measurement may use nouns or adjectives to apply description-based labels. For example, a variable like hair color can divide a crowd of people into categories like blonde, black and brown.
Who created the 4 levels of measurement?
Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens created these 4 levels of measurement in 1946 and they’re still the most popular. Here’s a quick table showing you the kind of calculations each one can be used for.
What are the four measurement scales used to capture and analyze data from surveys, questionnaires, and similar research instruments?
Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales can be defined as the 4 measurement scales used to capture and analyze data from surveys, questionnaires, and similar research instruments. All of the scales use multiple-choice questions.
Why are ordinal scales important?
It’s easy to remember because ordinal sounds like order and the ordinal data gains its significance from the order of the items being measured.
Why do nominal scales overlap with ordinal scales?
Nominal scales can, to an extent, overlap with ordinal scales because a few of them have order. For example, very short, short, tall, very tall could be considered a nominal scale with an order. Nominal data can be collected with an open-ended or multiple choice question but the open-ended approach is frowned upon.
What are the four scales used in qualitative research?
They’re referred to as nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales.
Which scale takes into account the label of the options?
To recap, nominal scales only take into consideration the label of the options while ignoring order. Ordinal scales take the label of the options into consideration as well as the order of those options. Both scales ignore the value of variables. Because of this, ordinal scales have more applications than a nominal scale.
What is nominal scale?
Nominal scales (also known as a categorical variable scale) refer to variables, categories, or options that don’t have a regular order or ranking that has universal application. For example, male and female are both categories but neither one can be ranked as number one or two in every situation.
Nominal measurement
This level of measurement consists in assigning numerals or symbols to different categories of a variable. The example of male and female applicants to an MBA program mentioned earlier is an example of nominal measurement. The numerals or symbols are just labels and have no quantitative value.
Ordinal Measurement
In this level of measurement, persons or objects are assigned numerals which indicate ranks with respect to one or more properties, either in ascending or descending order.
Interval measurement
This level of measurement is more powerful than the nominal and ordinal levels of measurement, since it has one additional characteristic, which is equality of distance. However, it does not have an origin or a true zero. This implies that it is not possible to multiply or divide the numbers on an interval scale.
Ratio measurement
This is the highest level of measurement and is appropriate when measuring characteristics which have an absolute zero point. This level of measurement has all three characteristics order, distance and origin.
Why is interval scale important?
In statistics, interval scale is frequently used as a numerical value can not only be assigned to variables but calculation on the basis of those values can also be carried out. Even if interval scales are amazing, they do not calculate the “true zero” value which is why the next scale comes into the picture.
What are the four basic levels of measurement scales used to capture data using surveys and questionnaires?
Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio are the four fundamental levels of measurement scales used to capture data using surveys and questionnaires.
What is nominal scale?
Nominal scale is a naming scale, where variables are simply “named” or labeled, with no specific order. Ordinal scale has all its variables in a specific order, beyond just naming them. Interval scale offers labels, order, as well as, a specific interval between each of its variable options. Ratio scale bears all the characteristics ...
What is the ratio scale?
Ratio scale bears all the characteristics of an interval scale, in addition to that , it can also accommodate the value of “zero” on any of its variables. Here’s more of the four levels of measurement in research and statistics: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio.
What is a scale in surveying?
Each scale is an incremental level of measurement, meaning, each scale fulfills the function of the previous scale, and all survey question scales such as Likert, Semantic Differential, Dichotomous, etc, are the derivation of this these 4 fundamental levels of variable measurement. Before we discuss all four levels of measurement scales in details, with examples, let’s have a quick brief look at what these scales represent.
What is statistical test?
Using statistical tests, you can conclude the average hourly rate of a larger population. The level of measurement of a variable decides the statistical test type to be used. The mathematical nature of a variable or in other words, how a variable is measured is considered as the level of measurement.
What is a variable in statistics?
First, let’s understand what a variable is. A quantity whose value changes across the population and can be measured is called variable. For instance, consider a sample of employed individuals.
What are the characteristics of interval data?
So let’s sum the key characteristics of the interval data and scales: Interval scales not only show you the order and the direction, but also the exact differences between the values. The distances between each value on the interval scale are meaningful and equal. There is no true zero point or fixed beginning.
What are the disadvantages of interval data?
However, there is one major disadvantage – the lack of absolute zero.
What is the highest level of data measurement?
Interval and ratio data are the highest levels of data measurements. But still, there is important differences between them that define the way you can analyze your data.
Why is it important to know the measurement level of data?
Knowing the measurement level of your data helps you to interpret and manipulate data in the right way. Let’s define the interval data: Interval data refers not only to classification and ordering the measurements, but it also specifies that the distances between each value on the scale are equal .
What is the difference between a 100 degree and 90 degree temperature?
The difference between a 100 degrees F and 90 degrees F is the same difference as between 60 degrees F and 70 degrees F.
Does the interval scale have a true zero?
They do not have a true zero even if one of the values carry the name “zero.”. For example, in the temperature, there is no point where the temperature can be zero. Zero degrees F does not mean the complete absence of temperature. Since the interval scale has no true zero point, you cannot calculate Ratios .
Can you do ratios with intervals?
So, with ratio data, you can do the same things as with interval data plus calculating ratios and correlations.
